
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
8th Edition
ISBN: 9780134581064
Author: Bruice, Paula Yurkanis
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 64P
What reagents are needed to carry out the following syntheses?
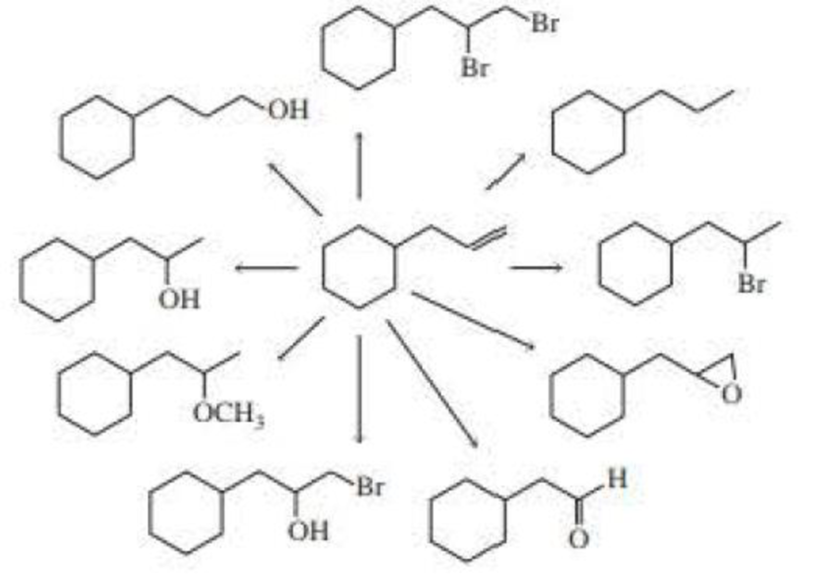
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions:
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used
therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the
following amino acids:
Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val
A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine.
B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus.
Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments:
Tyr-Val-His
Sar-Arg-Val
His-Pro-Ala
Val-Tyr-Val
Arg-Val-Tyr
What is the structure of saralasin?
What is the structure of the DNA backbone?
PLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when poss
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry; Organic Chemistry Study Guide A Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
Ch. 6.1 - Draw the mechanism for the reaction of cyclohexene...Ch. 6.2 - a. How many bond orbitals are avilable for...Ch. 6.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 6.2 - Prob. 4PCh. 6.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 6PCh. 6.4 - Prob. 7PCh. 6.4 - What alkene should be used to synthesize each of...Ch. 6.5 - The pKa of a protonated alcohol is about 2.5, and...Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 10P
Ch. 6.5 - Prob. 11PCh. 6.6 - a. What is the major product or each or the...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 14PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 15PCh. 6.7 - What is the major product obtained from the...Ch. 6.8 - Which is more highly regionselective: reaction of...Ch. 6.8 - Prob. 19PCh. 6.9 - What will be the product of the preceding reaction...Ch. 6.9 - Prob. 21PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 22PCh. 6.9 - Prob. 23PCh. 6.9 - What is the product of the addition of 1Cl to...Ch. 6.9 - What will be the major product obtained from the...Ch. 6.9 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 6.10 - Draw structures for the following: a. 24...Ch. 6.10 - What alkene would you treat with a peroxyacid in...Ch. 6.11 - What products are formed when the following...Ch. 6.11 - Prob. 31PCh. 6.11 - Prob. 32PCh. 6.11 - The following product was obtained from the...Ch. 6.12 - What characteristics must the reactant of a...Ch. 6.13 - Prob. 36PCh. 6.13 - What stereoisomers are obtained from each of the...Ch. 6.13 - Prob. 41PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 42PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 43PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 45PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 46PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 47PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 48PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 49PCh. 6.13 - Prob. 50PCh. 6.14 - Prob. 51PCh. 6.16 - Prob. 53PCh. 6.16 - Explain why 3-methykyclohexene should not be used...Ch. 6 - Prob. 55PCh. 6 - Prob. 56PCh. 6 - Prob. 57PCh. 6 - What is the major product of the reaction of...Ch. 6 - Give two names for each of the following:Ch. 6 - Prob. 60PCh. 6 - What are the products of the following reactions?...Ch. 6 - When 3-methyl-1-butene reacts with HBr, two alkyl...Ch. 6 - Draw curved arrows to show the flow of electrons...Ch. 6 - What reagents are needed to carry out the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 65PCh. 6 - Prob. 66PCh. 6 - Prob. 67PCh. 6 - What is more stable? a. CH3C+HCH3orCH3C+HCH2ClCh. 6 - Prob. 69PCh. 6 - a. Draw the product or products that will be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 71PCh. 6 - The second-order rate constant (in units of M1s1)...Ch. 6 - Which compound has the greater dipole moment?Ch. 6 - Prob. 74PCh. 6 - Prob. 75PCh. 6 - Prob. 76PCh. 6 - Prob. 77PCh. 6 - Prob. 78PCh. 6 - Prob. 79PCh. 6 - Prob. 80PCh. 6 - Prob. 81PCh. 