
A commercial refrigerator with refrigerant-134a as the working fluid is used to keep the refrigerated space at −35°C by rejecting waste heat to cooling water that enters the condenser at 18°C at a rate of 0.25 kg/s and leaves at 26°C. The refrigerant enters the condenser at 1.2 MPa and 50°C and leaves at the same pressure subcooled by 5°C. If the compressor consumes 3.3 kW of power, determine (a) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant, (b) the refrigeration load, (c) the COP, and (d) the minimum power input to the compressor for the same refrigeration load.
FIGURE P6–107
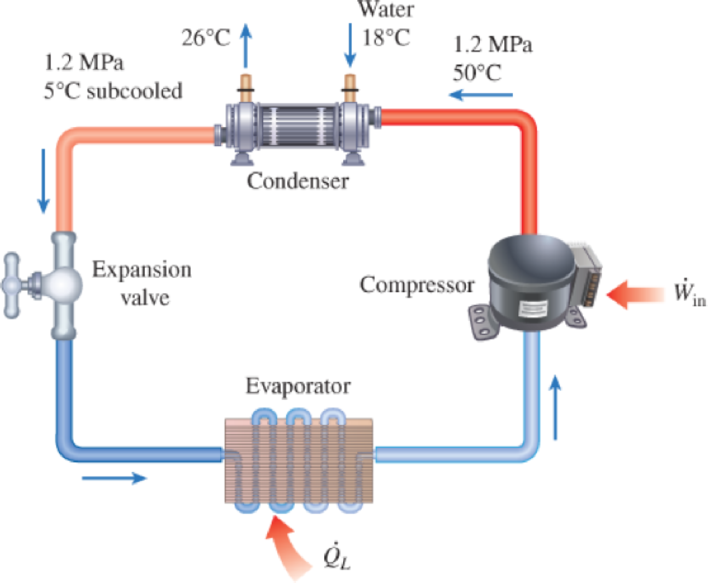
(a)
The mass flow rate of the refrigerant.
Answer to Problem 107P
The mass flow rate of the refrigerant is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the rate of heat transferred to the water.
Here, the mass flow rate of the water is
Determine the mass flow rate of a refrigerant.
Conclusion:
From the Table A-13, “Superheated refrigerant R-134a” obtain the value of enthalpy of the refrigerant at the inlet of the condenser at the 1.2 MPa of pressure and
From the Table A-13, “Superheated refrigerant R-134a” obtain the value of temperature of the refrigerant at the inlet of the condenser at the 1.2 MPa of pressure as,
Calculate the exit temperature of the refrigerant in the condenser.
Here, the temperature leave from the condenser is
Substitute
Refer to Table A-11, “Saturated refrigerant R-134a”, obtain the below exit enthalpy of the condenser at compressed liquid state on the basis of exit temperature of
Write the formula of interpolation method of two variables.
Here, the variables denote by x and y are temperature and enthalpy of vaporization.
Show the temperature at
| S. No |
Temperature, |
enthalpy of vaporization |
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 |
Calculate exit enthalpy of the condenser at compressed liquid state on the basis of exit temperature of
Substitute
From above calculation the exit enthalpy of the condenser at compressed liquid state on the basis of exit temperature of
Repeat the above Equation (IV) to obtain the value of enthalpy of saturated liquid that entering the inlet of the condenser at the
Repeat the above Equation (IV) to obtain the value of enthalpy of saturated liquid which is leaving the condenser at the
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the mass flow rate of the refrigerant is
(b)
The refrigeration load of the refrigerator.
Answer to Problem 107P
The refrigeration load of the refrigerator is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the refrigeration load of the refrigerator.
Here, the power input consumed by compressor is
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the refrigeration load of the refrigerator is
(c)
The COP of a reversible refrigerator operating between the same temperature limits.
Answer to Problem 107P
The COP of a reversible refrigerator operating between the same temperature limits is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the coefficient of performance of the refrigerator.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the COP of a reversible refrigerator operating between the same temperature limits is
(d)
The minimum power input to the compressor.
Answer to Problem 107P
The minimum power input to the compressor is
Explanation of Solution
Determine the maximum coefficient of performance of the reversible refrigerator operating between the same temperature limits.
Here, the temperature of higher temperature body is
Determine the minimum power input to the condenser for the same refrigerator load.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the minimum power input to the compressor is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
CENGEL'S 9TH EDITION OF THERMODYNAMICS:
- CORRECT AND DETAILED SOLUTION WITH FBD ONLY. I WILL UPVOTE THANK YOU. CORRECT ANSWER IS ALREADY PROVIDED. I REALLY NEED FBD. The roof truss shown carries roof loads, where P = 10 kN. The truss is consisting of circular arcs top andbottom chords with radii R + h and R, respectively.Given: h = 1.2 m, R = 10 m, s = 2 m.Allowable member stresses:Tension = 250 MPaCompression = 180 MPa1. If member KL has square section, determine the minimum dimension (mm).2. If member KL has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).3. If member GH has circular section, determine the minimum diameter (mm).ANSWERS: (1) 31.73 mm; (2) 35.81 mm; (3) 18.49 mmarrow_forwardPROBLEM 3.23 3.23 Under normal operating condi- tions a motor exerts a torque of magnitude TF at F. The shafts are made of a steel for which the allowable shearing stress is 82 MPa and have diameters of dCDE=24 mm and dFGH = 20 mm. Knowing that rp = 165 mm and rg114 mm, deter- mine the largest torque TF which may be exerted at F. TF F rG- rp B CH TE Earrow_forward1. (16%) (a) If a ductile material fails under pure torsion, please explain the failure mode and describe the observed plane of failure. (b) Suppose a prismatic beam is subjected to equal and opposite couples as shown in Fig. 1. Please sketch the deformation and the stress distribution of the cross section. M M Fig. 1 (c) Describe the definition of the neutral axis. (d) Describe the definition of the modular ratio.arrow_forward
- using the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I only need concise calculations with minimal explanations. The correct answers are provided at the bottomarrow_forwardMechanics of materialsarrow_forwardusing the theorem of three moments, find all the moments, I need concise calculations onlyarrow_forward
- Can you provide steps and an explaination on how the height value to calculate the Pressure at point B is (-5-3.5) and the solution is 86.4kPa.arrow_forwardPROBLEM 3.46 The solid cylindrical rod BC of length L = 600 mm is attached to the rigid lever AB of length a = 380 mm and to the support at C. When a 500 N force P is applied at A, design specifications require that the displacement of A not exceed 25 mm when a 500 N force P is applied at A For the material indicated determine the required diameter of the rod. Aluminium: Tall = 65 MPa, G = 27 GPa. Aarrow_forwardFind the equivalent mass of the rocker arm assembly with respect to the x coordinate. k₁ mi m2 k₁arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





