
Mechanics of Materials
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780133254426
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.5, Problem 6.14FP
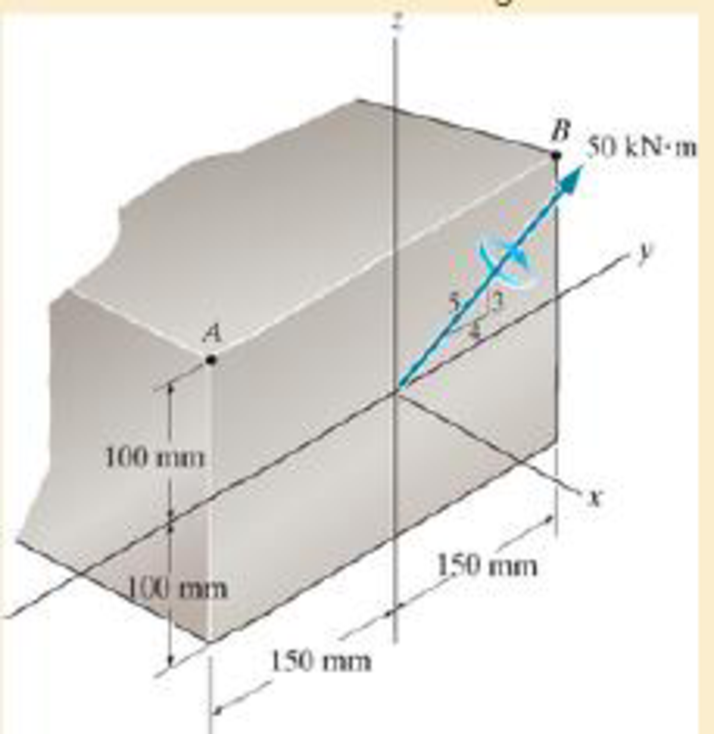
Determine the bending stress at corners A and B. What is the orientation of the neutral axis?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule10:24
Students have asked these similar questions
What is the difference between true stress/strain and engineering stess/strain? And how do I calculate them?
A rotating shaft of 20 mm diameter is simply supported.
The shaft is loaded with a transverse load of 10 kN as shown in
the figure. The shaft is made from AISI 1095 hot-rolled steel. The
surface has been machined. The shaft operate at
temperature T = 450 °C. Consider a reliability factor of 95%.
Determine
(a) Calculate the reaction forces R, and R₂ (2 points)
(b) Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams
and determine the maximum bending moment and
shear force. (6 points)
200 mm
20 mm
10,000 N
-50 mm-
A
Not to scale.
(c) Determine the critical location of the shaft and the maximum effective stresses. (3 points)
(d) Calculate the safety factor against yielding. Does the shaft undergo local yielding? (2 points)
(e) Determined the endurance limit, adjusted as necessary with Marin factors. (12 points)
(f) Calculate the fatigue factor of safety based on achieving infinite life. (2 points)
(g) If the fatigue factor of safety is less than 1 (hint: it should be for this problem), then…
(read image)
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mechanics of Materials
Ch. 6.2 - In each case, the beam is subjected to the...Ch. 6.2 - and then draw the shear and moment diagrams for...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, express the shear and moment...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, express the shear and moment...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, express the shear and moment...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - In each case, draw the shear and moment diagrams...Ch. 6.2 - If the force applied to the handle of the load...
Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft....Ch. 6.2 - The crane is used to support the engine, which has...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.4PCh. 6.2 - •6–5. Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - Express the internal shear and moment in terms of...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.7PCh. 6.2 - Prob. 6.8PCh. 6.2 - Prob. 6.9PCh. 6.2 - Members ABC and BD of the counter chair are...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.11PCh. 6.2 - A reinforced concrete pier is used to support the...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.13PCh. 6.2 - The industrial robot is held in the stationary...Ch. 6.2 - Determine the placement distance a of the roller...Ch. 6.2 - Express the internal shear and moment in the...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam,...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - The 150-lb man sits in the center of the boat,...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.22PCh. 6.2 - The footing supports the load transmitted by the...Ch. 6.2 - Express the shear and moment in terms of x for 0 ...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.29PCh. 6.2 - 6–30. The beam is bolted or pinned at A and rests...Ch. 6.2 - The support at A allows the beam to slide freely...Ch. 6.2 - The smooth pin is supported by two leaves A and B...Ch. 6.2 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 6.36PCh. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam...Ch. 6.2 - The beam is used to support a uniform load along...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the double...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the simply...Ch. 6.2 - The compound beam is fixed at A, pin connected at...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the...Ch. 6.2 - The compound beam is fixed at A, pin connected at...Ch. 6.2 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam....Ch. 6.2 - A short link at B is used to connect beams AB and...Ch. 6.2 - 6–46. Determine the placement b of the hooks to...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the moment of inertia of the cross...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the location of the centroid, y, and the...Ch. 6.4 - In each case, show how the bending stress acts on...Ch. 6.4 - Sketch the bending stress distribution over each...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a bending moment of M...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.47PCh. 6.4 - Determine the moment M that will produce a maximum...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the maximum tensile and compressive...Ch. 6.4 - 6–50. A member has the triangular cross section...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.51PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.52PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.53PCh. 6.4 - If the built-up beam is subjected to an internal...Ch. 6.4 - If the built-up beam is subjected to an internal...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.56PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.57PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.58PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.59PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.60PCh. 6.4 - 6–61. The beam is subjected to a moment of 15 kip...Ch. 6.4 - 6–62. A box beam is constructed from four pieces...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.63PCh. 6.4 - The axle of the freight car is subjected to a...Ch. 6.4 - A shaft is made of a polymer having an elliptical...Ch. 6.4 - Solve Prob. 6-65 if the moment M = 50 N m is...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.67PCh. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by smooth journal bearings...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.69PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.70PCh. 6.4 - The boat has a weight of 2300 lb and a center of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the smallest allowable diameter of the...Ch. 6.4 - The pin is used to connect the three links...Ch. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.76PCh. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to an internal moment of...Ch. 6.4 - If the allowable tensile and compressive stress...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to an internal moment of...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is subjected to a moment of M = 100 kN...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam is made of material having an...Ch. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by a smooth thrust bearing...Ch. 6.4 - The shaft is supported by a thrust bearing at A...Ch. 6.4 - If the intensity of the load w = 15 kN/m,...Ch. 6.4 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 150...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.86PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.87PCh. 6.4 - *6–88. If the beam has a square cross section of 9...Ch. 6.4 - If the compound beam in Prob. 642 has a square...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam in Prob. 628 has a rectangular cross...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in...Ch. 6.4 - Determine, to the nearest millimeter, the smallest...Ch. 6.4 - 6–93. The wing spar ABD of a light plane is made...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.94PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6.95PCh. 6.4 - A log that is 2 ft in diameter is to be cut into a...Ch. 6.4 - A log that is 2 ft in diameter is to be cut into a...Ch. 6.4 - If the beam in Prob.63 has a rectangular cross...