
Concept explainers
a.
Normalization:
The process used to minimize data redundancy and dependency in a relational
Second normal form (2NF):
- The value of all non-primary key attributes should be dependent on the primary key attribute.
- If any attribute is depending on the partial primary key then it should determine the other attributes for an instance of the entity.
- The partial dependencies should be removed from the data model.
Third normal form (3NF):
- The value of any non-primary key attributes will not depend on any other non-primary key attributes.
- If any non-primary key attributes depend on any other non-primary key attribute then it should be moved or deleted.
- It is termed as transitive dependency.
Partial dependency:
A partial dependency exists at that time of an attributes depends only a part of primary key. This dependency is related with 1st normal form.
Transitive dependency:
A transitive dependency exists at that time of an attributes depends on another attribute which is not part of primary key.
Functional dependency:
An association between two attributes or two set of attributes in a same relational database table, which is having some constraints is known as functional dependency.
- In a table one attribute is functionally dependent on another attribute to take one value.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Construct the dependency diagram with all partial and transitive dependencies:
The relational schema for given INVOICE table is given below:
Invoice(INV_NUM, PROD_NUM, SALE_DATE, PROD_LABEL, VEND_CODE, VEND_NAME, QUANT_SOLD, PROD_PRICE)
- Here, “INV_NUM” and “PROD_NUM” indicates the primary key.
The representation of dependency diagram with all partial and transitive dependencies is shown below:
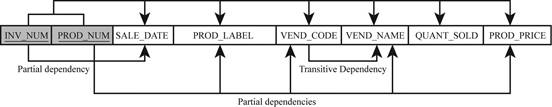
Explanation:
In the above dependency diagram,
- The partial dependencies are,
INV_NUM -> (SALE_DATE)
PROD_NUM -> (PROD_LABEL, VEND_CODE, VEND_NAME, PROD_PRICE)
- The transitive dependency is,
VEND_CODE -> (VEND_NAME)
b.
Normalization:
The process used to minimize data redundancy and dependency in a relational database is known as normalization. The database table is divided into two or more tables and defines the relationship between those tables.
Second normal form (2NF):
- The value of all non-primary key attributes should be dependent on the primary key attribute.
- If any attribute is depending on the partial primary key then it should determine the other attributes for an instance of the entity.
- The partial dependencies should be removed from the data model.
Third normal form (3NF):
- The value of any non-primary key attributes will not depend on any other non-primary key attributes.
- If any non-primary key attributes depend on any other non-primary key attribute then it should be moved or deleted.
- It is termed as transitive dependency.
Partial dependency:
A partial dependency exists at that time of an attributes depends only a part of primary key. This dependency is related with 1st normal form.
Transitive dependency:
A transitive dependency exists at that time of an attributes depends on another attribute which is not part of primary key.
Functional dependency:
An association between two attributes or two set of attributes in a same relational database table, which is having some constraints is known as functional dependency.
- In a table one attribute is functionally dependent on another attribute to take one value.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Construct the dependency diagram by removing all partial dependencies:
The new dependency diagram is represented by removing all partial dependencies in INVOICE table.
First table:
The relational schema for first table is given below:
3NF(INV_NUM, PROD_NUM, SALE_DATE, QUANT_SOLD)
- Here, “INV_NUM” and “PROD_NUM” indicates the primary keys.
- The relation is in third normal form (3NF), since there is no transitive dependency and no repeated attributes.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all partial dependencies in first table are shown below:

Second table:
The relational schema for second table is given below:
3NF(INV_NUM, SALE_DATE)
- Here, “INV_NUM” indicates the primary key.
- The relation is in third normal form (3NF), since there is no transitive dependency and no repeated attributes.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all partial dependencies in second table are shown below:

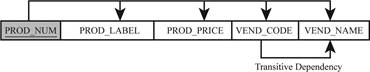
Third table:
The relational schema for third table is given below:
2NF(PROD_NUM, PROD_LABEL, VEND_CODE, VEND_NAME, PROD_PRICE)
- Here, “PROD_NUM” indicates the primary key.
- The relation is in third normal form (2NF), since there is transitive dependency in table.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all partial dependencies in third table are shown below:
c.
Normalization:
The process used to minimize data redundancy and dependency in a relational database is known as normalization. The database table is divided into two or more tables and defines the relationship between those tables.
Second normal form (2NF):
- The value of all non-primary key attributes should be dependent on the primary key attribute.
- If any attribute is depending on the partial primary key then it should determine the other attributes for an instance of the entity.
- The partial dependencies should be removed from the data model.
Third normal form (3NF):
- The value of any non-primary key attributes will not depend on any other non-primary key attributes.
- If any non-primary key attributes depend on any other non-primary key attribute then it should be moved or deleted.
- It is termed as transitive dependency.
Partial dependency:
A partial dependency exists at that time of an attributes depends only a part of primary key. This dependency is related with 1st normal form.
Transitive dependency:
A transitive dependency exists at that time of an attributes depends on another attribute which is not part of primary key.
Functional dependency:
An association between two attributes or two set of attributes in a same relational database table, which is having some constraints is known as functional dependency.
- In a table one attribute is functionally dependent on another attribute to take one value.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Construct the dependency diagram by removing all transitive dependencies:
The new dependency diagram is represented by removing all transitive dependencies in INVOICE table.
First table:
The relational schema for first table is given below:
3NF(INV_NUM, PROD_NUM, QUANT_SOLD)
- Here, “INV_NUM” and “PROD_NUM” indicates the primary keys.
- The relation is in third normal form (3NF), since there is no transitive dependency and no repeated attributes.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all partial dependencies in first table are shown below:

Second table:
The relational schema for second table is given below:
3NF(INV_NUM, SALE_DATE)
- Here, “INV_NUM” indicates the primary key.
- The relation is in third normal form (3NF), since there is no transitive dependency and no repeated attributes.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all transitive dependencies in second table are shown below:

Third table:
The relational schema for third table is given below:
3NF(VEND_CODE, VEND_NAME)
- Here, “VEND_CODE” indicates the primary key.
- The relation is in third normal form (3NF), since there is no transitive dependency and no repeated attributes.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all transitive dependencies in third table are shown below:

Fourth table:
The relational schema for final table is given below:
2NF(PROD_NUM, PROD_LABEL, VEND_CODE, PROD_PRICE)
- Here, “PROD_NUM” indicates the primary key.
- The relation is in third normal form (3NF), since there is no transitive dependency and no repeated attributes.
The representation of dependency diagram removes all transitive dependencies are shown below:

d.
Explanation of Solution
The representation of Crow’s Foot Entity Relational Diagram (ERD) is shown below:
The following data model shows the solution for the given question.
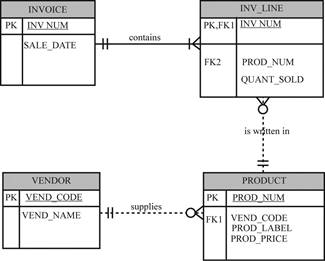
Explanation:
- In the above data model, one invoice can contains many invoice line.
- The “INVOICE” entity contains the “INV_NUM” and “SALE_DATE” attributes.
- The primary key of “INVOICE” entity is “INV_NUM”.
- The “INV_LINE” entity contains the “INV_NUM”, “PROD_NUM” and “QUANT_SOLD” attributes.
- The primary and foreign key of this entity is “INV_NUM”.
- The foreign key of this entity is “PROD_NUM”.
- The “INVOICE” entity contains the “INV_NUM” and “SALE_DATE” attributes.
- The product is written in more than one invoice line.
- The “PRODUCT” entity contains the “PROD_NUM”, “VEND_CODE”, “PROD_LABEL”, and “PROD_PRICE” attributes.
- The primary key of “PROD_NUM” for this entity.
- The foreign key of this entity is “VEND_CODE”.
- The “PRODUCT” entity contains the “PROD_NUM”, “VEND_CODE”, “PROD_LABEL”, and “PROD_PRICE” attributes.
- The vendor supplies more than one product.
- The “VENDOR” entity contains the “VEND_CODE” and “VEND_NAME” attributes.
- The primary key of “VEND_CODE” entity.
- The “VENDOR” entity contains the “VEND_CODE” and “VEND_NAME” attributes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Complete the JavaScript function addPixels () to calculate the sum of pixelAmount and the given element's cssProperty value, and return the new "px" value. Ex: If helloElem's width is 150px, then calling addPixels (hello Elem, "width", 50) should return 150px + 50px = "200px". SHOW EXPECTED HTML JavaScript 1 function addPixels (element, cssProperty, pixelAmount) { 2 3 /* Your solution goes here *1 4 } 5 6 const helloElem = document.querySelector("# helloMessage"); 7 const newVal = addPixels (helloElem, "width", 50); 8 helloElem.style.setProperty("width", newVal); [arrow_forwardSolve in MATLABarrow_forwardHello please look at the attached picture. I need an detailed explanation of the architecturearrow_forward
- Information Security Risk and Vulnerability Assessment 1- Which TCP/IP protocol is used to convert the IP address to the Mac address? Explain 2-What popular switch feature allows you to create communication boundaries between systems connected to the switch3- what types of vulnerability directly related to the programmer of the software?4- Who ensures the entity implements appropriate security controls to protect an asset? Please do not use AI and add refrencearrow_forwardFind the voltage V0 across the 4K resistor using the mesh method or nodal analysis. Note: I have already simulated it and the value it should give is -1.714Varrow_forwardResolver por superposicionarrow_forward
- Describe three (3) Multiplexing techniques common for fiber optic linksarrow_forwardCould you help me to know features of the following concepts: - commercial CA - memory integrity - WMI filterarrow_forwardBriefly describe the issues involved in using ATM technology in Local Area Networksarrow_forward
- For this question you will perform two levels of quicksort on an array containing these numbers: 59 41 61 73 43 57 50 13 96 88 42 77 27 95 32 89 In the first blank, enter the array contents after the top level partition. In the second blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the left-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. In the third blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the right-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. Print the numbers with a single space between them. Use the algorithm we covered in class, in which the first element of the subarray is the partition value. Question 1 options: Blank # 1 Blank # 2 Blank # 3arrow_forward1. Transform the E-R diagram into a set of relations. Country_of Agent ID Agent H Holds Is_Reponsible_for Consignment Number $ Value May Contain Consignment Transports Container Destination Ф R Goes Off Container Number Size Vessel Voyage Registry Vessel ID Voyage_ID Tonnagearrow_forwardI want to solve 13.2 using matlab please helparrow_forward
 Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781305627482Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285196145Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos CoronelPublisher:Cengage Learning A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
A Guide to SQLComputer ScienceISBN:9781111527273Author:Philip J. PrattPublisher:Course Technology Ptr
 Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285867168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course...Computer ScienceISBN:9781285867168Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning





