
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation : The volume of water in each beaker with the proper number of significant figures needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction : A number can be changed to given significant figure either by round off or by addition of zero. The rules for significant figures are:
- Non-zero digits are always significant.
- Any zeros between two significant digits are always significant.
- A final zero in the decimal portion is also significant.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9STP
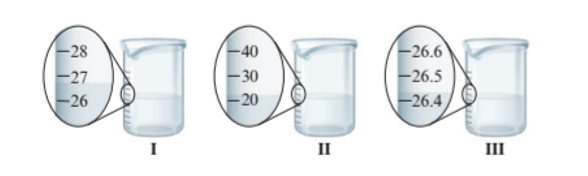
Beaker I = 27.0 mL
Beaker II = 20.0 mL
Beaker III = 26.4 mL
Explanation of Solution
Each beaker has its marking of volume. The beaker I and II have the difference of 1 unit of volume whereas beaker III has more precise value of volume as it has difference of 0.1 unit of volume. Thus, the volume of water in each beaker is:
- Beaker I = 27.0 mL
- Beaker II = 20.0 mL
- Beaker III = 26.4 mL
(b)
Interpretation : The digits in each measurement from part A needs to be identified as certain and uncertain.
Concept Introduction : A number can be changed to given significant figure either by round off or by addition of zero. The rules for significant figures are:
- Non-zero digits are always significant.
- Any zeros between two significant digits are always significant.
- A final zero in the decimal portion is also significant.
(b)
Answer to Problem 9STP
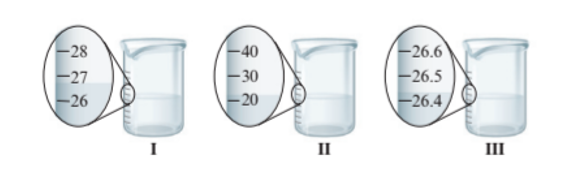
Beaker I = Uncertain
Beaker II = Uncertain
Beaker III = Certain
Explanation of Solution
The beaker I and II have the difference of 1 unit of volume whereas beaker III has more precise value of volume as it has difference of 0.1 unit of volume. Since beaker III has more precise volume so it has certain value of volume whereas beaker I and II has uncertain value of volume.
(c)
Interpretation : The total volume of water if all the three beakers pour in one container needs to be determined with correct number of significant figures.
Concept Introduction : A number can be changed to given significant figure either by round off or by addition of zero. The rules for significant figures are:
- Non-zero digits are always significant.
- Any zeros between two significant digits are always significant.
- A final zero in the decimal portion is also significant.
(c)
Answer to Problem 9STP
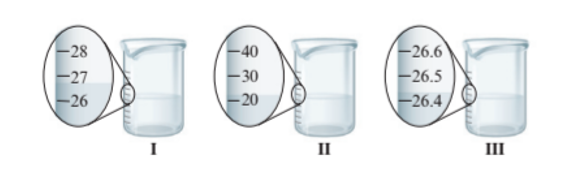
The total volume must be 27.0 +20.0 + 26.4 = 73.4 mL
Explanation of Solution
The beaker I and II have the difference of 1 unit of volume whereas beaker III has more precise value of volume as it has difference of 0.1 unit of volume. The volume of water in each beaker is:
- Beaker I = 27.0 mL
- Beaker II = 20.0 mL
- Beaker III = 26.4 mL
Thus, the total volume must be 27.0 +20.0 + 26.4 = 73.4 mL
Chapter 5 Solutions
World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
- These are in the wrong boxes. Why does the one on the left have a lower molar mass than the one on the right?arrow_forwardSYNTHESIS REACTIONS. For the following reactions, synthesize the given products from the given reactants. Multiple reactions/steps will be needed. For the one of the steps (ie reactions) in each synthesis, write out the mechanism for that reaction and draw an energy diagram showing the correct number of hills and valleys for that step's mechanism. CI b. a. Use acetylene (ethyne) and any alkyl halide as your starting materials Br C. d. "OH OH III. OHarrow_forwardCalculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.200 M HClarrow_forward
- Calculate the pH and the pOH of each of the following solutions at 25 °C for which the substances ionize completely: (a) 0.000259 M HClO4arrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forward
- A. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