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.99PCh. 6.4 - If d = 450 mm, determine the absolute maximum...Ch. 6.4 - If the allowable bending stress is allow = 6 MPa,...Ch. 6.4 - Prob. 6.102PCh. 6.4 - 6–103. If the overhanging beam is made of wood...Ch. 6.5 - Determine the bending stress at corners A and B....Ch. 6.5 - Determine the maximum bending stress in the beams...Ch. 6.5 - The member has a square cross section and is...Ch. 6.5 - The member has a square cross section and is...Ch. 6.5 - Consider the general case of a prismatic beam...Ch. 6.5 - 6–107. If the beam is subjected to the internal...Ch. 6.5 - 6-108. If the wood used for the T-beam has an...Ch. 6.5 - 6-109. The box beam is subjected to the internal...Ch. 6.5 - 6-110. If the wood used for the box beam has an...Ch. 6.5 - 6-111. If the beam is subjected to the internal...Ch. 6.5 - 6-112. If the beam is made from a material having...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 6.113PCh. 6.5 - 6-114. The T-beam is subjected to a bending moment...Ch. 6.5 - 6-115. The beam has a rectangular cross section....Ch. 6.5 - For the section, Iy' = 31.7(10-6) m4, Iz' =...Ch. 6.5 - For the section, Iy' = 31.7(10-6) m4, Iz' =...Ch. 6.5 - If the applied distributed loading of w = 4 kN/m...Ch. 6.5 - Determine the maximum allowable intensity w of the...Ch. 6.9 - The composite beam is made of steel (A) bonded to...Ch. 6.9 - The composite beam is made of steel (A) bonded to...Ch. 6.9 - Segment A of the composite beam is made from...Ch. 6.9 - Segment A of the composite beam is made from...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.124PCh. 6.9 - The wooden section of the beam is reinforced with...Ch. 6.9 - The wooden section of the beam is reinforced with...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.127PCh. 6.9 - The steel channel is used to reinforce the wood...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.129PCh. 6.9 - 6-130. The beam is made from three types of...Ch. 6.9 - 6-131. The concrete beam is reinforced with three...Ch. 6.9 - *6-132. The wide-flange section is reinforced with...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.133PCh. 6.9 - If the beam is subjected to a moment of M = 45 kN...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.135PCh. 6.9 - For the curved beam in Fig. 640a, show that when...Ch. 6.9 - The curved member is subjected to the moment of M...Ch. 6.9 - The curved member is made from material having an...Ch. 6.9 - The curved beam is subjected to a moment of M = 40...Ch. 6.9 - The curved beam is made from material having an...Ch. 6.9 - If P = 3 kN, determine the bending stress at...Ch. 6.9 - If the maximum bending stress at section a-a is...Ch. 6.9 - The elbow of the pipe has an outer radius of 0.75...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.144PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.145PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.146PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.147PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.148PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.149PCh. 6.9 - 6-150. The bar is subjected to a moment of M = 153...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.151PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.152PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 6.153PCh. 6.9 - 6-154. The simply supported notched bar is...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.155PCh. 6.9 - *6-156. Determine the length L of the center...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 6.157PCh. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the wide-flange...Ch. 6.10 - 6-159. The beam is made of an elastic plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Prob. 6.160PCh. 6.10 - Prob. 6.161PCh. 6.10 - Prob. 6.162PCh. 6.10 - Determine the plastic moment Mp that can be...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the beam. Prob....Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Determine the shape factor for the beam. Prob....Ch. 6.10 - The beam is made of an elastic perfectly plastic...Ch. 6.10 - Prob. 6.168PCh. 6.10 - Prob. 6.169PCh. 6.10 - 6-170. The box beam is made from an...Ch. 6.10 - 6-171. The beam is made from elastic-perfectly...Ch. 6.10 - *6-172. Determine the shape factor for the...Ch. 6.10 - Prob. 6.173PCh. 6.10 - Prob. 6.174PCh. 6.10 - 6-175. The box beam is made from an...Ch. 6.10 - The wide-flange member is made from an elastic...Ch. 6.10 - Prob. 6.177PCh. 6.10 - The plexiglass bar has a stress-strain curve that...Ch. 6.10 - The stress-strain diagram for a titanium alloy can...Ch. 6.10 - A beam is made from polypropylene plastic and has...Ch. 6.10 - Prob. 6.181PCh. 6.10 - The bar is made of an aluminum alloy having a...Ch. 6 - Using appropriate measurements and data, explain...Ch. 6 - Determine the shape factor for the wide-flange...Ch. 6 - Prob. 6.184RPCh. 6 - The compound beam consists of two segments that...Ch. 6 - The composite beam consists of a wood core and two...Ch. 6 - 6-187. Solve Prob. 6-186 if the moment is applied...Ch. 6 - If it resists a moment of M = 125 N m, determine...Ch. 6 - Determine the maximum bending stress in the handle...Ch. 6 - The curved beam is subjected to a bending moment...Ch. 6 - Determine the shear and moment in the beam as...Ch. 6 - A wooden beam has a square cross section as shown...Ch. 6 - Draw the shear and moment diagrams for the shaft...Ch. 6 - The strut has a square cross section a by a and is...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The following declaration appears in a program: short total Pay, basePay = 500, bonus = 1000; The following sta...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Write two different code segments that may be used to wrap an index back around to the beginning of an array wh...
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Write a program that inputs an integer. If the integer is greater than 100 or between 50 and 75 (inclusive) the...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
CONCEPT QUESTIONS
15.CQ3 The ball rolls without slipping on the fixed surface as shown. What is the direction ...
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Why is feed specified for a boring operation typically less than that specified for turning if the MRR equation...
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
True or False: A class may only implement one interface.
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forward(read image)arrow_forward6: Refer to the figure.Given: W1 = 200 kN/m; W2 = 300 kN/m; L1 = 2 m; L2 = 3 m; L3 = 2 m(a) Calculate the total length L so that the resulting upward pressureq is uniform. (b) draw the shear and moment diagram and determinethe maximum shear, maximum positive and negative bendingmoments.arrow_forward
- A six cylinder, four-stroke diesel engine develops a power of 200 kW at 2000 rpm. The bsfc is 0.2 kW/kg h of fuel with 34.9° API. The fuel is injected at an average pressure of 350 bar and the pressure in the combustion chamber is 40 bar. Assuming Ca for injector 0.75 and the atmospheric pressure 1 bar. Determine the period of injection in seconds if the total orifice area required per injector is 0.4876 × 10-6 m².arrow_forwardTrieed a detailed drawing Win explanatio LL Antsmi 1981x pu + 96252 اه 6. The Pre-combustion chamber design engines employ nozzle type commonly referred to as a ....... a. inward-opening nozzle b. multiple-hole nozzle. c. pintle nozzle. d. none of these. 7. If the temperature of the spark plug tip is less than 350 °C, ......... a. the plug might not work. b. the carbon deposits would increase. 8. Port injection sprays fuel....... c. pre-ignition will occur. d. none of these. a. towards the intake valve. b. in the engine cylinder. c. in the throttle body assembly. d. none of these. 9. When the fuel-air mixture changed from best power to a richer ratio, the spark advance should be........ a. increased. b. decreased. c. left unchanged. d. none of these. d. none of these. 10. Spark plugs are classified as hot plugs and cold plugs depending upon ........ a. spark gap. b. the type of plug c. the operating temperature insulator. range of the electrode tip. ---20125 750 x2.01 SP 5.arrow_forwardA 1. How does the octane number (O.N.) of the fuel a. Higher ignition advance is required for a high O.N. fuel. b. Higher ignition retard is required for a high O.N. fuel. affect spark ing:d. Nou does not affect spark timing. c. The octane number 2. How does the ignition system account for load change? these. of a. The throttle b. The vacuum ignition governor c. The mechanism of d. None of is wide opened. provide additional spark advance at part throttle positions. centrifugal advance does the job. these. 3. In the common rail fuel system the fuel is metered by ........ a. low pressure pump. b. injectors. c. high pressure pump. d. none of these. 4.......... is the time period, measured in degrees of cam rotation, during which the contact points remain closed between each opening. a. Distributor. b. Dwell. c. ECU. d. none of these. 5. The trigger wheel in TCI system replaces the ......... used in a contact breaker distributor. a. pickup coil. b. distributor cam. c. condenser. 750 x2.01…arrow_forward
- a い يكا 4 +91- pu Answer the following statements by true or false, giving the reason for your answer: 1. Injection pressure in CI engines should be sufficiently high. 2. The purpose of the condenser in battery ignition system is to prevent spark in the ignition coil assembly. 3. An idling engine requires lean mixture of fuel and air. 4. Factors which decide optimum engine firing order are engine vibration, engine cooling and back pressure. 5. It is the duty of the header to control over speeding during CI engine operation when drastic reduction in load occurs. ---20125 750 x2.01 SParrow_forward6. The Pre-combustion chamber design engines employ nozzle type commonly referred to as a a. inward-opening nozzle b. multiple-hole nozzle. c. pintle nozzle. d. none of these. 7. If the temperature of the spark plug tip is less than 350 °C, ........ a. the plug might b. the carbon deposits not work. would increase. c. pre-ignition will occur. d. none of these. 8. Port injection sprays fuel........ a. towards the intake valve. b. in the engine cylinder. c. in the throttle body d. none of assembly. these. 9. When the fuel-air mixture changed from best power to a richer ratio, the spark advance should be ........ a. increased. b. decreased. c. left unchanged. d. none of these. 10. Spark plugs are classified as hot plugs and cold plugs depending upon a. spark gap. b. the type of plug c. the operating temperature d. none of these. range of the electrode tip. insulator.arrow_forward1: A H = 6 m cantilever retaining wall is subjected to a soil pressurelinearly varying from zero at the top to 90 kPa at the bottom. As an additionalsupport, it is anchored at depth y = 2 m. with maximum tension equal to 25kN. Assume that the stem provides fully retrained support. Draw the shearand moment diagram of the wall to calculate the following: (a) Maximumpositive bending moment per linear meter; (b) maximum negative bendingmoment per linear meter; (c) maximum shear force per linear meter.arrow_forward
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH COMPLETE FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE. 9: The beam shown has a width of 80 mm and its allowable bending stress is not to exceed 120 MPa. Calculatethe required depth of the beam.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 4: A pre-stressed concrete pile of length L (m) is to be picked up by crane cables at two points, both equidistant from the ends. If the concrete pile has a cross-sectional area of A (m²) and concrete has unit weight of Yc (kN/m³), calculate the distance of the pick-up points from the end in terms of pile length. (Hint: to minimize the absolute maximum moment, the maximum negative and maximum negative moments should be equal)arrow_forwardCorrect and detailed solution only. Complete fbd. I will upvote.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Everything About COMBINED LOADING in 10 Minutes! Mechanics of Materials; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=N-PlI900hSg;License: Standard youtube license