
Nitric acid is a chemical intermediate primarily used in the synthesis of ammonium nitrate, which is used in the manufacture of fertilizers. The acid also is important in the production of other nitrates and in the separation of metals from ores.
Nitric acid may be produced by oxidizing ammonia to nitric oxide over a platinum—rhodium catalyst, then oxidizing the nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide in a separate unit where it is absorbed in water to form an aqueous solution of nitric acid.
The reaction sequence is as follows:
where, unless otherwise speci?ed, the species are gases. A side reaction in which ammonia is oxidized to form nitrogen and water can lower product yield:
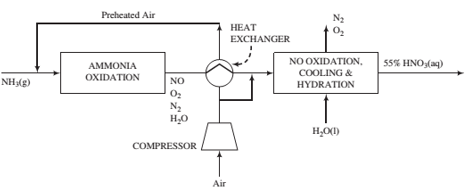
Ammonia vapor produced by vaporizng pure liquid ammonia at 820 kPa absolute is mixed with air, and the combined stream enters the ammonia oxidation unit. Air at 30°C, 1 atm absolute, and 50% relative humidity is compressed and fed to the process. A fraction of the air is sent to the cooling and hydration units, while the remainder is passed through a heat exchanger and mixed with the ammonia. The total oxygen fed to the process is the amount stoichiometrically required to convert all of the ammonia to HNO3, while the fraction sent to the ammonia oxidizer corresponds to the stoichiometric amount required to convert ammonia to NO.
The ammonia reacts completely in the oxidizer, with 97% forming NO and the rest forming N2. Only a negligible amount of NO2is formed in the oxidizer. However, the gas leaving the oxidizer is subjected to a series of cooling and hydration steps in which the NO is completely oxidized to NO2, which in turn combines with water (some of which is present in the gas from the oxidizer and the rest is added) to form a 55 wt% aqueous solution of nitric acid. The product gas from the process may be takento contain only N2and O2.
(a) Taking a basis of 100 kmol of ammonia fed to the process, calculate (i) the volumes (m3) of the ammonia vapor and air fed to the process using the compressibility-factor equation of state; (ii) the amount (kmol) and composition (in mole fractions) of the gas leaving the oxidation unit; (m) the required volume of liquid water(m3) that must be fed to the cooling and hydration units; and (iv) the fraction of the air fed to the ammonia oxidizer.
(b) Scale the results from Part (a) to a new basis of 100 metric tons per hour of 55% nitiic acid solution.
Exploratory Exercises—Research and Discover (c) Nitrogen oxides (collectively referred to as NOx) are a category of pollutants that are formed in many ways, including processes like that described in this problem. List the annual emission rates of the three largest sources of NOxemissions in your home region. What are the effects of exposure to excessive concentrations of NOx?
(d) A platinum—rhodium catalyst is used in ammonia oxidation. Explain the function of the catalyst, describe its structure, and explain the relationship of the structure to the function.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
ELEM PRIN CHEM PROCESS ETXT + WILEYPLUS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Modern Database Management
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
- Zeroth Order Reaction In a certain experiment the decomposition of hydrogen iodide on finely divided gold is zeroth order with respect to HI. 2HI(g) Au H2(g) + 12(9) Rate = -d[HI]/dt k = 2.00x104 mol L-1 s-1 If the experiment has an initial HI concentration of 0.460 mol/L, what is the concentration of HI after 28.0 minutes? 1 pts Submit Answer Tries 0/5 How long will it take for all of the HI to decompose? 1 pts Submit Answer Tries 0/5 What is the rate of formation of H2 16.0 minutes after the reaction is initiated? 1 pts Submit Answer Tries 0/5arrow_forwardangelarodriguezmunoz149@gmail.com Hi i need help with this question i am not sure what the right answers are.arrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardSaved v Question: I've done both of the graphs and generated an equation from excel, I just need help explaining A-B. Below is just the information I used to get the graphs obtain the graph please help. Prepare two graphs, the first with the percent transmission on the vertical axis and concentration on the horizontal axis and the second with absorption on the vertical axis and concentration on the horizontal axis. Solution # Unknown Concentration (mol/L) Transmittance Absorption 9.88x101 635 0.17 1.98x101 47% 0.33 2.95x101 31% 0.51 3.95x10 21% 0.68 4.94x10 14% 24% 0.85 0.62 A.) Give an equation that relates either the % transmission or the absorption to the concentration. Explain how you arrived at your equation. B.) What is the relationship between the percent transmission and the absorption? C.) Determine the concentration of the ironlll) salicylate in the unknown directly from the graph and from the best fit trend-line (least squares analysis) of the graph that yielded a straight…arrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





