
(a)
Interpretation:
Bond-dissociation energy should be identified for the red line bond in the given structure.
Concept introduction:
Bond-dissociation energy (
Bond-dissociation energy is mainly depends on the hybridization of the carbon atom and substitution on the carbon atom
It is also determined by the electronegativity of the molecule and polarization of the molecule to which carbon atom bonded with.
Sigma bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to end to end overlap of atomic orbitals.
Pi bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to side to side overlap of atomic orbitals
Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Polarization: A partial charge separation between the carbon and an other heteroatom due to its electronegativity difference.
(a)
Answer to Problem 19PP
Answer
The bond dissociation energy of the bonds in red line of the molecule (a) is given below
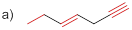
Carbon - carbon triple bond has more dissociation energy
Carbon - carbon triple bond has more dissociation energy than the carbon – carbon double bond and Carbon – carbon double bond more dissociation than the carbon – carbon single bond.
Explanation of Solution
To find: Bond-dissociation energy of the given compounds.
Draw the given molecule and analyze the nature of C-C bonds present in it.
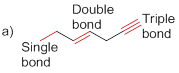
The given molecule is drawn and it has three types of C-C bonds. They are
Carbon – Carbon Single bond has less dissociation energy than carbon – carbon double bond and triple bond. Carbon – carbon triple bond (sp hybridization) has more dissociation energy because it consists of three bonds (two pi bonds and one sigma bond) so it requires more energy to break the bonds than the other carbon- carbon double bonds (one pi bonds and one sigma bond) and carbon – carbon single bond (only one sigma bond).
(b)
Interpretation:
Bond-dissociation energy should be identified for the red line bond in the given structure.
Concept introduction:
Bond-dissociation energy (BDE) is determined from the strength of a single chemical bond.
Bond-dissociation energy is mainly depends on the hybridization of the carbon atom and substitution on the carbon atom
It is also determined by the electronegativity of the molecule and polarization of the molecule to which carbon atom bonded with.
Sigma bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to end to end overlap of atomic orbitals.
Pi bond: A covalent bond formation is mainly due to side to side overlap of atomic orbitals
Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
Polarization: A partial charge separation between the carbon and an other heteroatom due to its electronegativity difference.
(b)
Answer to Problem 19PP
Answer
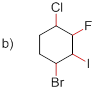
C-F bond has more dissociation energy
Explanation of Solution
To find: Bond-dissociation energy of the given compounds.
Draw the given molecule and analyze the nature of C-C bonds present in it.

The given molecule is drawn and it has four types of C-C bonds. They are
Bond dissociation energy depends on the electronegativity of the molecule and polarization of the molecule. If the molecule has high electronegativity (less polarizability) the dissociation energy of the molecule is high.
The electronegativity order in the halogen series given below
C-F has more Bond dissociation energy in the given molecule since it has more electronegativity than the other halogen atoms.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Provide the semi-developed formula of isooxazole obtained by reacting acetylacetone and hydroxylamine.arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound (R1-CO-CH2-CO-R2), indicate the formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardAn orange laser has a wavelength of 610 nm. What is the energy of this light?arrow_forward
- The molar absorptivity of a protein in water at 280 nm can be estimated within ~5-10% from its content of the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan and from the number of disulfide linkages (R-S-S-R) between cysteine residues: Ε280 nm (M-1 cm-1) ≈ 5500 nTrp + 1490 nTyr + 125 nS-S where nTrp is the number of tryptophans, nTyr is the number of tyrosines, and nS-S is the number of disulfide linkages. The protein human serum transferrin has 678 amino acids including 8 tryptophans, 26 tyrosines, and 19 disulfide linkages. The molecular mass of the most dominant for is 79550. Predict the molar absorptivity of transferrin. Predict the absorbance of a solution that’s 1.000 g/L transferrin in a 1.000-cm-pathlength cuvet. Estimate the g/L of a transferrin solution with an absorbance of 1.50 at 280 nm.arrow_forwardIn GC, what order will the following molecules elute from the column? CH3OCH3, CH3CH2OH, C3H8, C4H10arrow_forwardBeer’s Law is A = εbc, where A is absorbance, ε is the molar absorptivity (which is specific to the compound and wavelength in the measurement), and c is concentration. The absorbance of a 2.31 × 10-5 M solution of a compound is 0.822 at a wavelength of 266 nm in a 1.00-cm cell. Calculate the molar absorptivity at 266 nm.arrow_forward
- How to calculate % of unknown solution using line of best fit y=0.1227x + 0.0292 (y=2.244)arrow_forwardGiven a 1,3-dicarbonyl compound, state the (condensed) formula of the compound obtaineda) if I add hydroxylamine (NH2OH) to give an isooxazole.b) if I add thiosemicarbazide (NH2-CO-NH-NH2) to give an isothiazole.arrow_forwardComplete the following acid-base reactions and predict the direction of equilibrium for each. Justify your prediction by citing pK values for the acid and conjugate acid in each equilibrium. (a) (b) NHs (c) O₂N NH NH OH H₁PO₁arrow_forward
- 23.34 Show how to convert each starting material into isobutylamine in good yield. ཅ ནད ཀྱི (b) Br OEt (c) (d) (e) (f) Harrow_forwardPlease help me Please use https://app.molview.com/ to draw this. I tried, but I couldn't figure out how to do it.arrow_forwardPropose a synthesis of 1-butanamine from the following: (a) a chloroalkane of three carbons (b) a chloroalkane of four carbonsarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





