
Concept explainers
The flow rate and direction in each pipe?
If
Answer to Problem 6.127P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
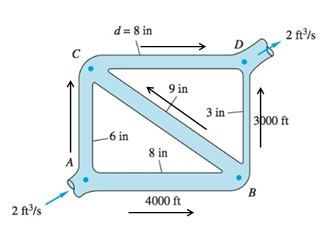
For all pipes, friction factor is equal to
The fluid is water at
Inlet and exit flow rate is equal to
The basic rules of pipe networks are,
“The net pressure change in a closed loop must be equal to zero”
“The net flow into a junction must be equal to zero”
“All pressure changes must satisfy moody and minor loss friction co-relation”
The head loss
In above equation,
The total head loss is equal to zero in a closed loop.
The pressure difference
Where,
Calculation:
According to the explanation given,
Equate head loss to find loss co efficient in each pipe.
For pipe AC,
Similarly, for each pipe
According to the definitions, the total head loss in a closed loop is equal to zero,
Therefore,
Assume the directions of the flow as in the figure above,
For closed loop ABC,
For closed loop BCD,
The net flow rate is equal to zero at all junctions, therefore,
By solving above equations,
We get,
To find the pressure at point B,
We know that,
Therefore,
Similarly,
Conclusion:
The flow rates in each pipe is equal to,
The pressure at point B, C and D are,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics, 8 Ed
- (read image) Answer:arrow_forward(read image) Answer:arrow_forward2nd Law of Thermodynamics A 1.5-ft3 rigid tank contains saturated refrigerant-134 at 170 psia. Initially, 20 percent of the volume isoccupied by liquid and the rest by vapor. A valve at the top of the tank is now opened, and vapor is allowedto escape slowly from the tank. Heat is transferred to the refrigerant such that the pressure inside the tankremains constant. The valve is closed when the last drop of liquid in the tank is vaporized. Determine thetotal heat transfer for this process.arrow_forward
- Draw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown, and determine the maximum normal stress due to bending. 4.8 kips/ft 32 kips B C D E I Hinge 8 ft. 2 ft 5 ft 5 ft W12 x 40arrow_forward2nd Law of Thermodynamics A rigid, insulated tank that is initially evacuated is connected through a valve to the supply line that carrieshelium at 300 kPa and 140◦C. Now the valve is opened, and helium is allowed to flow into the tank until thepressure reaches 300 kPa, at which point the valve is closed. Determine the flow work of the helium in thesupply line and the final temperature of the helium in the tank.arrow_forwardDraw the shear and bending-moment diagrams for the beam and loading shown, and determine the maximum normal stress due to bending. 5 kips 10 kips B I W14 x 22 -5 ft -8 ft 5 ft-arrow_forward
- 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Liquid water at 200 kPa and 25◦C is heated in a chamber by mixing it with superheated steam at 200 kPaand 250◦C. cold water enters the chamber at a rate of 2 kg/s. If the mixture leaves the mixing chamber at50◦C, determine the mass flow rate of the superheated steam required.arrow_forwardThe 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Refrigerant-134a enters the compressor of a refrigeration system as saturated vapor at 0.16 MPa, and leavesas superheated vapor at 0.9 MPa and 70◦C at a rate of 0.08 kg/s. Determine the rates of energy transfers bymass into and out of the compressor. Assume the kinetic and potential energies are negligible.arrow_forward2nd Law of Thermodynamics Water enters the tubes of a cold plate at 65◦C with an average velocity of 50 ft/min and leaves at 110◦F. Thediameter of the tubes is 0.2 in. Assuming 20 percent of the heat generated is dissipated from the componentsto the surroundings by convection and radiation, and the remaining 80 percent is removed by the coolingwater, determine the amount of heat generated by the electronic devices mounted on the cold plate.arrow_forward
- The 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Refrigerant-134a enters a diffuser steadily as saturated vapor 500 kPa with a velocity of 170 m/s, and it leavesat 600 kPa and 50◦C. the refrigerant is gaining heat at a rate of 2.5 kJ/s as it passes through the diffuser. Ifthe exit area is 75 percent greater than the inlet area, determine (a) the exit velocity (b) the mass flow rate of the refrigerant.arrow_forward2nd Law of Thermodynamics Refrigerant-134a is throttled from the saturated liquid state at 850 kPa to a pressure of 200 kPa. Determinethe temperature drop during this process and the final specific volume of the refrigerant.arrow_forward2nd Law of Thermodynamics An adiabatic gas turbine expands air at 1350 kPa and 525◦C to 125 kPa and 130◦C. Air enters the tur-bine through a 0.15-m2 opening with an average velocity of 50 m/s, and exhausts through a 1-m2 opening.Determine (a) the mass flow rate of air through the turbine (b) the power produced by the turbine.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





