
Concept explainers
6.70 through 6.74 classify as determinate or indeterminate. (All members act both in tension and in compression.)
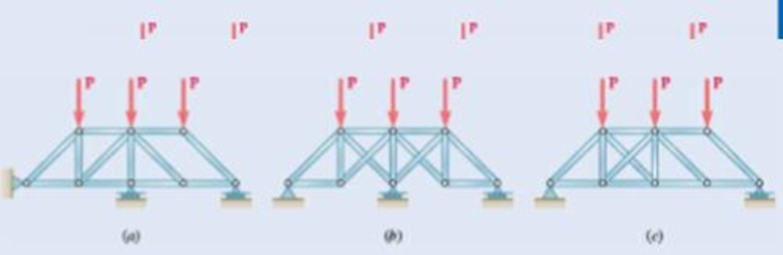
Fig. P6.74
(a)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.74P
The given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.74 (a). The arrangement can be redrawn by labeling different points in the truss and is given in Figure 1.
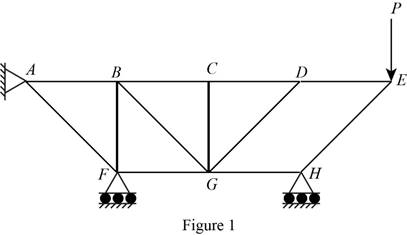
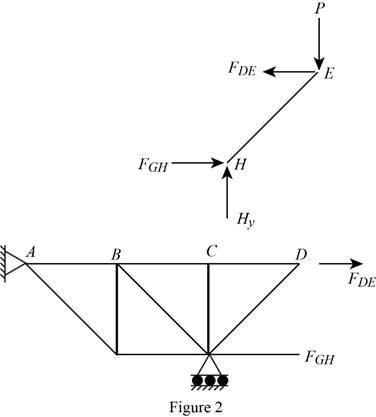
The free-body diagram of the section
Write the condition for a truss to be completely constrained.
Here,
Write the condition for a truss to be partially constrained.
Write the expression for a truss to be indeterminate.
Write the expression for the condition for equilibrium.
Here,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (IV) about point
Apply the condition for equilibrium in equation (V) about various points of the structure in the free-body diagrams given in Figure 2.
So, the truss
Therefore, the given structure is completely constrained and determinate.
(b)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.74P
The given structure is partially constrained.
Explanation of Solution
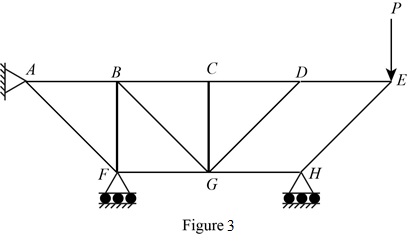
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.74 (b). The arrangement can be redrawn by labeling different points in the truss and is given in Figure 3.
From equations (I), (II), and (III), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Therefore, the given structure is partially constrained.
(c)
Classify the given structure as completely, partially, or improperly constrained and if completely constrained, further classify as determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 6.74P
The given structure is completely constrained and indeterminate.
Explanation of Solution
The structure is shown in Fig. P6.74 (c). The arrangement can be redrawn by labeling different points in the truss and is given in Figure 4.
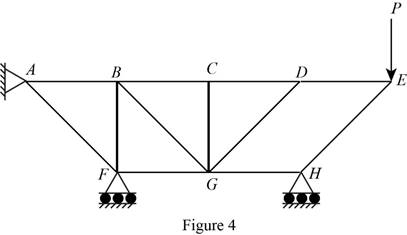
From equations (I), (II), and (III), the conditions for the state of constrain of the structure is as follows,
Conclusion:
For the given truss,
Compute
Compute
So, for the given system,
Therefore, the given structure is completely constrained and indeterminate.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with C++: Early Objects (9th Edition)
Vector Mechanics For Engineers
Java How to Program, Early Objects (11th Edition) (Deitel: How to Program)
Problem Solving with C++ (10th Edition)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
- A 4 ft 300 Ib 1000 Ib.ft 350 Ib C 2 ft 3. 45° 250 Ib B. 3ft B 25ft 200 Ib 150 Ib Replace the force system acting on the frame shown in the figure by a resultant force (magnitude and direction), and specify where its line of action intersects member (AB), measured from point (A).arrow_forwardCan you research the standard percentage of Steam Quality in:(1.) Boiler - leaving boilerBoiler -> Out(2.) Condenser - coming in condenser In -> CondenserProvide reference Also define: steam quality, its purpose and importancearrow_forwardNumbers 1 and 2 and 5 are are optional problems. However, I only need the values (with units) of 3, 4 and 6. Thank you :)arrow_forward
- Three cables are pulling on a ring located at the origin, as shown in the diagram below. FA is 200 N in magnitude with a transverse angle of 30° and an azimuth angle of 140°. FB is 240 N in magnitude with coordinate direction angles α = 135° and β = 45°. Determine the magnitude and direction of FC so that the resultant of all 3 force vectors lies on the z-axis and has a magnitude of 300 N. Specify the direction of FC using its coordinate direction angles.arrow_forwardturbomachieneryarrow_forwardauto controlsarrow_forward
- auto controlsarrow_forward1 Pleasearrow_forwardA spring cylinder system measures the pressure. Determine which spring can measure pressure between 0-1 MPa with a large excursion. The plate has a diameter of 20 mm. Also determine the displacement of each 0.1 MPa step.Spring power F=c x fF=Springpower(N)c=Spring constant (N/mm)f=Suspension (mm) How do I come up with right answer?arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





