
Concept explainers
The truss shown consists of nine members and is support by a ball-and-socket at B, a short link at C, and two short links at D. (a) Check that this truss is a simple truss, that completely constrained, and that the reactions at its suppo are statically determinate. (b) Determine the force in each member for P = (−1200 N)j and Q = 0.
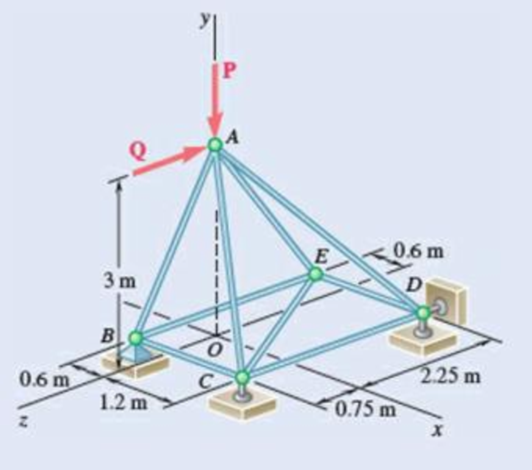
Fig. P6.39
(a)
Verify that the truss is a simple truss, completely constrained, and the reactions at the supports are statically determinate.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The reactions at supports B, C, and D is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The value of the force P is
The value of the force Q is zero.
Calculation:
Show the free-body diagram of the truss as in Figure 1.
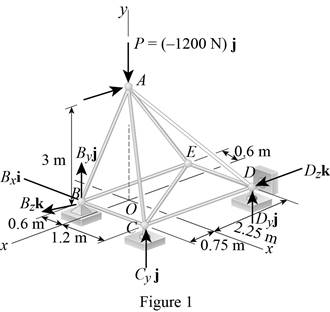
Find the vector coordinates by taking moment about point B.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of k to zero.
Substitute 300 N for
Resolve the force components in y-axis.
Substitute 300 N for
The unknown reactions can be calculated with the equilibrium equations. Therefore, the truss is statically determinate, completely constrained and simple truss.
Thus, the reactions at supports B, C, and D is
(b)
Find the force in each member of the truss.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The force in the member AB is
The force in the member BC is
The force in the member BE is
The force in the member AC is
The force in the member CE is
The force in the member CD is
The force in the member AD is
The force in the member DE is
The force in the member AE is
Explanation of Solution
Show the free-body diagram of the joint B as in Figure 2.
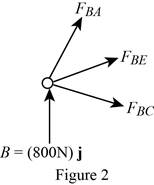
Resolve the force components as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of BA using the relation.
Find the force in the member AB as follows;
Substitute
Find the force in the member BC as follows;
Find the force in the member BE as follows;
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Substitute –840 N for
Equate the coefficients of k to zero.
Substitute –840 N for
Therefore,
The force in the member AB is
The force in the member BC is
The force in the member BE is
Show the free-body diagram of the joint C as in Figure 3.
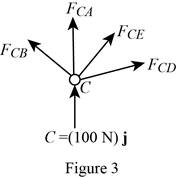
Resolve the force components as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of CA using the relation.
Find the force in the member AC as follows;
Substitute
Find the force in the member CB as follows;
Find the force in the member CD as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of CE using the relation.
Find the force in the member CE as follows;
Substitute
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Substitute –110.6 N for
Equate the coefficients of k to zero.
Substitute –110.6 N for
Therefore,
The force in the member AC is
The force in the member CE is
The force in the member CD is
Show the free-body diagram of the joint D as in Figure 4.
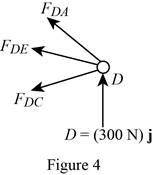
Resolve the force components as follows;
Write the vector value of
Find the scalar quantity of DA using the relation.
Find the force in the member AD as follows;
Substitute
Find the force in the member DC as follows;
Find the force in the member DE as follows;
Equate the coefficients of j to zero.
Equate the coefficients of i to zero.
Substitute –394 N for
Therefore,
The force in the member AD is
The force in the member DE is
Show the free-body diagram of the joint E as in figure 5.
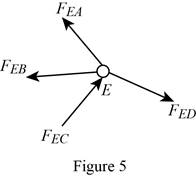
The member AE is not in the xz plane.
Therefore, the force in the member AE is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- Problem 5 (Optional, extra 6 points) A 6-lb homogeneous disk of radius 3 in. spins as shown at the constant rate w₁ = 60 rad/s. The disk is supported by the fork-ended rod AB, which is welded to the vertical shaft CBD. The system is at rest when a couple Mo= (0.25ft-lb)j is applied to the shaft for 2 s and then removed. Determine the dynamic reactions at C and D before and after the couple has been removed at 2 s. 4 in. C B Mo 5 in 4 in. Note: 2 rotating around CD induced by Mo is NOT constant before Mo is removed. and ₂ (two unknowns) are related by the equation: ₂ =0+ w₂t 3 in. Partial Answer (after Mo has been removed): C-7.81+7.43k lb D -7.81 7.43 lbarrow_forwardProblem 4. A homogeneous disk with radius and mass m is mounted on an axle OG with length L and a negligible mass. The axle is pivoted at the fixed-point O, and the disk is constrained to roll on a horizontal surface. The disk rotates counterclockwise at the constant rate o₁ about the axle. (mg must be included into your calculation) (a). Calculate the linear velocity of G and indicate it on the figure. (b). Calculate ₂ (constant), which is the angular velocity of the axle OG around the vertical axis. (c). Calculate the linear acceleration ā of G and indicate it on the figure. (d). Determine the force (assumed vertical) exerted by the floor on the disk (e). Determine the reaction at the pivot O. 1 Answers: N = mg +mr(r/L)² @² |j mr w IIG C R L i+ 2L =arrow_forwardProblem 2. The homogeneous disk of weight W = 6 lb rotates at the constant rate co₁ = 16 rad/s with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating at the constant rate 2 = 8 rad/s. Assume the rod weight is negligible compared to the disk. Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E (ignore mg). Answers: D=-7.12ĵ+4.47k lb r-8 in. 9 in. B D E=-1.822+4.47 lb 9 in. E 12 in. 12 in. xarrow_forward
- Problem 3. Each of the right angle rods has a mass of 120 g and is welded to the shaft, which rotates at a steady speed of 3600 rpm. Ignore the weight of the shaft AB. Find the bearing dynamic reaction at A due to the dynamic imbalance of the shaft. (ignore mgs) 100 N A 100 100 100 100 100 (Dimensions in millimeters) Answer: A=-8521-426j N Barrow_forwardThermodynamics. Need help solving this. Step by step with unitsarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2=6mm, and for w3 is h3 -6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm 133 mm 140 mm w3 wiarrow_forward
- E W X FO FB F10 F11 F12 Home Q: Consider the square of Figure below.The left face is maintained at 100°C and the top face at 500°C, while the other two faces are exposed to an environment at1 00°C, h=10 W/m². C and k=10 W/m.°C. The block is 1 m square. Compute the temperature of the various nodes as indicated in Figure below and the heat flows at the boundaries. T= 500°C Alt Explain to me in detail how to calculate the matrix in the Casio calculator type (fx-991ES plus) T= 100°C 1 2 4 7 1 m- 3 1 m 5 6 T= 100°C 8 9arrow_forwardWhich of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 1-2n 2) a = 1+2n 1/n 3 16) a = n In n 17) an = n 1/n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n² -2n+1 n! 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forwardA steel alloy contains 95.7 wt% Fe, 4.0 wt% W, and 0.3 wt% C.arrow_forward
- b. A horizontal cantilever of effective length 3a, carries two concentrated loads W at a distance a from the fixed end and W' at a distance a from the free end. Obtain a formula for the maximum deflection due to this loading using Mohr's method. If the cantilever is 250 mm by 150mm steel I beam, 3 m long having a second moment of area I as 8500 cm4, determine W and W'to give a maximum deflection of 6 mm when the maximum stress due to bending is 90 Mpa. Take Young's modulus of material E as 185 Gpa.arrow_forwardWhich of the following sequences converge and which diverge? 1/n 1) a₁ = 2+(0.1)" 3 16) a = n 1-2n 2) a = In n 1+2n 17) an = 1/n n 1-5n4 3) an = n² +8n³ 18) an = √4" n n! n² -2n+1 20) a = 4) an = 106 5) n-1 a₁ =1+(-1)" n+1 a-(+) (1-4) 6) = 7) a = 2n (-1)"+1 2n-1 21) an = n -A" 1/(Inn) 3n+1 22) a = 3n-1 1/n x" 23) a = , x>0 2n+1 3" x 6" 24) a = 2™" xn! 2n 8) a = n+1 πT 1 9) a„ = sin +- 2 n sin n 10) an = n 25) a = tanh(n) 26) a = 2n-1 27) a = tan(n) 1 -sin n n 11) a = 2" 28) an == " 1 + 2" In(n+1) 12) a = n (In n) 200 29) a = n 13) a = 8/n 14) a 1+ =(1+²)" 15) an 7 n = 10n 30) an-√√n²-n 1"1 31) adx nixarrow_forwardCalculate the angle of incidence of beam radiation on a collector located at (Latitude 17.40S) on June 15 at 1030hrs solar time. The collector is tilted at an angle of 200, with a surface azimuth angle of 150.arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
