
Physics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780321733627
Author: Douglas C. Giancoli
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6, Problem 13P
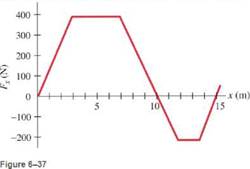
The force on a particle, acting along the x axis, varies as shown in Fig. 6-38. Determine the work done by this force to move the particle along the x axis: (a) from x=0.0 to x=10.0 m; (b) from x=0.0 to x=15.0 m.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
An object is subjected to a friction force with magnitude 5.49 N, which acts against the object's velocity. What is the work (in J) needed to move the object at constant speed for the following routes?
y (m)
C
B
(5.00, 5.00)
A
x (m)
©
(a) the purple path O to A followed by a return purple path to O
]
(b) the purple path O to C followed by a return blue path to O
]
(c) the blue path O to C followed by a return blue path to O
]
(d) Each of your three answers should be nonzero. What is the significance of this observation?
○ The force of friction is a conservative force.
○ The force of friction is a nonconservative force.
A block of mass m = 2.50 kg is pushed d = 2.30 m along a frictionless horizontal table by a constant applied force of magnitude F = 10.0 N directed at an angle
25.0° below the horizontal as shown in the figure below.
m
(a) Determine the work done by the applied force.
]
(b) Determine the work done by the normal force exerted by the table.
]
(c) Determine the work done by the force of gravity.
]
(d) Determine the work done by the net force on the block.
]
A man pushing a crate of mass m = 92.0 kg at a speed of v = 0.845 m/s encounters a rough horizontal surface of length = 0.65 m as in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and rough surface is 0.357 and he exerts a constant horizontal force of 294 N on
the crate.
e
(a) Find the magnitude and direction of the net force on the crate while it is on the rough surface.
magnitude
direction
---Select---
N
(b) Find the net work done on the crate while it is on the rough surface.
]
(c) Find the speed of the crate when it reaches the end of the rough surface.
m/s
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics
Ch. 6 - A skier starts at the top of a hill. On which run...Ch. 6 - In what ways is the word “work’' as used in...Ch. 6 - Can a centripetal force ever do work on an object?...Ch. 6 - Why is it tiring to push hard against a solid wall...Ch. 6 - Can the normal force on an object ever do work?...Ch. 6 - You have two springs that are identical except...Ch. 6 - If the speed of a particle triples, by what factor...Ch. 6 - List some everyday forces that are not...Ch. 6 - A hand exerts a constant horizontal force on a...Ch. 6 - You lift heavy book from a table to a high shelf....
Ch. 6 - A hill has a height h. A child on a sled (total...Ch. 6 - Analyze the motion of a simple swinging pendulum...Ch. 6 - In Fig. 6-31, water balloons are tossed from the...Ch. 6 - What happens to the gravitational potential energy...Ch. 6 - Experienced hikers prefer to step over a fallen...Ch. 6 - The energy transformations in pole vaulting and...Ch. 6 - Prob. 16QCh. 6 - 17. Two identical arrows, one with twice the speed...Ch. 6 - Prob. 18QCh. 6 - Prob. 19QCh. 6 - Describe the energy transformations that take...Ch. 6 - Prob. 21QCh. 6 - Prob. 22QCh. 6 - Prob. 23QCh. 6 - Prob. 1MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 2MCQCh. 6 - When the speed of your car is doubled, by what...Ch. 6 - Prob. 4MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 7MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 8MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 9MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 10MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 11MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 12MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 13MCQCh. 6 - Prob. 14MCQCh. 