
CENGEL'S 9TH EDITION OF THERMODYNAMICS:
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260917055
Author: CENGEL
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5.5, Problem 121P
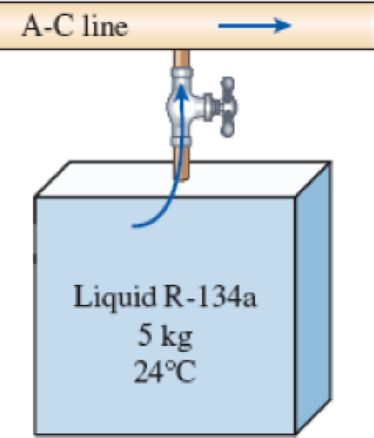
An air-conditioning system is to be filled from a rigid container that initially contains 5 kg of liquid R-134a at 24°C. The valve connecting this container to the air-conditioning system is now opened until the mass in the container is 0.25 kg, at which time the valve is closed. During this time, only liquid R-134a flows from the container. Presuming that the process is isothermal while the valve is open, determine the final quality of the R-134a in the container and the total heat transfer.
FIGURE P5–121
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
My answers are incorrect
Picture
What is the weight of a 5-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s², kgf, Ibm-ft/s², and lbf?
The weight of a 5-kg substance in N is 49.05
N.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kN is
KN.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kg·m/s² is 49.05
kg-m/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in kgf is 5.0 kgf.
The weight of a 5-kg substance in Ibm-ft/s² is 11.02 lbm-ft/s².
The weight of a 5-kg substance in lbf is 11.023
lbf.
Chapter 5 Solutions
CENGEL'S 9TH EDITION OF THERMODYNAMICS:
Ch. 5.5 - Name four physical quantities that are conserved...Ch. 5.5 - Define mass and volume flow rates. How are they...Ch. 5.5 - Does the amount of mass entering a control volume...Ch. 5.5 - Consider a device with one inlet and one outlet....Ch. 5.5 - The ventilating fan of the bathroom of a building...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters a 16-cm-diameter pipe steadily at 200...Ch. 5.5 - A steam pipe is to transport 200 lbm/s of steam at...Ch. 5.5 - A garden hose attached with a nozzle is used to...Ch. 5.5 - A steady-flow compressor is used to compress...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters the 1-m2 inlet of an aircraft engine at...
Ch. 5.5 - A 2-m3 rigid tank initially contains air whose...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters a nozzle steadily at 2.21 kg/m3 and 40...Ch. 5.5 - A spherical hot-air balloon is initially filled...Ch. 5.5 - Water enters the constant 130-mm inside-diameter...Ch. 5.5 - A desktop computer is to be cooled by a fan whose...Ch. 5.5 - A hair dryer is basically a duct of constant...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters a 28-cm-diameter pipe...Ch. 5.5 - What are the different mechanisms for transferring...Ch. 5.5 - How do the energies of a flowing fluid and a fluid...Ch. 5.5 - An air compressor compresses 6 L of air at 120 kPa...Ch. 5.5 - A house is maintained at 1 atm and 24C, and warm...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters the compressor of a...Ch. 5.5 - Steam is leaving a pressure cooker whose operating...Ch. 5.5 - How is a steady-flow system characterized?Ch. 5.5 - Can a steady-flow system involve boundary work?Ch. 5.5 - A diffuser is an adiabatic device that decreases...Ch. 5.5 - The kinetic energy of a fluid increases as it is...Ch. 5.5 - The stators in a gas turbine are designed to...Ch. 5.5 - The diffuser in a jet engine is designed to...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters a nozzle steadily at 50 psia, 140F, and...Ch. 5.5 - Air at 600 kPa and 500 K enters an adiabatic...Ch. 5.5 - Carbon dioxide enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily...Ch. 5.5 - Steam enters a nozzle at 400C and 800 kPa with a...Ch. 5.5 - Air at 80 kPa and 127C enters an adiabatic...Ch. 5.5 - Air at 13 psia and 65F enters an adiabatic...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a at 700 kPa and 120C enters an...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters a diffuser steadily as...Ch. 5.5 - Air at 80 kPa, 27C, and 220 m/s enters a diffuser...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters an adiabatic nozzle steadily at 300...Ch. 5.5 - Consider an adiabatic turbine operating steadily....Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 42PCh. 5.5 - Somebody proposes the following system to cool a...Ch. 5.5 - Air is expanded from 1000 kPa and 600C at the...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 45PCh. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor at 100 kPa...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters a compressor at 180 kPa as...Ch. 5.5 - Steam flows steadily through an adiabatic turbine....Ch. 5.5 - Steam flows steadily through a turbine at a rate...Ch. 5.5 - Steam enters an adiabatic turbine at 8 MPa and...Ch. 5.5 - An adiabatic air compressor compresses 10 L/s of...Ch. 5.5 - Carbon dioxide enters an adiabatic compressor at...Ch. 5.5 - Steam flows steadily into a turbine with a mass...Ch. 5.5 - Air is compressed by an adiabatic compressor from...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters the compressor of a gas-turbine plant...Ch. 5.5 - A portion of the steam passing through a steam...Ch. 5.5 - Why are throttling devices commonly used in...Ch. 5.5 - Would you expect the temperature of air to drop as...Ch. 5.5 - During a throttling process, the temperature of a...Ch. 5.5 - Someone claims, based on temperature measurements,...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a is throttled from the saturated...Ch. 5.5 - A saturated liquidvapor mixture of water, called...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 64PCh. 5.5 - A well-insulated valve is used to throttle steam...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters the expansion valve of a...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 68PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 69PCh. 5.5 - Consider a steady-flow heat exchanger involving...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 71PCh. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a at 700 kPa, 70C, and 8 kg/min is...Ch. 5.5 - Hot and cold streams of a fluid are mixed in a...Ch. 5.5 - A hot-water stream at 80C enters a mixing chamber...Ch. 5.5 - Water at 80F and 20 psia is heated in a chamber by...Ch. 5.5 - An adiabatic open feedwater heater in an electric...Ch. 5.5 - Cold water (cp = 4.18 kJ/kgC) leading to a shower...Ch. 5.5 - Steam is to be condensed on the shell side of a...Ch. 5.5 - Air (cp = 1.005 kJ/kgC) is to be preheated by hot...Ch. 5.5 - An open feedwater heater heats the feedwater by...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a at 1 MPa and 90C is to be cooled...Ch. 5.5 - The evaporator of a refrigeration cycle is...Ch. 5.5 - An air-conditioning system involves the mixing of...Ch. 5.5 - A well-insulated shell-and-tube heat exchanger is...Ch. 5.5 - Steam is to be condensed in the condenser of a...Ch. 5.5 - Steam is to be condensed in the condenser of a...Ch. 5.5 - Two streams of water are mixed in an insulated...Ch. 5.5 - Two mass streams of the same ideal gas are mixed...Ch. 5.5 - Water is heated in an insulated, constant-diameter...Ch. 5.5 - A 110-volt electrical heater is used to warm 0.3...Ch. 5.5 - The ducts of an air heating system pass through an...Ch. 5.5 - The fan on a personal computer draws 0.3 ft3/s of...Ch. 5.5 - Saturated liquid water is heated in a steady-flow...Ch. 5.5 - Water enters the tubes of a cold plate at 70F with...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 96PCh. 5.5 - A computer cooled by a fan contains eight PCBs,...Ch. 5.5 - A desktop computer is to be cooled by a fan. The...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 99PCh. 5.5 - A 4-m 5-m 6-m room is to be heated by an...Ch. 5.5 - A house has an electric heating system that...Ch. 5.5 - A long roll of 2-m-wide and 0.5-cm-thick 1-Mn...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 103PCh. 5.5 - Prob. 104PCh. 5.5 - Argon steadily flows into a constant-pressure...Ch. 5.5 - Steam enters a long, horizontal pipe with an inlet...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters the condenser of a...Ch. 5.5 - A hair dryer is basically a duct in which a few...Ch. 5.5 - A hair dryer is basically a duct in which a few...Ch. 5.5 - Air enters the duct of an air-conditioning system...Ch. 5.5 - An insulated rigid tank is initially evacuated. A...Ch. 5.5 - A rigid, insulated tank that is initially...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 115PCh. 5.5 - A 2-m3 rigid tank initially contains air at 100...Ch. 5.5 - A 0.2-m3 rigid tank equipped with a pressure...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 118PCh. 5.5 - An insulated 40-ft3 rigid tank contains air at 50...Ch. 5.5 - A 4-L pressure cooker has an operating pressure of...Ch. 5.5 - An air-conditioning system is to be filled from a...Ch. 5.5 - Oxygen is supplied to a medical facility from ten...Ch. 5.5 - A 0.05-m3 rigid tank initially contains...Ch. 5.5 - A 0.12-m3 rigid tank contains saturated...Ch. 5.5 - A 0.3-m3 rigid tank is filled with saturated...Ch. 5.5 - The air-release flap on a hot-air balloon is used...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 127PCh. 5.5 - An insulated 0.15-m3 tank contains helium at 3 MPa...Ch. 5.5 - A vertical pistoncylinder device initially...Ch. 5.5 - A vertical piston-cylinder device initially...Ch. 5.5 - A pistoncylinder device initially contains 0.6 kg...Ch. 5.5 - The weighted piston of the device shown in Fig....Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 136RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 137RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 138RPCh. 5.5 - Air at 4.18 kg/m3 enters a nozzle that has an...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 140RPCh. 5.5 - An air compressor compresses 15 L/s of air at 120...Ch. 5.5 - A steam turbine operates with 1.6 MPa and 350C...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a enters an adiabatic compressor at...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 144RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 145RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 146RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 147RPCh. 5.5 - Steam enters a nozzle with a low velocity at 150C...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 149RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 150RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 151RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 152RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 153RPCh. 5.5 - Cold water enters a steam generator at 20C and...Ch. 5.5 - An ideal gas expands in an adiabatic turbine from...Ch. 5.5 - Determine the power input for a compressor that...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 157RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 158RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 159RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 160RPCh. 5.5 - In a dairy plant, milk at 4C is pasteurized...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 162RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 163RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 164RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 165RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 166RPCh. 5.5 - The average atmospheric pressure in Spokane,...Ch. 5.5 - The ventilating fan of the bathroom of a building...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 169RPCh. 5.5 - Determine the rate of sensible heat loss from a...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 171RPCh. 5.5 - An air-conditioning system requires airflow at the...Ch. 5.5 - A building with an internal volume of 400 m3 is to...Ch. 5.5 - The maximum flow rate of standard shower heads is...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 176RPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 177RPCh. 5.5 - Steam enters a turbine steadily at 7 MPa and 600C...Ch. 5.5 - Reconsider Prob. 5178. Using appropriate software,...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 180RPCh. 5.5 - A liquid R-134a bottle has an internal volume of...Ch. 5.5 - A pistoncylinder device initially contains 2 kg of...Ch. 5.5 - A pistoncylinder device initially contains 1.2 kg...Ch. 5.5 - A pressure cooker is a pot that cooks food much...Ch. 5.5 - A tank with an internal volume of 1 m3 contains...Ch. 5.5 - In a single-flash geothermal power plant,...Ch. 5.5 - An adiabatic air compressor is to be powered by a...Ch. 5.5 - The turbocharger of an internal combustion engine...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 189RPCh. 5.5 - Consider an evacuated rigid bottle of volume V...Ch. 5.5 - An adiabatic heat exchanger is used to heat cold...Ch. 5.5 - A heat exchanger is used to heat cold water at 15C...Ch. 5.5 - An adiabatic heat exchanger is used to heat cold...Ch. 5.5 - In a shower, cold water at 10C flowing at a rate...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 195FEPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 196FEPCh. 5.5 - Hot combustion gases (assumed to have the...Ch. 5.5 - Steam expands in a turbine from 4 MPa and 500C to...Ch. 5.5 - Steam is compressed by an adiabatic compressor...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a is compressed by a compressor...Ch. 5.5 - Refrigerant-134a at 1.4 MPa and 70C is throttled...Ch. 5.5 - Prob. 202FEPCh. 5.5 - Prob. 203FEPCh. 5.5 - Air at 27C and 5 atm is throttled by a valve to 1...Ch. 5.5 - Steam at 1 MPa and 300C is throttled adiabatically...Ch. 5.5 - Air is to be heated steadily by an 8-kW electric...Ch. 5.5 - Saturated water vapor at 40C is to be condensed as...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mych CD 36280 kg. 0.36 givens Tesla truck frailer 2017 Model Vven 96154kph ronge 804,5km Cr Powertrain Across PHVAC rwheel 0.006 0.88 9M² 2 2kW 0.55M ng Zg Prated Trated Pair 20 0.95 1080 kW 1760 Nm 1,2 determine the battery energy required to meet the range when fully loaded determine the approximate time for the fully-loaded truck-trailor to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph while Ignoring vehicle load forcesarrow_forward12-217. The block B is sus- pended from a cable that is at- tached to the block at E, wraps around three pulleys, and is tied to the back of a truck. If the truck starts from rest when ID is zero, and moves forward with a constant acceleration of ap = 0.5 m/s², determine the speed of the block at D the instant x = 2 m. Neglect the size of the pulleys in the calcu- lation. When xƊ = 0, yc = 5 m, so that points C and D are at the Prob. 12-217 5 m yc =2M Xparrow_forwardsolve both and show matlab code auto controlsarrow_forward
- 12-82. The roller coaster car trav- els down the helical path at con- stant speed such that the paramet- ric equations that define its posi- tion are x = c sin kt, y = c cos kt, z = h - bt, where c, h, and b are constants. Determine the mag- nitudes of its velocity and accelera- tion. Prob. 12-82 Narrow_forwardGiven: = refueling Powertran SOURCE EMISSIONS vehide eff eff gasoline 266g co₂/kwh- HEV 0.90 0.285 FLgrid 411ilg Co₂/kWh 41111gCo₂/kWh EV 0.85 0.80 Production 11x10% og CO₂ 13.7 x 10°g CO₂ A) Calculate the breakeven pont (in km driven) for a EV against on HEV in Florida of 0.1kWh/kM Use a drive cycle conversion 5) How efficient would the powertrain of the HEV in this example have to be to break even with an EV in Florida after 150,000 Miles of service (240,000) km Is it plausible to achieve the answer from pert b Consideans the HaXINERY theoretical efficiency of the Carnot cycle is 5020 and there are additional losses of the transMISSION :- 90% efficiency ? c A what do you conclude is the leading factor in why EVs are less emissive than ICE,arrow_forwardsolve autocontrolsarrow_forward
- Problem 3.21P: Air at 100F(38C) db,65F(18C) wb, and sea-level pressure is humidified adiabatically with steam. The steam supplied contains 20 percent moisture(quality of 0.80) at 14.7psia(101.3kpa). The air is humidified to 60 percent relative humidity. Find the dry bulb temperature of the humidified air using (a)chart 1a or 1b and (b) the program PSYCH.arrow_forwardPUNTO 4. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 5. Groundarrow_forwardPUNTO 2. PUNTO 3. calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. III IAarrow_forward
- calculate their DoF using Gruebler's formula. PUNTO 6. PUNTO 7. (Ctrl)arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.given that: summation of K gate valve = 0.25check valve=390 degree elbow= 0.75foot valve= 0.78arrow_forwardA pump delivering 230 lps of water at 30C has a 300-mm diameter suction pipe and a 254-mm diameter discharge pipe as shown in the figure. The suction pipe is 3.5 m long and the discharge pipe is 23 m long, both pipe's materials are cast iron. The water is delivered 16m above the intake water level. Considering head losses in fittings, valves, and major head loss. a) Find the total dynamic head which the pump must supply. b)It the pump mechanical efficiency is 68%, and the motor efficiency is 90%, determine the power rating of the motor in hp.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
First Law of Thermodynamics, Basic Introduction - Internal Energy, Heat and Work - Chemistry; Author: The Organic Chemistry Tutor;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NyOYW07-L5g;License: Standard youtube license