
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:Sets of below
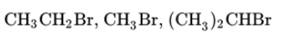
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or
A general
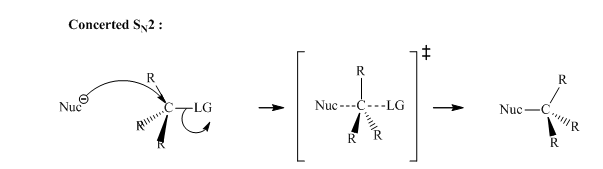
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of
(b)
Interpretation:Below chloroalkanes should be ranked in increasing order of their reactivity towards
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or
A general
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of
(c)
Interpretation:Below alkyl halides should be ranked in increasing order of their reactivity towards
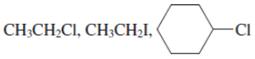
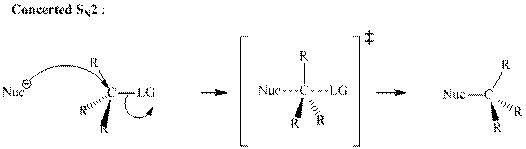
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or
A general
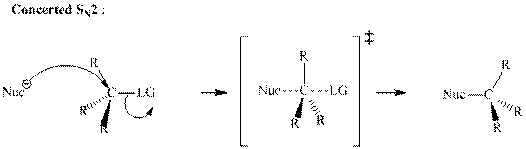
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of
(d)
Interpretation: Sets of below alkyl bromides should be ranked in increasing order of their reactivity towards
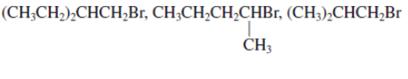
Concept introduction: Bimolecular substitution or
A general
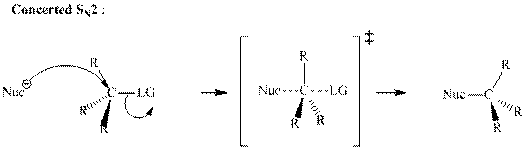
Polar-aprotic solvents accelerate the rate of
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Structure and Function
- Calculate equilibrium concentrations for the following reaction:N2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇋ 2 NO (g) Kc = 0.10 at 2273K initially [N2] = 0.200M; [O2] = 0.200arrow_forwardFor each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forwardThe following reaction is run in which the initial conditions include only methane (CH4) at a concentration of0.115 M. Once equilibrium was established, the concentration of acetylene (C2H2) was measured to be 0.035M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K?2 CH4 (g) ⇋ C2H2 (g) + 3 H2 (g)arrow_forward
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of carbon dioxide for the following reaction:2 COF2 (g) ⇋ CF4 (g) + CO2 (g) Kc = 2.00 at 10.00 °C. at equilibrium [COF2] = 0.255M; [CF4] = 0.118Marrow_forwardIn a benzene derivative that has -CH2CH3, indicate how it can be substituted by -COOH.arrow_forwardIn a sulfonated derivative of benzene, indicate how -SO3H can be eliminated.arrow_forward
- What is the equilibrium expression (law of mass action) for the following reaction:CO2 (g) + H2O (l) ⇋ H+ (aq) + HCO3- (aq)arrow_forwardIndicate the compound resulting from adding NaOH cyclopentane-CH2-CHO.arrow_forwardUse the provided information to calculate Kc for the following reaction at 550 °C: H2(g) + CO2(g) ⇌ CO(g) + H2O(g) Kc = ?CoO(s) + CO(g) ⇌ Co(s) + CO2(g) Kc1 = 490CoO(s) + H2(g) ⇌ Co(s) + H2O(g) Kc2 = 67arrow_forward
- Calculate Kc for the reaction: I2 (g) ⇋ 2 I (g) Kp = 6.26 x 10-22 at 298Karrow_forwardFor each scenario below, select the color of the solution using the indicator thymol blue during the titration. When you first add indicator to your Na2CO3solution, the solution is basic (pH ~10), and the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . At the equivalence point for the titration, the moles of added HCl are equal to the moles of Na2CO3. One drop (or less!) past this is called the endpoint. The added HCl begins to titrate the thymol blue indicator itself. At the endpoint, the indicator color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you weren't paying attention and added too much HCl (~12 mL extra), the color is ["", "", "", "", ""] . When you really weren't paying attention and reached the second equivalence point of Na2CO3, the color isarrow_forwardTo convert cyclopentane-CH2-CHO to cyclopentane-CH2-CH3, compound A is added, followed by (CH3)3CO-K+, DMS at 100oC. Indicate which compound A is.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

