
(a)
Interpretation:
The engineering stress-strain curve should be plotted and the 0.2 % offset yield strength should be calculated for the given data of polyvinyl chloride.
Concept Introduction:
The maximum amount of elastic deformation which is bearable by any material is defined as yield strength.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The yield strength for 0.2% offset is 11,600 psi for a given sample of polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
The tabular data providing details about the load and length difference for a given sample.
Let us calculate the stress for the sample with the help of below formula:
| Load (lb.) | |
| 0 | 0.00000 |
| 300 | 0.00746 |
| 600 | 0.01496 |
| 900 | 0.02374 |
| 1200 | 0.032 |
| 1500 | 0.046 |
| 1660 | 0.07 (maximum load) |
| 1600 | 0.094 |
| 1420 | 0.12 (fracture) |
For determining the strain of the a given sample,
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as follows:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
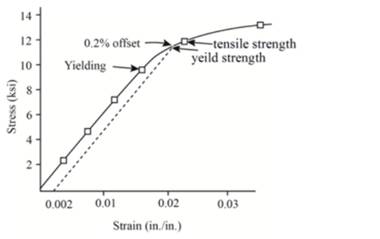
The above graph can provide the value of yield strength for 0.2% offset as 11,600 psi.
Therefore, polyvinyl chloride sample has the yield strength for 0.2% offset as 11,600 psi.
(b)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the tensile strength should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Tensile strength can be defined as the measurement of maximum deformation which can be bearable by any material without undergoing necking condition.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The tensile strength will be 12728.72 psi for a given sample of polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
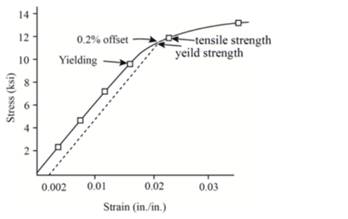
The above graph can provide the value of tensile strength as 12728.72 psi.
Therefore, the given sample of polyvinyl chloride has the tensile strength of12728.72 psi.
(c)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of modulus of elasticity should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Modulus of elasticity is also known as coefficient of elasticity or elastic modulus and can be defined as the ratio of the stress in the a given object body to the corresponding strain.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of modulus of elasticity is 603193 psi for give polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
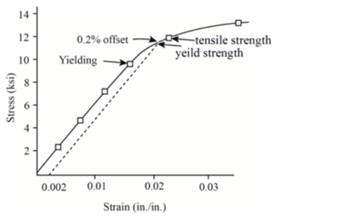
The formula of Hook's law can be used for calculating modulus of elasticity.
Therefore, the value of modulus of elasticity for given polyvinyl chloride is 603193 psi.
(d)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of % elongation should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Elongation is defined as term used to determine the change in gauge length of any material when it is on static tension test.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of % elongation is 4.5 % for a given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
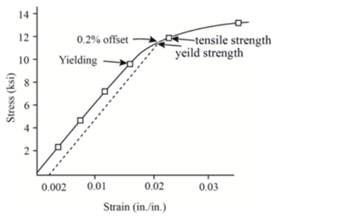
The following formula can be used to determine the value of % elongation.
Therefore, thevalue of % elongationis 4.5% for given polyvinyl chloride sample.
(e)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of % reduction in area should be calculated.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction if area of any material is directly related to the reduction in cross-section area of the tensile test piece after fracture.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of % reduction in area is 3.5 % for a given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
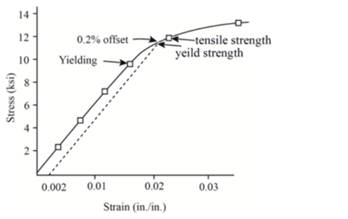
The following formula can be used to determine the value of % reduction in area.
Therefore, the given polyvinyl chloride sample carries 3.5% the value of % reduction in area.
(f)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the engineering stress should be determined at fracture.
Concept Introduction:
Engineering stress is a term explained as a force or applied load on the a given object's cross-sectional area and it is also known as nominal stress.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The engineering stress is 11,296.74 psi fora given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
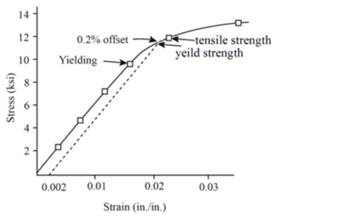
Above graph is extended upto fracture strength as follows:
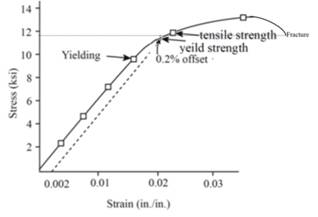
Therefore,the value of engineering stress will be 11,296.74 psi for a given polyvinyl chloride.
(g)
Interpretation:
With the help of plotted engineering stress-strain curve, the value of modulus of resilience should be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The amount of energy required to get absorbed by the material to return back to its original state is defined as resilience.
Modulus of resilience can be defined as the energy required by the material to return from its stress condition from zero to the yield stress limit.
Answer to Problem 6.39P
The value of modulus of resilience is 76.37 psi for a given polyvinyl chloride.
Explanation of Solution
With the use of a givenspreadsheet and applied loads, one can tabulate the engineering stress and strain as below:
| Load (F) | Length ( | Change in length ( | Gage length | Stress ( | Strain ( |
| 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 300 | 2 | 0.00746 | 2.00746 | 2386.635 | 0.00373 |
| 600 | 2 | 0.01496 | 2.01496 | 4773.27 | 0.00748 |
| 900 | 2 | 0.02374 | 2.02374 | 7159.905 | 0.0.1187 |
| 1200 | 2 | 0.032 | 2.032 | 9546.539 | 0.016 |
| 1500 | 2 | 0.046 | 2.046 | 11933.17 | 0.023 |
| 1660 | 2 | 0.07 | 2.07 | 13206.05 | 0.035 |
| 1600 | 2 | 0.094 | 2.094 | 12728.72 | 0.047 |
| 1420 | 2 | 0.12 | 2.12 | 11296.74 | 0.06 |
Now, one can plot the stress-strain curve from the above gathered tabular data as below:
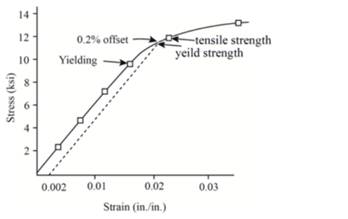
From the graph, the value of modulus of resilience is 9546.539 psi.
Now,
Therefore, the sample of polyvinyl chloride has 76.37 psi as the value of modulus of resilience.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering, Si Edition
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the slope deflection method, draw the resulting shear force diagran and bending moment diagram. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m, L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200 GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardProblem 2 (A is fixed and C is a pin) Find the reactions and A and C. 10 k- 6 ft 6 ft B A 2 k/ft 15 ftarrow_forward6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forward
- Problem 5 (A, B, C and D are fixed). Find the reactions at A and D 8 k B 15 ft A -20 ft C 10 ft Darrow_forwardProblem 4 (A, B, E, D and F are all pin connected and C is fixed) Find the reactions at A, D and F 8 m B 6m E 12 kN D F 4 marrow_forward##2# Superheated steam powers a steam turbine for the production of electrical energy. The steam expands in the turbine and at an intermediate expansion pressure (0.1 Mpa) a fraction is extracted for a regeneration process in a surface regenerator. The turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 90% Design the simplified power plant schematic Analyze it on the basis of the attached figure Determine the power generated and the thermal efficiency of the plant ### Dados in the attached imagesarrow_forward
- Problem 1 (A, C and D are pins) Find the reactions and A, C and D. D 6 m B 12 kN/m 8 m A C 6 marrow_forwardUniform Grade of Pipe Station of Point A is 9+50.00. Elevation Point A = 250.75.Station of Point B is 13+75.00. Elevation Point B = 244.10 1) Calculate flowline of pipe elevations at every 50 ft. interval (Half Station). 2) Tabulate station and elevation for each station like shown on example 3) Draw Sketcharrow_forward### To make a conclusion for a report of an experiment on rockets, in which the openrocket software was used for the construction and modeling of two rockets: one one-stage and one two-stage. First rocket (single-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 100 m/s and a maximum height of 500 m The second rocket (two-stage) reached a maximum vertical speed of 50 m/s and a maximum height of 250 m To make a simplified conclusion, taking into account the efficiency of the software in the study of rocketsarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





