
(a)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
(b)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents approaches same side of
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
(c)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of phi bonds between carbon-carbon multiple bonds and addition of alcohol to more substituted position of carbon in the molecule.
First step is the acid donates proton to the alkene which leads to the formation of more stable carbo cation.
Then, the water is added to the given alkene through acid catalyzed reaction where the water gets added to the carbo cation finally, the removal of one proton from oxonium ion (oxygen with one positive charge) using water results in the formation of product.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
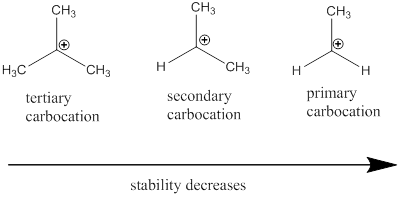
(d)
Interpretation:
The stereoisomer products for the given reaction should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
In addition reaction of alkenes when two substituents approaches same side of
Oxidation Reaction: It involves loss of electrons, addition of oxygen atoms or removal of hydrogen atoms.
E configuration: The geometric isomers are given E configuration if high priority groups are placed on opposite sides of the bond.
Z configuration: The geometric isomers are given Z configuration if high priority groups are placed on same sides of the bond.
Stereo specific: The reaction is considered as stereo specific if the reactant is stereo isomers that give rise to different set of stereo isomers.
Stereoisomers: Two compounds with same molecular formula but different in their orientation are considered as isomers.
The presence of atom with non-super impossible mirror image is defined as enantiomers which are given
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Pearson eText Organic Chemistry -- Instant Access (Pearson+)
- b. H3C CH3 H3O+ ✓ H OHarrow_forward2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. CH3arrow_forwardIdentify and provide an explanation that distinguishes a qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- Identify and provide an explanation of the operational principles behind a Atomic Absorption Spectrometer (AAS). List the steps involved.arrow_forwardInstructions: Complete the questions in the space provided. Show all your work 1. You are trying to determine the rate law expression for a reaction that you are completing at 25°C. You measure the initial reaction rate and the starting concentrations of the reactions for 4 trials. BrO³¯ (aq) + 5Br¯ (aq) + 6H* (aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + 3H2O (l) Initial rate Trial [BrO3] [H*] [Br] (mol/L) (mol/L) | (mol/L) (mol/L.s) 1 0.10 0.10 0.10 8.0 2 0.20 0.10 0.10 16 3 0.10 0.20 0.10 16 4 0.10 0.10 0.20 32 a. Based on the above data what is the rate law expression? b. Solve for the value of k (make sure to include proper units) 2. The proposed reaction mechanism is as follows: i. ii. BrО¸¯ (aq) + H+ (aq) → HBrO3 (aq) HBrO³ (aq) + H* (aq) → H₂BrO3* (aq) iii. H₂BrO³* (aq) + Br¯ (aq) → Br₂O₂ (aq) + H2O (l) [Fast] [Medium] [Slow] iv. Br₂O₂ (aq) + 4H*(aq) + 4Br(aq) → 3Br₂ (l) + H2O (l) [Fast] Evaluate the validity of this proposed reaction. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardе. Д CH3 D*, D20arrow_forward
- H3C. H3C CH 3 CH 3 CH3 1. LDA 2. PhSeCl 3. H2O2arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions: 1.03 2. H₂O NaNH, 1. n-BuLi 2. Mel A H₂ 10 9 0 H2SO4, H₂O HgSO4 Pd or Pt (catalyst) B 9 2 n-BuLi ♡ D2 (deuterium) Lindlar's Catalyst 1. NaNH2 2. EtBr Na, ND3 (deuterium) 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. (Sia)2BH с Darrow_forwardin the scope of ontario SCH4U grade 12 course, please show ALL workarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
