
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9780073380322
Author: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala
Publisher: MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 59P
The impeller of a centrifugal blower has a radius of 18 cm and a blade width of 6.1 cm at the inlet, and a radius of 30 cm and a blade width of 3.4 cm at the outlet. The blower delivers atmospheric air at 20°C and 95 kPa. Disregarding any losses and assuming the tangential components of air velocity at the inlet and the outlet to be equal to the impeller velocity at respective locations, determine the volumetric flow rate of air when the rotational speed of the shaft is 900 rpm and the power consumption of the blower is 120 W. Also determine the normal components of velocity at the inlet and outlet of the impeller.
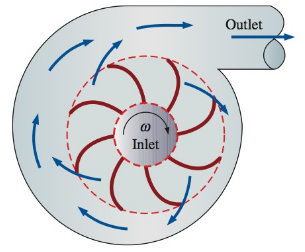
FIGURE P6−59
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
ased on the corresponding mass flow rates (and NOT the original volumetric flow rates) determine:
a) The mass flow rate of the mixed air (i.e., the combination of the two flows) leaving the chamber in kg/s.
b) The temperature of the mixed air leaving the chamber.
Please use PyscPro software for solving this question.
Notes:
For part (a), you will first need to find the density or specific volume for each state (density = 1/specific volume).
The units the 'v' and 'a' are intended as subscripts:
· kgv = kg_v = kgv = kilogram(s) [vapour]
kga = kg_a =kga = kilogram(s) [air]
The answers to this question s wasn't properly given, I need expert handwritten solutions
I need expert handwritten solutions to this only
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
Ch. 6 - Express Newton’s first, second, and third laws.Ch. 6 - Express Newton’s second law of motion for rotating...Ch. 6 - Is momentum a vector? If so, in what direction...Ch. 6 - Express the conservation of momentum principle....Ch. 6 - Two firefighters are fighting a fire with...Ch. 6 - How do surface forces arise in the momentum...Ch. 6 - Explain the importance of the Reynolds transport...Ch. 6 - What is the importance of the momentum-flux...Ch. 6 - Write the momentum equation for steady...Ch. 6 - In the application of the momentum equation,...
Ch. 6 - A rocket in space (no friction or resistance to...Ch. 6 - Describe in terms of momentum and airflow how a...Ch. 6 - Does it take more, equal, or less power for a...Ch. 6 - In a given location, would a helicopter require...Ch. 6 - A horizontal water jet from a nozzle of constant...Ch. 6 - Describe body forces and surface forces, and...Ch. 6 - A constant-velocity horizontal water jet from a...Ch. 6 - A horizontal water jet of constant velocity V from...Ch. 6 - Water enters a 10-cm-diameter pipe steadily with a...Ch. 6 - A 2.5-cm-diameter horizontal water jet with a...Ch. 6 - A horizontal water jet of constant velocity V...Ch. 6 - A 90 elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to direct...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-20 for the case of another...Ch. 6 - A horizontal water jet impinges against a vertical...Ch. 6 - A reducing elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-24 for the case of = 125°.Ch. 6 - Reconsider Prob. 627. If the mass of the cart is...Ch. 6 - A 100-ft3/s water jet is moving in the positive...Ch. 6 - Reconsider Prob. 6-26E. Using appropriate...Ch. 6 - A horizontal 5-cm-diameter water jet with a...Ch. 6 - A fan with 24-in-diameter blades moves 2000 cfm...Ch. 6 - A 3-in-diameter horizontal jet of water, with...Ch. 6 - Firefighters are holding a nozzle at the end of a...Ch. 6 - A 5-cm-diameter horizontal jet of water with a...Ch. 6 - A 3-in-diameter horizontal water jet having a...Ch. 6 - An unloaded helicopter of mass 12,000 kg hovers at...Ch. 6 - Water is flowing through a 10-cm-diameter water...Ch. 6 - The weight of a water tank open to the atmosphere...Ch. 6 - Commercially available large wind turbines have...Ch. 6 - Water enters a centrifugal pump axially at...Ch. 6 - An incompressible fluid of density and viscosity ...Ch. 6 - Consider the curved duct of Prob. 6-41, except...Ch. 6 - As a follow-up to Prob. 6-41, it turns out that...Ch. 6 - An incompressible fluid of density and viscosity ...Ch. 6 - Water of density =998.2kg/m3 flows through a...Ch. 6 - Water flowing in a horizontal 25-cm-diameter pipe...Ch. 6 - A sluice gate, which controls flow rate in a...Ch. 6 - How is the angular momentum equation obtained from...Ch. 6 - Prob. 52CPCh. 6 - Prob. 53CPCh. 6 - Prob. 54CPCh. 6 - Water is flowing through a 15-cm-diameter pipe...Ch. 6 - A large lawn sprinkler with two identical arms is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 57EPCh. 6 - Prob. 58PCh. 6 - The impeller of a centrifugal blower has a radius...Ch. 6 - Prob. 60PCh. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-56 for a water flow rate of 60 L/s.Ch. 6 - Prob. 62PCh. 6 - Water enters the impeller of a centrifugal pump...Ch. 6 - A lawn sprinkler with three identical antis is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 66PCh. 6 - Water flowing steadily at a rate of 0.16 m3/s is...Ch. 6 - Repeat Prob. 6-66 by taking into consideration the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 70PCh. 6 - Water enters vertically and steadily at a rate of...Ch. 6 - Repeal Prob. 6-69 for the case of unequal anus-the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 73PCh. 6 - Prob. 74PCh. 6 - Prob. 75PCh. 6 - Prob. 76PCh. 6 - A spacecraft cruising in space at a constant...Ch. 6 - A 60-kg ice skater is standing on ice with ice...Ch. 6 - Prob. 80PCh. 6 - Water is flowing into and discharging from a pipe...Ch. 6 - Indiana Jones needs So ascend a 10-m-high...Ch. 6 - Prob. 83EPCh. 6 - Prob. 84PCh. 6 - A walnut with a mass of 50 g requires a force of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 86PCh. 6 - Prob. 87PCh. 6 - Show that the force exerted by a liquid jet on a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 89PCh. 6 - Prob. 90PCh. 6 - Prob. 91PCh. 6 - Water enters a two-armed lawn sprinkler along the...Ch. 6 - Prob. 94PCh. 6 - Prob. 95PCh. 6 - Prob. 96PCh. 6 - Water flows steadily through a splitter as shown...Ch. 6 - Prob. 98PCh. 6 - Prob. 99PCh. 6 - Consider water flow through a horizontal, short...Ch. 6 - Consider water flow through a horizontal. short...Ch. 6 - Prob. 103PCh. 6 - Prob. 104PCh. 6 - Prob. 105PCh. 6 - Prob. 106PCh. 6 - The velocity of wind at a wind turbine is measured...Ch. 6 - The ve1ocity of wind at a wind turbine is measured...Ch. 6 - Prob. 109PCh. 6 - Prob. 110PCh. 6 - Prob. 111PCh. 6 - Prob. 112PCh. 6 - Consider the impeller of a centrifugal pump with a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 114P
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two large tanks, each holding 100 L of liquid, are interconnected by pipes, with the liquid flowing from tank A into tank B at a rate of 3 L/min and from B into A at a rate of 1 L/min (see Figure Q1). The liquid inside each tank is kept well stirred. A brine solution with a concentration of 0.2 kg/L of salt flows into tank A at a rate of 6 L/min. The diluted solution flows out of the system from tank A at 4 L/min and from tank B at 2 L/min. If, initially, tank A contains pure water and tank B contains 20 kg of salt. A 6 L/min 0.2 kg/L x(t) 100 L 4 L/min x(0) = 0 kg 3 L/min B y(t) 100 L y(0) = 20 kg 2 L/min 1 L/min Figure Q1 - Mixing problem for interconnected tanks Determine the mass of salt in each tank at time t > 0: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forwardTwo springs and two masses are attached in a straight vertical line as shown in Figure Q3. The system is set in motion by holding the mass m₂ at its equilibrium position and pushing the mass m₁ downwards of its equilibrium position a distance 2 m and then releasing both masses. if m₁ = m₂ = 1 kg, k₁ = 3 N/m and k₂ = 2 N/m. www.m k₁ = 3 (y₁ = 0). m₁ = 1 k2=2 (y₂ = 0) |m₂ = 1 Y2 y 2 System in static equilibrium (Net change in spring length =32-31) System in motion Figure Q3 - Coupled mass-spring system Determine the equations of motion y₁(t) and y₂(t) for the two masses m₁ and m₂ respectively: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward100 As a spring is heated, its spring constant decreases. Suppose the spring is heated and then cooled so that the spring constant at time t is k(t) = t sin N/m. If the mass-spring system has mass m = 2 kg and a damping constant b = 1 N-sec/m with initial conditions x(0) = 6 m and x'(0) = -5 m/sec and it is subjected to the harmonic external force f(t) = 100 cos 3t N. Find at least the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about t = 0, i.e. Maclaurin series expansion, for the displacement: Analytically (hand calculations)arrow_forward
- this is answer to a vibrations question. in the last part it states an assumption of x2, im not sure where this assumption comes from. an answer would be greatly appreciatedarrow_forwardPlease answer with the sketches.arrow_forwardThe beam is made of elastic perfectly plastic material. Determine the shape factor for the cross section of the beam (Figure Q3). [Take σy = 250 MPa, yNA = 110.94 mm, I = 78.08 x 106 mm²] y 25 mm 75 mm I 25 mm 200 mm 25 mm 125 Figure Q3arrow_forward
- A beam of the cross section shown in Figure Q3 is made of a steel that is assumed to be elastic- perfectectly plastic material with E = 200 GPa and σy = 240 MPa. Determine: i. The shape factor of the cross section ii. The bending moment at which the plastic zones at the top and bottom of the bar are 30 mm thick. 15 mm 30 mm 15 mm 30 mm 30 mm 30 mmarrow_forwardA torque of magnitude T = 12 kNm is applied to the end of a tank containing compressed air under a pressure of 8 MPa (Figure Q1). The tank has a 180 mm inner diameter and a 12 mm wall thickness. As a result of several tensile tests, it has been found that tensile yeild strength is σy = 250 MPa for thr grade of steel used. Determine the factor of safety with respect to yeild, using: (a) The maximum shearing stress theory (b) The maximum distortion energy theory T Figure Q1arrow_forwardAn external pressure of 12 MPa is applied to a closed-end thick cylinder of internal diameter 150 mm and external diameter 300 mm. If the maximum hoop stress on the inner surface of the cylinder is limited to 30 MPa: (a) What maximum internal pressure can be applied to the cylinder? (b) Sketch the variation of hoop and radial stresses across the cylinder wall. (c) What will be the change in the outside diameter when the above pressure is applied? [Take E = 207 GPa and v = 0.29]arrow_forward
- so A 4 I need a detailed drawing with explanation し i need drawing in solution motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the か ---2-125 750 x2.01 98Parrow_forwardFigure below shows a link mechanism in which the link OA rotates uniformly in an anticlockwise direction at 10 rad/s. the lengths of the various links are OA=75 mm, OB-150 mm, BC=150 mm, CD-300 mm. Determine for the position shown, the sliding velocity of D. A 45 B Space Diagram o NTS (Not-to-Scale) C Darrow_forwardI need a detailed drawing with explanation so Solle 4 يكا Pax Pu + 96** motion is as follows; 1- Dwell 45°. Plot the displacement diagram for a cam with flat follower of width 14 mm. The required 2- Rising 60 mm in 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 3- Dwell 90°. 4- Falling 60 mm for 90° with Simple Harmonic Motion. 5- Dwell 45°. cam is 50 mm. Then design the cam profile to give the above displacement diagram if the minimum circle diameter of the 55 ---20125 750 X 2.01 1989arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Fluid Mechanics - Viscosity and Shear Strain Rate in 9 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_0aaRDAdPTY;License: Standard youtube license