
Concept explainers
The truss shown consists of nine members and is supported by a ball and socket at A, two short links at B, and a short link at C. Determine the force in each of the members for the given loading.
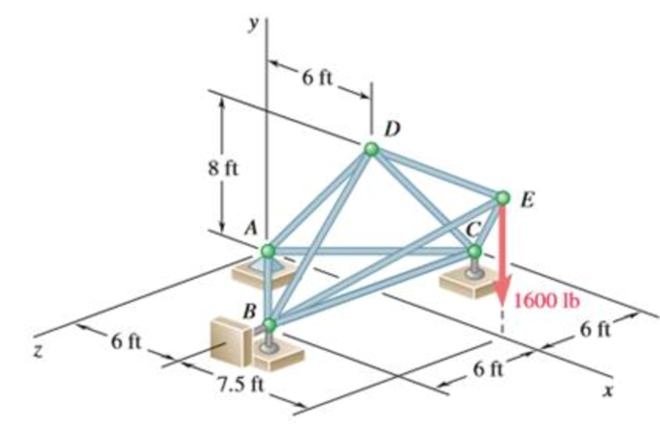
The force in each of the members of the truss for the given loading.
Answer to Problem 6.38P
The force in member
Explanation of Solution
The free-body diagram of the entire truss is shown in figure 1.
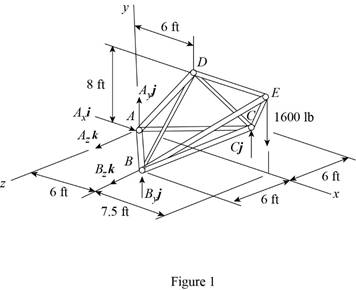
Refer to figure 1 and use symmetry.
Here,
The
Here,
Sum of the moments must be equal to zero.
Here,
Write the equation for
Here,
Put the above equation in equation (I).
Write the expression for the reaction at the point A.
Here,
Substitute
Use symmetry.
Here,
The
Here,
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (II).
Write the expression for the reaction at the point A.
Here,
Substitute
Consider the free body
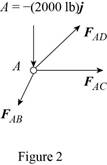
The net force must be equal to zero.
Here,
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (III).
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Put equations (V), (VI) and (VII) in equation (IV).
Factorize
Equate the coefficient of
Equate the coefficient of
Equate the coefficient of
Put equation (X) in equation (IX).
Substitute
Put the above equation in equation (X).
Consider the free-body joint B. The free-body diagram of joint B is shown in figure 3.
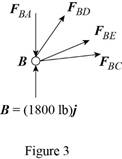
Refer to figure (3) and write the expression for the forces.
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (III).
Put equations (XI), (XII), (XIII) , (XIV) and substitute
Equate the coefficient of
Equate the coefficient of
Substitute
Equate the coefficient of
Substitute
Use symmetry.
Here,
Substitute
Consider the free body joint D. The free body diagram is shown in figure 4.
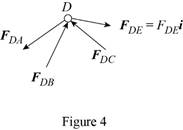
Write the expression for
Put the above equation in equation (III).
Only
Equate the coefficient of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus, the force in member
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
VECTOR MECH...,STAT.+DYN.(LL)-W/ACCESS
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardRequired information An eccentric force P is applied as shown to a steel bar of 25 × 90-mm cross section. The strains at A and B have been measured and found to be εΑ = +490 μ εB=-70 μ Know that E = 200 GPa. 25 mm 30 mm 90 mm 45 mm B Determine the distance d. The distance dis 15 mm mm.arrow_forward
- handwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forwardhandwritten-solutions, please!arrow_forward! Required information Assume that the couple shown acts in a vertical plane. Take M = 25 kip.in. r = 0.75 in. A B 4.8 in. M 1.2 in. [1.2 in. Determine the stress at point B. The stress at point B is ksi.arrow_forward
- Problem 6 (Optional, extra 6 points) 150 mm 150 mm 120 mm 80 mm 60 mm PROBLEM 18.103 A 2.5 kg homogeneous disk of radius 80 mm rotates with an angular velocity ₁ with respect to arm ABC, which is welded to a shaft DCE rotating as shown at the constant rate w212 rad/s. Friction in the bearing at A causes ₁ to decrease at the rate of 15 rad/s². Determine the dynamic reactions at D and E at a time when ₁ has decreased to 50 rad/s. Answer: 5=-22.01 +26.8} N E=-21.2-5.20Ĵ Narrow_forwardProblem 1. Two uniform rods AB and CE, each of weight 3 lb and length 2 ft, are welded to each other at their midpoints. Knowing that this assembly has an angular velocity of constant magnitude c = 12 rad/s, determine: (1). the magnitude and direction of the angular momentum HD of the assembly about D. (2). the dynamic reactions (ignore mg) at the bearings at A and B. 9 in. 3 in. 03 9 in. 3 in. Answers: HD = 0.162 i +0.184 j slug-ft²/s HG = 2.21 k Ay =-1.1 lb; Az = 0; By = 1.1 lb; B₂ = 0.arrow_forwardProblem 5 (Optional, extra 6 points) A 6-lb homogeneous disk of radius 3 in. spins as shown at the constant rate w₁ = 60 rad/s. The disk is supported by the fork-ended rod AB, which is welded to the vertical shaft CBD. The system is at rest when a couple Mo= (0.25ft-lb)j is applied to the shaft for 2 s and then removed. Determine the dynamic reactions at C and D before and after the couple has been removed at 2 s. 4 in. C B Mo 5 in 4 in. Note: 2 rotating around CD induced by Mo is NOT constant before Mo is removed. and ₂ (two unknowns) are related by the equation: ₂ =0+ w₂t 3 in. Partial Answer (after Mo has been removed): C-7.81+7.43k lb D -7.81 7.43 lbarrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
