
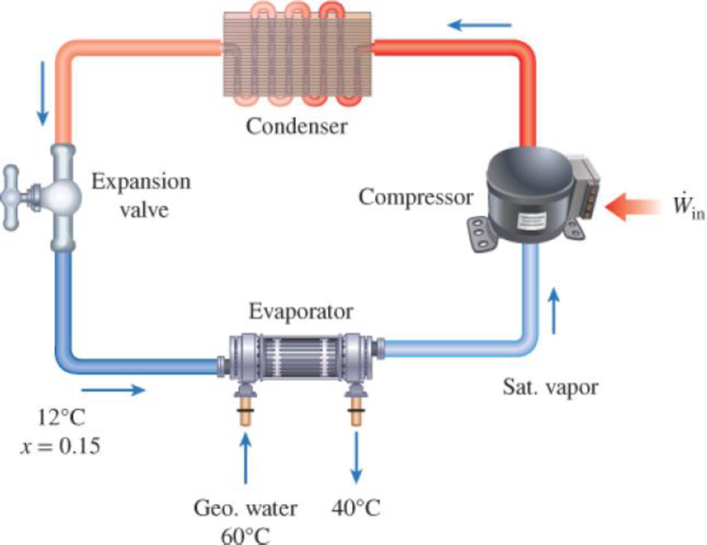
A heat pump with refrigerant-134a as the working fluid is used to keep a space at 25°C by absorbing heat from geothermal water that enters the evaporator at 60°C at a rate of 0.065 kg/s and leaves at 40°C. Refrigerant enters the evaporator at 12°C with a quality of 15 percent and leaves at the same pressure as saturated vapor. If the compressor consumes 1.6 kW of power, determine (a) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant, (b) the rate of heat supply, (c) the COP, and (d) the minimum power input to the compressor for the same rate of heat supply.
FIGURE P6–152
(a)
The mass flow rate of the refrigerant.
Answer to Problem 152RP
The mass flow rate of the refrigerant is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the rate of heat absorbed from the water.
Here, the mass flow rate of the water is
Determine the mass flow rate of a refrigerant.
Conclusion:
From the Table A-11, “Saturated refrigerant R-134a”, obtain the value of saturated pressure of the refrigerant at the inlet temperature of
Here, the pressure of refrigerant is constant in evaporation.
From the Table A-11, “Saturated refrigerant R-134a” to obtain the value of specific enthalpy of the refrigerant at the outlet pressure of
From the Table A-11, “Saturated refrigerant R-134a” to obtain the value of specific enthalpy of saturated liquid and specific enthalpy change upon vaporization of the refrigerant at the inlet temperature of
Calculate the specific enthalpy of refrigerant at evaporator inlet.
Here, the specific enthalpy of saturated liquid is
Substitute
From the Table A-4, “Saturated water-temperature” to obtain the value of specific enthalpy of saturated liquid of water at the inlet temperature of
From the Table A-4, “Saturated water-temperature” to obtain the value of specific enthalpy of saturated liquid of water at the outlet temperature of
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the mass flow rate of the refrigerant is
(b)
The heating load of the heat pump.
Answer to Problem 152RP
The heating load of the heat pump is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the heating load of the heat pump.
Here, the power input consumed by compressor is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the heating load of the heat pump is
(c)
The COP of a heat pump operating between the same temperature limits.
Answer to Problem 152RP
The COP of a heat pump operating between the same temperature limits is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the coefficient of performance of the heat pump.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the COP of a heat pump operating between the same temperature limits is
(d)
The minimum power input to the compressor.
Answer to Problem 152RP
The minimum power input to the compressor is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the maximum coefficient of performance of the heat pump operating between the same temperature limits.
Here, the temperature of higher temperature body is
Determine the minimum power input to the condenser for the same heat pump load.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the minimum power input to the compressor is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
CENGEL'S 9TH EDITION OF THERMODYNAMICS:
- answer the fallowing Brake Specific Fuel Consumption - 0.3 kg/kwh, Mechanical Efficiency- 90% Calorific Value of Fuel -45 MJ/kg. Given these values, find the indicated power, indicated thermal efficiency and brake thermal efficiencyarrow_forwardProblem 6. The circular plate shown rotates about its vertical diameter. At the instant shown, the angular velocity ₁ of the plate is 10 rad/s and is decreasing at the rate of 25 rad/s². The disk lies in the XY plane and Point D of strap CD moves upward. The relative speed u of Point D of strap CD is 1.5 m/s and is decreasing at the rate of 3 m/s². Determine (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: =0.75 +1.299]-1.732k m/s a=-28.6 +3.03-10.67k m/s² 200 mm x Zarrow_forwardProblem 1. The flywheel A has an angular velocity o 5 rad/s. Link AB is connected via ball and socket joints to the flywheel at A and a slider at B. Find the angular velocity of link AB and the velocity of slider B at this instant. (Partial Answer: @ABN = -2î + 2.25; red Z -1.2 ft C -7 Y -1.5 ft- B 2.0 ftarrow_forward
- Need help pleasearrow_forwardPROBLEM 15.225 The bent rod shown rotates at the constant rate @₁ = 5 rad/s and collar C moves toward point B at a constant relative speed u = 39 in./s. Knowing that collar C is halfway between points B and D at the instant shown, determine its velocity and acceleration. Answers: v=-45 +36.6)-31.2 k in./s āc = -2911-270} in./s² 6 in 20.8 in. 14.4 in.arrow_forwardNeed help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!..arrow_forward
- Need help, please show all work, steps, units and please box out and round answers to 3 significant figures. Thank you!...arrow_forwardFL y b C Z Determine the moment about O due to the force F shown, the magnitude of the force F = 76.0 lbs. Note: Pay attention to the axis. Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 1.90 ft b 2.80 ft с 2.60 ft d 2.30 ft Mo 144 ft-lb = -212 × 1 + xk) ☑+212arrow_forward20 in. PROBLEM 15.206 Rod AB is connected by ball-and-socket joints to collar A and to the 16-in.-diameter disk C. Knowing that disk C rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate ₁ =3 rad/s in the zx plane, determine the velocity of collar A for the position shown. 25 in. B 8 in. Answer: -30 in/s =arrow_forward
- B Z 001 2.5 ft PROBLEM 15.236 The arm AB of length 16 ft is used to provide an elevated platform for construction workers. In the position shown, arm AB is being raised at the constant rate de/dt = 0.25 rad/s; simultaneously, the unit is being rotated about the Y axis at the constant rate ₁ =0.15 rad/s. Knowing that 20°, determine the velocity and acceleration of Point B. Answers: 1.371 +3.76)+1.88k ft/s a=1.22 -0.342)-0.410k ft/s² Xarrow_forwardF1 3 5 4 P F2 F2 Ꮎ Ꮎ b P 3 4 5 F1 The electric pole is subject to the forces shown. Force F1 245 N and force F2 = 310 N with an angle = 20.2°. Determine the moment about point P of all forces. Take counterclockwise moments to be positive. = Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value a 2.50 m b 11.3 m C 13.0 m The moment about point P is 3,414 m. × N- If the moment about point P sums up to be zero. Determine the distance c while all other values remained the same. 1.26 m.arrow_forwardZ 0.2 m B PROBLEM 15.224 Rod AB is welded to the 0.3-m-radius plate, which rotates at the constant rate ₁ = 6 rad/s. Knowing that collar D moves toward end B of the rod at a constant speed u = 1.3 m, determine, for the position shown, (a) the velocity of D, (b) the acceleration of D. Answers: 1.2 +0.5-1.2k m/s a=-7.21-14.4k m/s² A 0.25 m 0.3 marrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





