
Jeremy is deeply in love with Jasmine. Jasmine lives where cell phone coverage is poor, so he can either call her on the land-line phone for five cents per minute or he can drive to see her, at a round—trip cost of
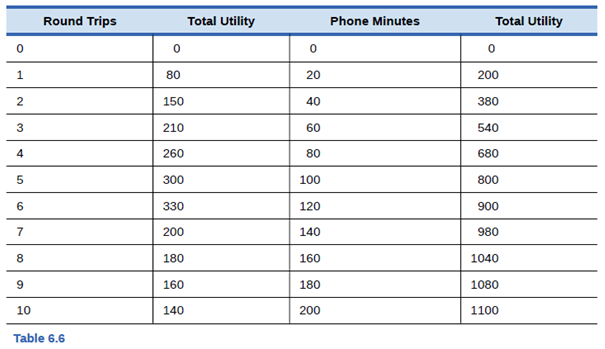
Using the values in given table, find out the points on Jeremy’s consumption choice budget constraint and identify his utility maximizing point?
Answer to Problem 1SCQ
The maximum total utility is 1120 on round 1 with 80 utility and 160 minutes of phone minutes within the given $10.
Explanation of Solution
It is given that Jeremy has total $10 to spend ,a round trips costs him $2 and phone calls costs $0.05 per minute. With the given money, he can either go for 5 round trips or no phone calls. second option is no round trips and 200 minutes of phone calls. there can be the combination of two in between. hence the budget constraint formulae is
Total amount=Price of round trips*Quantity of round trips+ Price of phone calls*Quantity of phone calls
A =P(r)*Q(r)+P(pc)*Q(pc)
$10=$2*Q(r)+$0.05*Q(pc)
dividing the whole equation by $0.05
$10/0.05=($2*Q(r)+$0.05*Q(pc))/0.05
200= 40*Q(r)+Q(pc)
Q(pc)=200-40*Q(r)
Hence with the given budget constraint and table, below table is constructed which shows zero to five round trips and how many phone minutes can be afforded with the given budget with total utility of each.
Concept introduction:
Budget Constraint: It represent all the possible combination of goods and services that a consumer can purchase with the given prices and income.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles Of Economics V8.0
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
MARKETING:REAL PEOPLE,REAL CHOICES
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
- Ask one question at a time. Keep questions specific and include all details. Need more help? Subject matter experts with PhDs and Masters are standing by 24/7 to answer your question.**arrow_forward1b. (5 pts) Under the 1990 Farm Bill and given the initial situation of a target price and marketing loan, indicate where the market price (MP), quantity supplied (QS) and demanded (QD), government stocks (GS), and Deficiency Payments (DP) and Marketing Loan Gains (MLG), if any, would be on the graph below. If applicable, indicate the price floor (PF) on the graph. TP $ NLR So Do Q/yrarrow_forwardNow, let us assume that Brie has altruistic preferences. Her utility function is now given by: 1 UB (xA, YA, TB,YB) = (1/2) (2x+2y) + (2x+2y) What would her utility be at the endowment now? (Round off your answer to the nearest whole number.) 110arrow_forward
- Problema 4 (20 puntos): Supongamos que tenemos un ingreso de $120 y enfrentamos los precios P₁ =6 y P₂ =4. Nuestra función de utilidad es: U(x1, x2) = x0.4x0.6 a) Planteen el problema de optimización y obtengan las condiciones de primer orden. b) Encuentren el consumo óptimo de x1 y x2. c) ¿Cómo cambiará nuestra elección óptima si el ingreso aumenta a $180?arrow_forwardPlease draw the graph for number 4 and 5, I appreciate it!!arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward• Prismatic Cards: A prismatic card will be a card that counts as having every suit. We will denote, e.g., a prismatic Queen card by Q*. With this notation, 2.3045 Q would be a double flush since every card is a diamond and a heart. • Wild Cards: A wild card counts as having every suit and every denomination. Denote wild cards with a W; if there are multiple, we will denote them W₁, W2, etc. With this notation, W2 20.30054 would be both a three-of-a-kind (three 2's) and a flush (5 diamonds). If we add multiple wild cards to the deck, they count as distinct cards, so that (e.g.) the following two hands count as "different hands" when counting: W15 5Q and W255◊♡♡♣♣ In addition, 1. Let's start with the unmodified double-suited deck. (a) Call a hand a flush house if it is a flush and a full house, i.e. if all cards share a suit and there are 3 cards of one denomination and two of another. For example, 550. house. How many different flush house hands are there? 2. Suppose we add one wild…arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- In a classic oil-drilling example, you are trying to decide whether to drill for oil on a field that might or might not contain any oil. Before making this decision, you have the option of hiring a geologist to perform some seismic tests and then predict whether there is any oil or not. You assess that if there is actually oil, the geologist will predict there is oil with probability 0.85 . You also assess that if there is no oil, the geologist will predict there is no oil with probability 0.90. Please answer the two questions below, as I am trying to ensure that I am correct. 1. Why will these two probabilities not appear on the decision tree? 2. Which probabilities will be on the decision tree?arrow_forwardAsap pleasearrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
 Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
 Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





