
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168277
Author: William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher: OpenStax - Rice University
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 62P
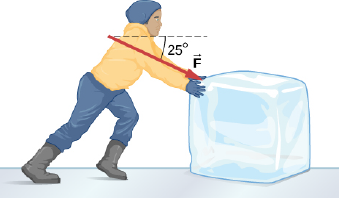
A contestant in a winter sporting event pushes a 45.0-kg block of ice across a frozen lake as shown below. (a) Calculate the minimum force
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
8.
With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load,
(a) Closed circuit
(b) Open circuit
Lab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation.
I am having trouble with this part of the lab.
Mick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?
Chapter 6 Solutions
University Physics Volume 1
Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding Now calculate the scale...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding Calculate the...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding Determine a general...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding The soccer player stops...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding Find the direction of the...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding If atmospheric resistance...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding A block of mass 1.0 kg...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding The snowboarder is now...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding A car moving at 96.8 km/h...Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding Find the terminal...
Ch. 6 - Check Your Understanding suppose the resistive...Ch. 6 - Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws To sirmulate...Ch. 6 - Friction The glue on a piece of tape can exert...Ch. 6 - When you learn to drive, you discover that you...Ch. 6 - When you push a pices of chalk across a...Ch. 6 - A physics major is cooking breakfast en she...Ch. 6 - Centripetal Force If you wish to reduce the stress...Ch. 6 - Define centripetal force. Can any type of force...Ch. 6 - If centripetal force is directed toward the...Ch. 6 - Race car drivers routinely cut corners, as shown...Ch. 6 - Many amusement parks have rides that make vertical...Ch. 6 - What causes water to be removed from clothes in a...Ch. 6 - As a skater forms a circle, what force is...Ch. 6 - Suppose a child is riding on a merry-go-round at a...Ch. 6 - Do you feel yourself thro to either side when you...Ch. 6 - Suppose a mass is moving in a circular path on a...Ch. 6 - When a toilet is flushed or a sink Is drained, the...Ch. 6 - A car rounds a curve and encounters a patch of ice...Ch. 6 - In one amusement park ride, riders enter a large...Ch. 6 - Two friends are having a conversation. Anna says a...Ch. 6 - A nonrotating frame of reference placed at the...Ch. 6 - Athletes such as swimmers and bicyclists wear body...Ch. 6 - Two expressions were used for the drag force...Ch. 6 - As cars travel, oil and gasoline leaks onto the...Ch. 6 - Why can a squirrel jump from a tree branch to the...Ch. 6 - Solving Problems with Newton’s Laws A 30.0-kg girl...Ch. 6 - Find the tension in each of the three cables...Ch. 6 - Three forces act on an object, considered to be a...Ch. 6 - A flea jumps by exerting a force of...Ch. 6 - Two muscles in the back of the leg pull upward on...Ch. 6 - After a mishap, a 76.0-kg circus performer clings...Ch. 6 - A 35.0-kg dolphin decelerates from 12.0 to 7.50 m/...Ch. 6 - When starting a foot race, a 70.0-kg sprinter...Ch. 6 - A large rocket has a mass of 2.00106kgat takeoff,...Ch. 6 - A basketball player jumps straight up for a ball....Ch. 6 - A 2.50-kg fireworks shell is fired straight up...Ch. 6 - A 0.500-kg potato is fired at an angle of 80.0...Ch. 6 - An elevator filled with passengers has a mass of...Ch. 6 - A 20.O-g ball hangs from the roof of a freight car...Ch. 6 - A student’s backpack, full of textbooks, is hung...Ch. 6 - A service elevator takes a load of garbage, mass...Ch. 6 - A roller coaster car starts from rest at the top...Ch. 6 - The device shown below is the Atwood’s machine...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are connected by a massless rope as...Ch. 6 - Shown below are two carts connected by a cord that...Ch. 6 - A 2.00 kg block (mass 1) and a 4.00 kg block (mass...Ch. 6 - Friction (a) When rebuilding his car’s engine, a...Ch. 6 - (a) What is the maximum frictional force in the...Ch. 6 - Suppose you have a 120-kg wooden crate resting on...Ch. 6 - (a) If half of the weight of a small...Ch. 6 - A team of eight dogs pulls a sled with waxed wood...Ch. 6 - Consider the 65.0-kg ice skater being pushed by...Ch. 6 - Show that the acceleration of any object down a...Ch. 6 - Show that the acceleration of any object down an...Ch. 6 - Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going...Ch. 6 - A machine at a post office sends packages out a...Ch. 6 - If an object is to rest o an incline without...Ch. 6 - Calculate the maximum acceleration of a car that...Ch. 6 - Calculate the maximum acceleration of a car that...Ch. 6 - Repeat the preceding problem for a car with four-...Ch. 6 - A freight train consists of two 8.00105kgengines...Ch. 6 - Consider the 52.0-kg mountain climber shown below....Ch. 6 - A contestant in a winter sporting event pushes a...Ch. 6 - The contestant now pulls the block of ice with a...Ch. 6 - At a post office, a parcel that is a 20.0-kg box...Ch. 6 - (a) A 22.0-kg child is riding a playground...Ch. 6 - Calculate the centripetal force on the end of a...Ch. 6 - What Is the ideal banking angle for a gentle turn...Ch. 6 - What is the ideal speed to take a 100.0-m-radius...Ch. 6 - (a) What is the radius of a bobsled turn banked at...Ch. 6 - Part of riding a bicycle involves leaning at the...Ch. 6 - If a car takes a banked curve at less than the...Ch. 6 - Modem roller coasters have vertical loops like the...Ch. 6 - A child of mass 40.0 kg is in a roller coaster car...Ch. 6 - In the simple Bohr model of the ground state of...Ch. 6 - Railroad tracks follow a circular curve of radius...Ch. 6 - The CERN particle accelerator is circular with a...Ch. 6 - A car rounds an unbanked curve of radius 65 m. If...Ch. 6 - A banked highway is designed for traffic moving at...Ch. 6 - Drag Force and Terminal Speed The terminal...Ch. 6 - A 60.0-kg and a 90.0-kg skydiver jump from an...Ch. 6 - A 560-g squirrel with a surface area of...Ch. 6 - To maintain a constant speed, the force provided...Ch. 6 - By what factor does the drag force on a car...Ch. 6 - Calculate the velocity a spherical rain drop would...Ch. 6 - Using Stokes’ law, verify that the units for...Ch. 6 - Find the terminal velocity of a spherical...Ch. 6 - Stokes’ law describes sedimentation of particles...Ch. 6 - Suppose that the resistive force of the air on a...Ch. 6 - A small diamond of mass 10.0 g drops from a...Ch. 6 - (a) What is the final velocity of a car originally...Ch. 6 - A 75.0-kg man stands on a bathroom scale in an...Ch. 6 - (a) Calculate the minimum coefficient of friction...Ch. 6 - As shown below, if M=5.50kg , what is the tension...Ch. 6 - As shown below, if F=60.0Nand M=4.00kg, what is...Ch. 6 - As shown below, if M=6.0kg, what is the tension in...Ch. 6 - A small space probe Is released from a spaceship....Ch. 6 - A half-full recycling bin has mass 10 kg and is...Ch. 6 - A child has mass 6.0 kg and slides down a...Ch. 6 - The two barges shown here are coupled by a cable...Ch. 6 - If the order of the barges of the preceding...Ch. 6 - An object with mass m moves along the x -axis. Its...Ch. 6 - A helicopter with mass 2.35104kg has a position...Ch. 6 - Located at the origin, an electric car of mass mis...Ch. 6 - A particle of mass mis located at the origin. It...Ch. 6 - A 2.0-kg object has a velocity of at t=0 . A...Ch. 6 - A 1.5-kg mass has an acceleration of (4.0 i 3.0 j...Ch. 6 - A box is dropped onto a conveyor belt moving at...Ch. 6 - Shown below is a 10.0-kg block being pushed by a...Ch. 6 - As shown below, the mass of block 1 is m1=4.0kg ....Ch. 6 - A student is attempting to move a 30-kg...Ch. 6 - A crate of mass 100.0 kg rests on a rough surface...Ch. 6 - A car is moving at high speed along a highway when...Ch. 6 - A crate having mass 50.0 kg falls horizontally off...Ch. 6 - A 15-kg sled is pulled across a horizontal,...Ch. 6 - A 30.O-g ball at the end of a stung is swung in a...Ch. 6 - A particle of mass 0.50 kg starts moves through a...Ch. 6 - A stunt cyclist rides on the interior of a...Ch. 6 - When a body of mass 0.25 kg is attached to a...Ch. 6 - A piece of bacon starts to slide down the pan when...Ch. 6 - A plumb bob bangs from the roof of a railroad car....Ch. 6 - An airplane flies at 120.0 m/s and banks at a...Ch. 6 - The position of a particle is given by r(t)=A(cost...Ch. 6 - Two blocks connected by a string are pulled across...Ch. 6 - As shown below, the coefficient of kinetic...Ch. 6 - In the figure, the coefficient of kinetic friction...Ch. 6 - Two blocks are stacked as shown below, and rest on...Ch. 6 - A box rests on the (horizontal) back of a truck....Ch. 6 - A double-incline plane is shown below. The...Ch. 6 - In a later chapter, you will find that the weight...Ch. 6 - A large centrifuge, like the one shown below, is...Ch. 6 - A car of mass 1000.0 kg is traveling along a level...Ch. 6 - An airplane flying at 200.0 m/s makes a turn that...Ch. 6 - A skydiver is at an altitude of 1520 m. After 10.0...Ch. 6 - In a television commercial, a small, spherical...Ch. 6 - A boater and motor boat ate at rest on a lake....
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Match the following cell types with their correct definition. _________Macrophage _________NK cell _________Eos...
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
How does an obligate aerobe differ from a facultative aerobe?
Brock Biology of Microorganisms (15th Edition)
The following results were obtained from a broth dilution test for microbial susceptibility. Antibiotic Concent...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Plants use the process of photosynthesis to convert the energy in sunlight to chemical energy in the form of su...
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Gray whales (Eschrichtius robustus) gather each winter near Baja California to give birth. How might such behav...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Distinguish between microevolution, speciation, and macroevolution.
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardYou are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forward
- A planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forwardWhat are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forward
- A circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forwardAn L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's Second Law of Motion: F = ma; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xzA6IBWUEDE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY