
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal
alkane .
(a)
Answer to Problem 31P
1-chloroethane.
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(b)
Answer to Problem 31P
1,2-dibromoethane.
Explanation of Solution
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following molecule should be determined.
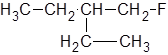
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(c)
Answer to Problem 31P
2-ethyl-1-fluorobutane.
Explanation of Solution
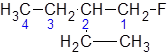
The longest carbon chain giving the halide atom the lowest number has four carbons. So, this is a butane. There is a fluorine atom attached at C-1 and an ethyl group at C-2. Alphabetically, ethyl substituent should be written before, fluoro-. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2-ethyl-1-fluorobutane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(d)
Answer to Problem 31P
2,2-dimethyl-1-iodopropane.
Explanation of Solution
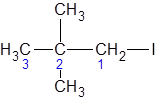
The longest carbon chain giving the halide atom the lowest number has three carbons. So, this is a propane. There is an iodine atom attached at C-1 and two methyl groups at C-2. Alphabetically, iodo- substituent should be written before, methyl. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2,2-dimethyl-1-iodopropane.
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following molecule should be determined.
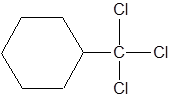
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(e)
Answer to Problem 31P
1-trichloromethylcyclohexane.
Explanation of Solution
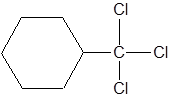
This is a substituted cycloalkane. The cycloalkane has six carbons, so, it is named as cyclohexane. There is a trichloromethyl group attached to C-1 of cyclohexane. So, IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-trichloromethylcyclohexane.
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(f)
Answer to Problem 31P
Tribromomethane.
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Name the following molecules with IUpacarrow_forwardWhat is the molecular orbital for cyclopropenyl anion and is it aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic?arrow_forwardUsing the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid and its impact on the protein.arrow_forward
- How to get the predicted product of this reaction belowarrow_forwardPlease help me fill out the chart then using the chart describe the change from cystine to tyrosine and its impact on the protein. Then using the chart describe the change from histidine to aspartic acid.arrow_forwardWrite the Esterification reaction mechanism for acetic acid, and one propanol to make propanol ethanoate (molecule that gives peas its odor in flavor)arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





