
Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Modified Mastering Engineering with eText and Access Card (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780134229287
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.6, Problem 88P
It consists of two toggles ABC and DBF, which are operated by the hydraulic cylinder H. The toggles push the movable oar G forward, pressing the plate p into the cavity. If the force which the plate exerts on the head is P = 12 kN, determine the force F in the hydraulic cylinder when θ = 30°.
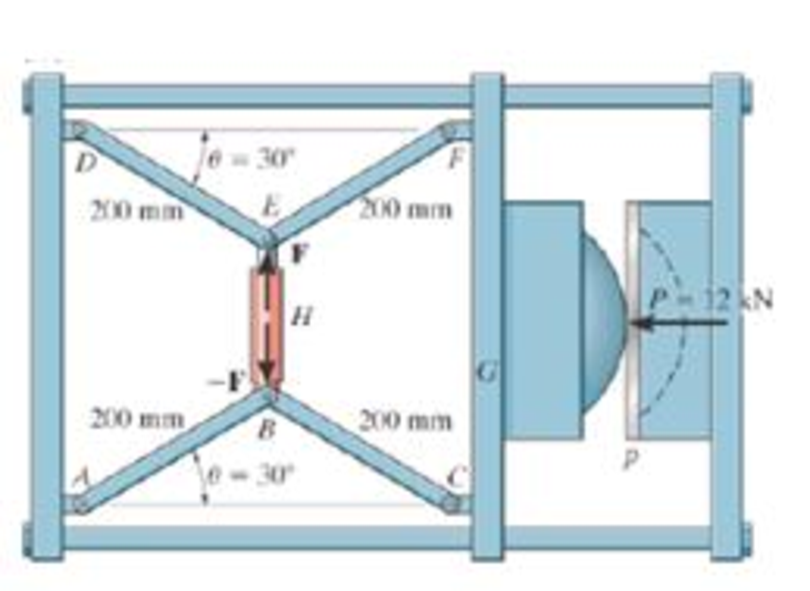
Prob. 6-88
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
handwritten-solutions, please!
handwritten-solutions, please!
No use chatgpt
Chapter 6 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Modified Mastering Engineering with eText and Access Card (14th Edition)
Ch. 6.3 - In each case, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 20 kN, P2 = 10 kN. Probs. 6-1/2Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 45 kN, P2 = 30 kN. Probs. 6-1/2
Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 6 kN, P2 = 9 kN. Probs. 6-9/10Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - If a = 6 ft, determine the greatest load P the...Ch. 6.3 - State whether the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 10 kN, P2 = 8 kN. Probs. 6-18/19Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 9 kN, P2 = 15 kN. Probs. 6-20/21Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the double...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude of load P that can...Ch. 6.3 - Take P = 2 kN. Probs. 6-25/26Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the two loads...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GF, CD, and GC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GH, BC, and BG of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BE, EF, and CB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BF, BG, and AB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CH, GH, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, and KJ and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members JK, CJ, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6.6 - Also, determine the proper placement x of the hook...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and B....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at D. Prob. F6-20Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6.6 - The block weighs 100 lb. Prob. 6-62Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - The suspended cylinder has a mass of 75 kg. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - There is a hinge (pin) at D. Determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P exerted on each of the...Ch. 6.6 - The toggle clamp is subjected to a force F at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force the load creates in member DB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force developed on the...Ch. 6.6 - Also, find the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the guy cable AI and the...Ch. 6.6 - When the walking beam ABC is horizontal, the force...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 6.6 - It consists of two toggles ABC and DBF, which are...Ch. 6.6 - The 600-N load is applied to the pin. Prob. 6-89Ch. 6.6 - If the wheel at A exerts a normal force of FA = 80...Ch. 6.6 - The shovel load has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force P that is exerted...Ch. 6.6 - If each coin weighs 0.0235 lb, determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Assuming the blades are pin connected at B and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - The cable is attached to D, passes over the smooth...Ch. 6.6 - The grip at B on member DAB resists both...Ch. 6.6 - If the compression in the spring is 20 mm when the...Ch. 6.6 - If a clamping force of 300 N is required at A,...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder AB...Ch. 6.6 - The spring has a stiffness of k = 6 kN/m. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - If d = 0.75 ft and the spring has an unstretched...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6.6 - If there is a 300-kg stone in the bucket, with...Ch. 6.6 - when the mechanism is in the position shown. The...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 110PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 111PCh. 6.6 - If the sprig has a stiffness of k = 15 lb/in., and...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - If only vertical forces are supported at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 6 (Optional, extra 6 points) 150 mm 150 mm 120 mm 80 mm 60 mm PROBLEM 18.103 A 2.5 kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates with an angular velocity ₁ with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating as shown at the constant rate w212 rad/s. Friction in the bearing at A causes ₁ to decrease at the rate of 15 rad/s². Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E at a time when ₁ has decreased to 50 rad/s. Answer: 5=-22.01 +26.8} N E=-21.2-5.20Ĵ Narrow_forwardProblem 1. Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3 lb and length 2 ft, are welded to each other at their midpoints. Knowing that this assembly has an angular velocity of constant magnitude c = 12 rad/s, determine: (1). the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum HD of the assembly about D. (2). the dynamic reactions (ignore mg) at the bearings at A and B. 9 in. 3 in. 03 9 in. 3 in. Answers: HD = 0.162 i +0.184 j slug-ft²/s HG = 2.21 k Ay =-1.1 lb; Az = 0; By = 1.1 lb; B₂ = 0.arrow_forwardProblem 5 (Optional, extra 6 points) A 6-lb homogeneous disk of radius 3 in. spins as shown at the constant rate w₁ = 60 rad/s. The disk is supported by the fork-ended rod AB, which is welded to the vertical shaft CBD. The system is at rest when a couple Mo= (0.25ft-lb)j is applied to the shaft for 2 s and then removed. Determine the dynamic reactions at C and D before and after the couple has been removed at 2 s. 4 in. C B Mo 5 in 4 in. Note: 2 rotating around CD induced by Mo is NOT constant before Mo is removed. and ₂ (two unknowns) are related by the equation: ₂ =0+ w₂t 3 in. Partial Answer (after Mo has been removed): C-7.81+7.43k lb D -7.81 7.43 lbarrow_forward
- Problem 4. A homogeneous disk with radius and mass m is mounted on an axle OG with length L and a negligible mass. The axle is pivoted at the fixed-point O, and the disk is constrained to roll on a horizontal surface. The disk rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate o₁ about the axle. (mg must be included into your calculation) (a). Calculate the linear velocity of G and indicate it on the figure. (b). Calculate ₂ (constant), which is the angular velocity of the axle OG around the vertical axis. (c). Calculate the linear acceleration ā of G and indicate it on the figure. (d). Determine the force (assumed vertical) exerted by the floor on the disk (e). Determine the reaction at the pivot O. 1 Answers: N = mg +mr(r/L)² @² |j mr w IIG C R L i+ 2L =arrow_forwardProblem 2. The homogeneous disk of weight W = 6 lb rotates at the constant rate co₁ = 16 rad/s with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating at the constant rate 2 = 8 rad/s. Assume the rod weight is negligible compared to the disk. Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E (ignore mg). Answers: D=-7.12ĵ+4.47k lb r-8 in. 9 in. B D E=-1.822+4.47 lb 9 in. E 12 in. 12 in. xarrow_forwardProblem 3. Each of the right angle rods has a mass of 120 g and is welded to the shaft, which rotates at a steady speed of 3600 rpm. Ignore the weight of the shaft AB. Find the bearing dynamic reaction at A due to the dynamic imbalance of the shaft. (ignore mgs) 100 N A 100 100 100 100 100 (Dimensions in millimeters) Answer: A=-8521-426j N Barrow_forward
- Thermodynamics. Need help solving this. Step by step with unitsarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2=6mm, and for w3 is h3 -6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm 133 mm 140 mm w3 wiarrow_forwardE W X FO FB F10 F11 F12 Home Q: Consider the square of Figure below.The left face is maintained at 100°C and the top face at 500°C, while the other two faces are exposed to an environment at1 00°C, h=10 W/m². C and k=10 W/m.°C. The block is 1 m square. Compute the temperature of the various nodes as indicated in Figure below and the heat flows at the boundaries. T= 500°C Alt Explain to me in detail how to calculate the matrix in the Casio calculator type (fx-991ES plus) T= 100°C 1 2 4 7 1 m- 3 1 m 5 6 T= 100°C 8 9arrow_forward
- Which of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 1-2n 2) a = 1+2n 1/n 3 16) a = n In n 17) an = n 1/n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n² -2n+1 n! 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forwardA steel alloy contains 95.7 wt% Fe, 4.0 wt% W, and 0.3 wt% C.arrow_forwardb. A horizontal cantilever of effective length 3a, carries two concentrated loads W at a distance a from the fixed end and W' at a distance a from the free end. Obtain a formula for the maximum deflection due to this loading using Mohr's method. If the cantilever is 250 mm by 150mm steel I beam, 3 m long having a second moment of area I as 8500 cm4, determine W and W'to give a maximum deflection of 6 mm when the maximum stress due to bending is 90 Mpa. Take Young's modulus of material E as 185 Gpa.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License