6 - A 75.0-kg firefighter climbs a flight of stairs...Ch. 6 - The head of a hammer with a mass of 1.2 kg is...Ch. 6 - How much work did the movers do (horizontally)...Ch. 6 - A 1200-N crate rests on the floor. How much work...Ch. 6 - What is the minimum work needed to push a 950-kg...Ch. 6 - Estimate the work you do to mow a lawn 10 m by 20...Ch. 6 - In a certain library the first shelf is 15.0 cm...Ch. 6 - A lever such as that shown in Fig. 6-35 can be...Ch. 6 - A box of mass 4.0 kg is accelerated from rest by a...Ch. 6 - A 380-kg piano slides 2.9 m down a 25° incline and...Ch. 6 - Recall from Chapter 4, Example 4-14, that you can...Ch. 6 - A grocery cart with mass of 16 kg is being pushed...Ch. 6 - The force on a particle, acting along the x axis,...Ch. 6 - A 17,000-kg jet takes off from an aircraft carrier...Ch. 6 - At room temperature, an oxygen molecule, with mass...Ch. 6 - (a) If the kinetic energy of a particle is...Ch. 6 - How much work is required to stop an electron...Ch. 6 - How much work must be done to stop a 925-kg car...Ch. 6 - Prob. 19PCh. 6 - A baseball (m = 145 g) traveling 32 m/s moves a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 21PCh. 6 - Prob. 22PCh. 6 - Prob. 23PCh. 6 - 24. (Ill) One car has twice the mass of a second...Ch. 6 - 25. (Ill) A 265-kg load is lifted 18.0 m...Ch. 6 - 26. (I) By how much does the gravitational...Ch. 6 - A spring has a spring constant k of 88.0 N/m. How...Ch. 6 - Prob. 28PCh. 6 - 29. (II) A 66.5-kg hiker starts at an elevation of...Ch. 6 - Prob. 30PCh. 6 - A novice skier starting from rest, slides down an...Ch. 6 - 32. (I) Jane, looking for Tarzan, is running at...Ch. 6 - A sled is initially given a shove up a...Ch. 6 - Prob. 34PCh. 6 - 35. (II) A spring with k=83 N/m hangs vertically...Ch. 6 - Prob. 36PCh. 6 - Prob. 37PCh. 6 - Prob. 38PCh. 6 - Prob. 39PCh. 6 - Prob. 40PCh. 6 - Prob. 41PCh. 6 - 42. (II) What should be the spring constant k of a...Ch. 6 - 43. (Ill) An engineer is designing a spring to be...Ch. 6 - Prob. 44PCh. 6 - 45. (III) A cyclist intends to cycle up a 7.50°...Ch. 6 - Prob. 46PCh. 6 - Prob. 47PCh. 6 - Prob. 48PCh. 6 - Prob. 49PCh. 6 - Prob. 50PCh. 6 - Prob. 51PCh. 6 - 52. (II) You drop a ball from a height of 2.0 m,...Ch. 6 - 53. (II) A 66-kg skier starts from rest at the top...Ch. 6 - 54. (II) A projectile is fired at an upward angle...Ch. 6 - 55. (II) The Lunar Module could make a safe...Ch. 6 - 56. (III) Early test flights for the space shuttle...Ch. 6 - How long will It take a 2750-W motor to lift a...Ch. 6 - 58. (I) (a) Show that one British horsepower (550...Ch. 6 - An 85-kg football player traveling 5.0 m/s is...Ch. 6 - Prob. 60PCh. 6 - Prob. 61PCh. 6 - A shot-putter accelerates a 7.3-kg shot from rest...Ch. 6 - Prob. 63PCh. 6 - 64. (II) How much work can a 2.0-hp motor do in...Ch. 6 - Prob. 65PCh. 6 - Prob. 66PCh. 6 - Prob. 67PCh. 6 - Prob. 68PCh. 6 - Prob. 69PCh. 6 - 70. (II) What minimum horsepower must a motor have...Ch. 6 - Prob. 71PCh. 6 - Prob. 72GPCh. 6 - Prob. 73GPCh. 6 - Prob. 74GPCh. 6 - Prob. 75GPCh. 6 - Prob. 76GPCh. 6 - Prob. 77GPCh. 6 - Prob. 78GPCh. 6 - Prob. 79GPCh. 6 - Prob. 80GPCh. 6 - Prob. 81GPCh. 6 - Prob. 82GPCh. 6 - Prob. 83GPCh. 6 - Prob. 84GPCh. 6 - Prob. 85GPCh. 6 - Prob. 86GPCh. 6 - Prob. 87GPCh. 6 - Prob. 88GPCh. 6 - Prob. 89GPCh. 6 - Prob. 90GPCh. 6 - Prob. 91GPCh. 6 - Prob. 92GPCh. 6 - Prob. 93GPCh. 6 - Prob. 94GP
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
7. A horse is looking straight ahead at a person who is standing quite close. The image of the person spans mu...
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
What is the difference between cellular respiration and external respiration?
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Chlorine has two isotopes, 35Cl and 37Cl; 75.77% of chlorine is 35Cl, and 24.23% is 37Cl. The atomic mass of 35...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
47. A block hangs in equilibrium from a vertical spring. When a second identical block is added, the original ...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following Explain your reasoning. 8.How does the habitable zone around a ...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
explain the function of fermentation and the conditions under which it occurs?
