
Concept explainers
(a)
Copy and complete the table
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Concept Used:
(b)
Find the absolute error and range of absolute error.
(b)
Answer to Problem 38PPS
Absolute error and range are:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
You measured a length of 12.8 am. Compute the absolute error and then write the range of possible measures.
Concept Used:
The absolute error of a measurement is equal to one half of the unit of measure
Measurement of length is 12.8.
Absolute error:
Range:
Calculation:
Thus, absolute error and range are:
(c)
Find what precision you would have to measure a length in cm to have an absolute error of less than 0.05 cm.
(c)
Answer to Problem 38PPS
To the nearest hundredth place
Explanation of Solution
Given:
To what precision would you have to measure a length in cm to have an absolute error of less than 0.05 cm?
Concept Used:
The absolute error of a measurement is equal to one half of the unit of measure
If the absolute error of loss is 0.05 cm, then the error is to the nearest hundredth place.
Calculation:
Thus, to the nearest hundredth place
(d)
Find the relative error of the volume of the box.
(d)
Answer to Problem 38PPS
The relative errors:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
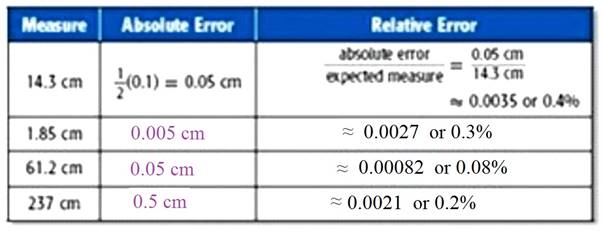
To find the relative error of an area or volume calculation, add the relative errors of each linear measure. If the measures of the sides of a rectangular box are 6.5 cm, 7.2 cm and 10.25 cm, what is the relative error of the volume of the box?
Concept Used:
The absolute error of a measurement is equal to one half of the unit of measure and the relative error is of a measure is the ratio of the absolute error to the expected measure.
Calculation:
| Measure | Absolute error | Relative error |
| 6.5 cm | 0.05 cm | |
| 7.2 cm | 0.05 cm | |
| 10.25cm | 0.005 cm |
Add the relative errors:
Thus, the relative errors:
Chapter 5 Solutions
Algebra 1
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (2nd Edition)
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Using and Understanding Mathematics: A Quantitative Reasoning Approach (6th Edition)
- 1. vector projection. Assume, ER1001 and you know the following: ||||=4, 7=-0.5.7. For each of the following, explicitly compute the value. འབ (a) (b) (c) (d) answer. Explicitly compute ||y7||. Explain your answer. Explicitly compute the cosine similarity of and y. Explain your Explicitly compute (x, y). Explain your answer. Find the projection of onto y and the projection of onto .arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions using vectors u and v. --0-0-0 = find the the cosine similarity and the angle between u and v. འརྒྱ (a) (b) find the scalar projection of u onto v. (c) find the projection of u onto v. (d) (e) (f) find the scalar projection of onto u. find the projection of u onto u. find the projection of u onto and the projection of onto . (Hint: find the inner product and verify the orthogonality)arrow_forwardPlease type out answerarrow_forward
- The function f(x) = log x is transformed to produce g(x) = log (x) – 3. Identify the type of transformation and describe the change. Please type out answerarrow_forwardEach graph below is the graph of a system of three linear equations in three unknowns of the form Ax = b. Determine whether each system has a solution and, if it does, the number of free variables. A. O free variables ✓ B. no solution C. no solution D. no solution E. 1 free variable F. 1 free variablearrow_forwardSolve the following systems of equations and show all work.y = x2 + 3y = x + 5 Please type out answerarrow_forward
- Solve the following system of equations. Show all work and solutions.y = 2x2 + 6x + 1y = −4x2 + 1 Please type out answerarrow_forwardDalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work. Dear Student If You Face any issue let me know i will solve your all doubt. I will provide solution again in more detail systematic and organized way. I would also like my last 3 questions credited to mearrow_forwardDalia buys 20 collectible gems per month. Grace sells 10 gems from her collection of 120 each month. When will Dalia have more gems than Grace? Show your work.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