6 - Prob. 82PCh. 6 - Prob. 83PCh. 6 - Prob. 84PCh. 6 - Prob. 85PCh. 6 - Prob. 86PCh. 6 - Draw the products of the following reactions. If...Ch. 6 - Prob. 88PCh. 6 - Prob. 89PCh. 6 - Prob. 90PCh. 6 - Two chemists at Dupont found that lCH2Znl is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 92PCh. 6 - Prob. 93PCh. 6 - What alkene gives the product shown after...Ch. 6 - Prob. 95PCh. 6 - Prob. 96PCh. 6 - Prob. 97PCh. 6 - Prob. 98PCh. 6 - Prob. 99PCh. 6 - Prob. 100PCh. 6 - Propose a mechanism for the following reaction:Ch. 6 - Prob. 102PCh. 6 - Prob. 103P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- . M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forwardPlease use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forward
- Briefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forwardAnswe Answer A and B pleasearrow_forward3. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: Isoelectric point Amino Acid Arginine 10.76 Glutamic Acid 3.22 Tryptophan 5.89 A. Define isoelectric point. B. The most basic amino acid is C. The most acidic amino acid is sidizo zoarrow_forward
- 3. A gas mixture contains 50 mol% H2 and 50 mol% He. 1.00-L samples of this gas mixture are mixed with variable volumes of O2 (at 0 °C and 1 atm). A spark is introduced to allow the mixture to undergo complete combustion. The final volume is measured at 0 °C and 1 atm. Which graph best depicts the final volume as a function of the volume of added O2? (A) 2.00 1.75 Final Volume, L 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 2.00 (B) 1.75 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50- 0.25 0.00 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 2 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2 2.00 2.00 (C) (D) 1.75 1.75 1.50 1.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 Final Volume, L 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.25 0.50 0.75 1.00 0.00 0.25 Volume O₂ added, L 0.50 0.75 1.00 Volume O₂ added, L 2arrow_forwardLeucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid. It has pai 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60. H2N-C(R)H-COOH and R is -CH2-CH(CH3)2 A. Draw the condensed structure for leucine, and label all chirality centers with an asterisk. B. How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there? C. Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S. D. What is the p/ of leucine? E. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at 10.00. F. Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50. G. Leucine is described as an essential amino acid. What does this mean? H. Show the alkyl halide you would use to prepare leucine by the amidomalonate method. =arrow_forwarda) Write out 6 completely different reactions of acetophenone (reagent, product). b) Write out 3 preparations of 1-methylcyclohexanol, using a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain. c) Write out 3 preparations of 2-ethoxybenzoic acid, a different starting material for each one. You may use preps where you just change the functional group, and/or preps where you construct the carbon chain.arrow_forward
- 12. CH3 OH OH H&C CH3 H₂C N OH H₂C CH3 H&C CH3 H₂C' CH3 H.C CH3OH H.C CH2CH3OH CH3CEN Which one of these 17 compounds is represented by this IR and this 'H NMR spectrum? IR Spectrum 3000 4000 3000 NMR Spectrum 2000 £500 RAVENUMBER 2000 1500 9 8 6 5 10 HP-00-290 ppm m 1000 500 1000 4 °arrow_forwardDraw the structure of (E,6R) 6-methoxy-4-hepten-2-one. Give the IUPAC name of this compound, including stereochemistry. Draw the most stable chair conformation of (cis) 1,3-isobutylcyclohexane. H HC=CCH₂ CH2CH3 EN(CH3)2 -CN(CH3)2arrow_forward10. Write out the mechanism (intermediate/transition state) for this reaction; indicate stereochemistry in product. H3C CH₂OH CH3 SN1 Harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

How to Design a Total Synthesis; Author: Chemistry Unleashed;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9jRfAJJO7mM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY