
Interpretation:
The reaction which occurs faster in each of the given reactions is to be determined and the reason is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl iodides are several times more reactive than alkyl bromides. These reactivity differences can be related to the carbon-halogen bond strength and the basicity of the halide anion. Alkyl iodides have the weakest carbon-halogen bond and require the lowest activation energy to break.
Regarding basicity of the halide leaving the group, iodide is the weakest base. Generally, it is true that, the less basic the leaving group, the smaller the energy requirement for cleaving its bond to carbon and the faster the rate.
Alkyl groups that are adjacent to the carbon atom to the point of nucleophilic attack decrease the rate of the
Protic solvents having
In
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
a)
b)
c) Cyclohexyl chloride reacts faster than hexyl chloride by the
d) Tert-butyl bromide reacts faster than
e) sec-butyl bromide reacts faster than isobutyl bromide by the
f) The reaction of
g) The reaction of
Explanation of Solution
a)
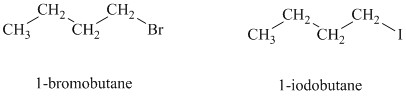
Both the given
b)
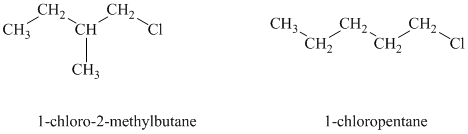
Both the given alkyl halides are primary alkyl halides. The reagent is sodium iodide in acetone. Both these suggest an
c)
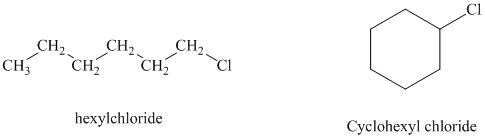
Hexyl chloride is a primary alkyl halide whereas cyclohexyl chloride is a secondary alkyl halide. The solvent is ethanol, which is a polar protic solvent. The nucleophile is the azide ion, which is a good nucleophile. Solvation of the azide ion by ethanol reduces the rate of bimolecular substitution. Polar protic solvents favor
d)

The solvent is ethanol, which is a polar protic solvent. It favors the
e)
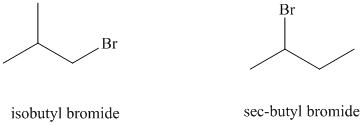
The solvent is aqueous formic acid, which is a polar protic solvent. It favors the
f)
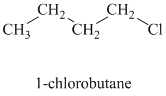
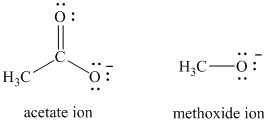
As long as the nucleophilic atom is the same, the more basic the nucleophile, the more reactive it is. The methoxide ion is more basic and more nucleophilic than the acetate ion. Thus, the reaction of
g)
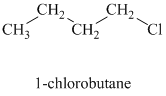
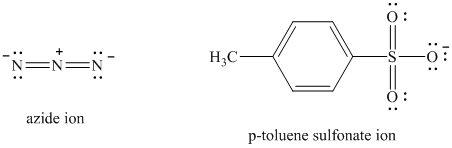
Comparing the nucleophilic atoms, the azide ion is more nucleophilic than the p-toluene sulfonate ion since nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen. Thus, the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Ideally nonpolarizable electrodes can1. participate as reducers in reactions.2. be formed only with hydrogen.3. participate as oxidizers in reactions.4. form open and closed electrochemical systems.arrow_forwardIndicate the options for an electrified interface:1. Temperature has no influence on it.2. Not all theories that describe it include a well-defined electrical double layer.3. Under favorable conditions, its differential capacitance can be determined with the help of experimental measurements.4. A component with high electronic conductivity is involved in its formation.arrow_forwardTo describe the structure of the interface, there are theories or models that can be distinguished by:1. calculation of the charge density.2. distribution of ions in the solution.3. experimentally measured potential difference.4. external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forward
- Indicate the correct options when referring to Luther's equation:1. It is not always easy to compare its results with experimental results.2. It depends on the number of electrons exchanged in the species involved.3. Its foundation is thermodynamic.4. The values calculated with it do not depend on temperature.arrow_forwardIndicate which of the unit options correspond to a measurement of current density.1. A s m-22. mC s-1 m-23. Ω m-24. V J-1 m-2arrow_forwardIndicate the options that are true when referring to electrode membranes:1. The Donnan potential, in general, does not always intervene in membranes.2. There are several ways to classify the same membrane.3. Any membrane can be used to determine the pH of a solution.4. Only one solution and one membrane are needed to determine the pH of that solution.arrow_forward
- Calculate the maximum volume of carbon dioxide gasarrow_forwardIn galvanic cells, their potential1. can be measured with a potentiometer2. does not depend on the equilibrium constant of the reaction occurring within them3. is only calculated from the normal potentials of the electrodes they comprise4. can sometimes be considered a variation in a potential differencearrow_forwardIf some molecules in an excited state collide with other molecules in a ground state, this process1. can occur in solution and in the gas phase.2. can be treated as a bimolecular process.3. always results in collisional deactivation.4. does not compete with any other process.arrow_forward
- Radiation of frequency v is incident on molecules in their ground state. The expected outcome is that1. the molecules do not change their state.2. the molecules transition to an excited state.3. the molecules undergo a secondary process.4. collisional deactivation occurs.arrow_forwardPredict the major product of the following reaction and then draw a curved arrow mechanism for its formation. Part: 0/2 Part 1 of 2 H₂SO heat : OH 90 Draw the structure of the major product. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 3arrow_forwardDraw a curved arrow mechanism for the reaction, adding steps as necessary. Be sure to include all electrons that are necessary to the mechanism and all nonzero formal charges. C Ö-H H + -S-OH .0. Add/Remove step X टे Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