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. × J 37° Barrow_forwardYou are working for the Highway Department. In mountainous regions, highways sometimes include a runaway truck ramp, and you are asked to help with the design of such a ramp. A runaway truck ramp is often a lane of gravel adjacent to a long downhill section of roadway where trucks with failing brakes may need assistance to stop. Working with your supervisor, you develop a worst-case scenario: a truck with a mass of 6.00 × 104 kg enters a runaway truck lane traveling at 34.1 m/s. Assume that the maximum constant value for safe acceleration of the truck is -5.00 m/s². Any higher magnitude of acceleration increases the likelihood that semi-trailer rigs could jackknife. Your supervisor asks you to advise her on the required length (in m) of a runaway truck lane on a flat section of ground next to the roadway. marrow_forwardA large cruise ship of mass 6.20 × 107 kg has a speed of 10.2 m/s at some instant. (a) What is the ship's kinetic energy at this time? ] (b) How much work is required to stop it? (Give the work done on the ship. Include the sign of the value in your answer.) ] (c) What is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 3.10 km? Narrow_forward
- A 7.80 g bullet is initially moving at 660 m/s just before it penetrates a block of wood to a depth of 6.20 cm. (a) What is the magnitude of the average frictional force (in N) that is exerted on the bullet while it is moving through the block of wood? Use work and energy considerations to obtain your answer. N (b) Assuming the frictional force is constant, how much time (in s) elapses between the moment the bullet enters the block of wood and the moment it stops moving? Sarrow_forwardPlease don't use Chatgpt will upvote and give handwritten solutionarrow_forwardTwo blocks, A and B (with mass 45 kg and 120 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in the figure below. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is μk = 0.26. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to ①, a distance of 15 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 15 m) if the system starts from rest. ] 37° A © Barrow_forward
- A skateboarder with his board can be modeled as a particle of mass 80.0 kg, located at his center of mass. As shown in the figure below, the skateboarder starts from rest in a crouching position at one lip of a half-pipe (point). On his descent, the skateboarder moves without friction so that his center of mass moves through one quarter of a circle of radius 6.20 m. i (a) Find his speed at the bottom of the half-pipe (point Ⓡ). m/s (b) Immediately after passing point Ⓑ, he stands up and raises his arms, lifting his center of mass and essentially "pumping" energy into the system. Next, the skateboarder glides upward with his center of mass moving in a quarter circle of radius 5.71 m, reaching point D. As he passes through point ①, the speed of the skateboarder is 5.37 m/s. How much chemical potential energy in the body of the skateboarder was converted to mechanical energy when he stood up at point Ⓑ? ] (c) How high above point ① does he rise? marrow_forwardA 31.0-kg child on a 3.00-m-long swing is released from rest when the ropes of the swing make an angle of 29.0° with the vertical. (a) Neglecting friction, find the child's speed at the lowest position. m/s (b) If the actual speed of the child at the lowest position is 2.40 m/s, what is the mechanical energy lost due to friction? ]arrow_forwardA force acting on a particle moving in the xy plane is given by F = (2yî + x²), where F is in newtons and x and y are in meters. The particle moves from the origin to a final position having coordinates x = 5.60 m and y = 5.60 m, as shown in the figure below. y (m) B (x, y) x (m) (a) Calculate the work done by F on the particle as it moves along the purple path (0 Ⓐ©). ] (b) Calculate the work done by ♬ on the particle as it moves along the red path (0 BC). J (c) Is F conservative or nonconservative? ○ conservative nonconservativearrow_forward
- A 3.5-kg block is pushed 2.9 m up a vertical wall with constant speed by a constant force of magnitude F applied at an angle of 0 = 30° with the horizontal, as shown in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and wall is 0.30, determine the following. (a) the work done by F J (b) the work done by the force of gravity ] (c) the work done by the normal force between block and wall J (d) By how much does the gravitational potential energy increase during the block's motion? ]arrow_forwardPhysics different from a sea breeze from a land breezearrow_forwardFile Preview Design a capacitor for a special purpose. After graduating from medical school you and a friend take a three hour cruise to celebrate and end up stranded on an island. While looking for food, a spider falls on your friend giving them a heart attack. Recalling your physics, you realize you can build a make-shift defibrillator by constructing a capacitor from materials on the boat and charging it using the boat's battery. You know that the capacitor must hold 100 J of energy and be at 1000 V (fortunately this is an electric boat which has batteries that are 1000 V) to work. You decide to construct the capacitor by tightly sandwiching a single layer of Saran wrap between sheets of aluminum foil. You read the Saran wrap box and fortunately they tell you that it has a thickness 0.01 mm and dielectric constant of 2.3. The Saran wrap and foil are 40 cm wide and very long. How long is the final capacitor you build that saves your friend?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanical work done (GCSE Physics); Author: Dr de Bruin's Classroom;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OapgRhYDMvw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY