
Principles of Modern Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305079113
Author: David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 64P
For each of the following molecules, construct the
(a) Cyclobutadiene HC

(b) Allyl radical
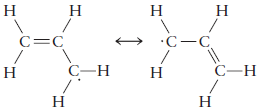
Indicate which, if any, of these orbitals have identical energies from symmetry considerations. Show the number of electrons occupying each
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Indicate one aspect that benefits and another that makes it difficult to use the hydroquinone electrode to measure pH.
At an electrified interface according to the Gouy-Chapman model, what types of interactions do NOT occur between the ions and the solvent according to this theory?
Please predict the products for each of the
following reactions.
Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov
vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry
(syn- vs anti- or both).
If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please
draw all the enantiomers.
Hint: In this case you must choose the best
answer to demonstrate the stereochemistry of
H2 addition.
1.03
2. (CH3)2S
BIZ
CH₂OH
2. DMS
KMnO4, NaOH
ΖΗ
Pd or Pt (catalyst)
HBr
20 1
HBr
ROOR (peroxide)
HO
H-SO
HC
12 11 10
BH, THE
2. H2O2, NaOH
Brz
cold
HI
19
18
17
16
MCPBA
15
14
13
A
Br
H₂O
BH3⚫THF
Brz
EtOH
Pd or Ni (catalyst)
D₂ (deuterium)
1. Os04
2. H2O2
CH3CO3H
(peroxyacid)
1. MCPBA
2. H₂O*
H
B
+
H
H
H
"H
C
H
H
D
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Modern Chemistry
Ch. 6 - Determine the number of nodes along the...Ch. 6 - Determine the number of nodes along the...Ch. 6 - Sketch the shape of each of the molecular...Ch. 6 - Sketch the shape of each of the molecular...Ch. 6 - Compare the electron density in the 1g and 1u*...Ch. 6 - Explain why 1g is the ground state for H2+ . By...Ch. 6 - Prob. 7PCh. 6 - Predict the ground electronic state of the He22+...Ch. 6 - Prob. 9PCh. 6 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 6 - Without consulting tables of data, predict which...Ch. 6 - Without consulting tables of data, predict which...Ch. 6 - Without consulting tables of data, on the same...Ch. 6 - Without consulting tables of data, on the same...Ch. 6 - Suppose we supply enough energy to H2 to remove...Ch. 6 - Suppose we supply enough energy to He2+ to remove...Ch. 6 - Prob. 17PCh. 6 - When one electron is added to an oxygen molecule,...Ch. 6 - Predict the valence electron configuration and the...Ch. 6 - Predict the valence electron configuration and the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 21PCh. 6 - For each of the following valence electron...Ch. 6 - For each of the electron configurations in Problem...Ch. 6 - For each of the electron configurations in Problem...Ch. 6 - Following the pattern of Figure 6.21, work out the...Ch. 6 - Following the pattern of Figure 6.21, work out the...Ch. 6 - The bond length of the transient diatomic molecule...Ch. 6 - The compound nitrogen oxide (NO) forms when the...Ch. 6 - What would be the electron configuration for a HeH...Ch. 6 - The molecular ion HeH+ has an equilibrium bond...Ch. 6 - Prob. 31PCh. 6 - Predict the ground state electronic configuration...Ch. 6 - The bond dissociation energies for the species NO,...Ch. 6 - The ionization energy of CO is greater than that...Ch. 6 - Photoelectron spectra were acquired from a sample...Ch. 6 - Photoelectron spectra were acquired from a sample...Ch. 6 - Prob. 37PCh. 6 - From the n=0 peaks in the photoelectron spectrum...Ch. 6 - The photoelectron spectrum of HBr has two main...Ch. 6 - The photoelectron spectrum of CO has four major...Ch. 6 - Write simple valence bond wave functions for the...Ch. 6 - Write simple valence bond wave functions for the...Ch. 6 - Both the simple VB model and the LCAO method...Ch. 6 - Both the simple VB model and the LCAO method...Ch. 6 - Write simple valence bond wave functions for...Ch. 6 - Write simple valence bond wave functions for...Ch. 6 - Write simple valence bond wave functions for the...Ch. 6 - Write simple valence bond wave functions for the...Ch. 6 - Formulate a localized bond picture for the amide...Ch. 6 - Formulate a localized bond picture for the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 51PCh. 6 - Draw a Lewis electron dot diagram for each of the...Ch. 6 - Describe the hybrid orbitals on the chlorine atom...Ch. 6 - Describe the hybrid orbitals on the chlorine atom...Ch. 6 - The sodium salt of the unfamiliar orthonitrate ion...Ch. 6 - Describe the hybrid orbitals used by the carbon...Ch. 6 - Describe the bonding in the bent molecule NF2 ....Ch. 6 - Describe the bonding in the bent molecule OF2 ....Ch. 6 - The azide ion (N3) is a weakly bound molecular...Ch. 6 - Formulate the MO structure of (NO2+) for localized...Ch. 6 - Discuss the nature of the bonding in the nitrite...Ch. 6 - Discuss the nature of the bonding in the nitrate...Ch. 6 - The pyridine molecule (C5H5N) is obtained by...Ch. 6 - For each of the following molecules, construct the...Ch. 6 - (a) Sketch the occupied MOs of the valence shell...Ch. 6 - Calcium carbide (CaC2) is an intermediate in the...Ch. 6 - The B2 molecule is paramagnetic; show how this...Ch. 6 - The Be2 molecule has been detected experimentally....Ch. 6 - Prob. 69APCh. 6 - The molecular ion HeH+ has an equilibrium bond...Ch. 6 - The MO of the ground state of a heteronuclear...Ch. 6 - The stable molecular ion H3+ is triangular, with...Ch. 6 - According to recent spectroscopic results,...Ch. 6 - trans-tetrazene (N4H4) consists of a chain of four...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Explain how Beer’s Law can be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forward
- Briefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. Briefly describe the Gibbs model and the Gibbs absorption equation.arrow_forwardThermodynamic analysis of electrified interfaces.arrow_forward
- What is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Gerade and Ungerade Molecular Orbitals. (SYMMETRY OF MOLECULAR ORBITALS); Author: Edmerls;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dPY-lT5LN60;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Symmetry and chemical bonding part – 5 Molecular orbital formation (CHE); Author: Vidya-mitra;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-42GmpBu0I;License: Standard Youtube License