
A manager is trying to decide whether to purchase a certain part or to have it produced internally. Internal production could use either of two processes. One would entail a variable cost of $17 per unit and an annual fixed cost of $200,000; the other would entail a variable cost of $14 per unit and an annual fixed cost of $240,000. Three vendors are willing to provide the part. Vendor A has a price of $20 per unit for any volune up to 30,000 units. Vendor B has a price of $22 per unit for demand of 1,000 units or less, and $18 per unit for larger quantities. Vendor C offers a price of $21 per unit for the first 1,000 units, and $19 per unit for additional units.
a)
To determine: The best alternative from a cost standpoint for an annual volume of 10,000 units and 20,000 units.
Introduction: Decision-making is the process that helps to make decision. It is the process of choosing a best alternative by evaluating many alternatives.
Answer to Problem 8P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A manager has to decide whether to purchase a product or produce it internally. Internal production consists of two processes. Variable cost and fixed cost of the first process is $17 and $200,000 respectively. Variable cost and fixed cost of the second process is $14 and $240,000 respectively.
There are three vendors available to purchase a product. Vendor A has a price of $20 per unit up to 30,000 units. Vendor B has a price of $22 per unit if the demand is 1,000 units or less and $18 for larger volumes. Vendor C has a price of $21 per unit for first 1,000 units and $19 per unit for additional units.
Determine the best alternative from a cost standpoint for an annual volume of 10,000 units:
Calculate the total cost for the first internal process:
It is calculated by adding the fixed cost with the value attained by multiplying the variable cost and the annual volume. Annual volume is given as 10,000 units. Hence, the total cost for the first internal process is $370,000.
Calculate the total cost for the second internal process:
It is calculated by adding the fixed cost with the value attained by multiplying the variable cost and the annual volume. Annual volume is given as 10,000 units. Hence, the total cost for the first internal process is $380,000.
Calculate the total cost for the Vendor A:
It is calculated by multiplying the price and the annual volume. Hence, the total cost for Vendor A is $200,000.
Calculate the total cost for the Vendor B:
It is calculated by multiplying the price and the annual volume. It is given that the price is $22 if the volume is less than 1,000 and $18 if the volume is larger. As the annual volume is more than 1,000, the price is $18. Hence, the total cost for Vendor B is $180,000.
Calculate the total cost for the Vendor C:
It is calculated by multiplying the price and the annual volume. It is given that the price is $21 for the volume up to 1,000 and $19 for the additional volume. Thus, price is $21 for the 1,000 units and $19 for additional 9,000 units. Hence, the total cost for Vendor C is $192,000.
At the annual volume of 10,000 units, Vendor B has the lowest total cost of ($180,000). Hence, it should be chosen from a cost standpoint.
Determine the best alternative from a cost standpoint for an annual volume of 20,000 units:
Calculate the total cost for the first internal process:
It is calculated by adding the fixed cost with the value attained by multiplying the variable cost and the annual volume. Annual volume is given as 20,000 units. Hence, the total cost for the first internal process is $540,000.
Calculate the total cost for the second internal process:
It is calculated by adding the fixed cost with the value attained by multiplying the variable cost and the annual volume. Annual volume is given as 20,000 units. Hence, the total cost for the first internal process is $520,000.
Calculate the total cost for the Vendor A:
It is calculated by multiplying the price and the annual volume. Hence, the total cost for Vendor A is $400,000.
Calculate the total cost for the Vendor B:
It is calculated by multiplying the price and the annual volume. It is given that the price is $22 if the volume is less than 1,000 and $18 if the volume is larger. As the annual volume is more than 1,000, the price is $18. Hence, the total cost for Vendor B is $360,000.
Calculate the total cost for the Vendor C:
It is calculated by multiplying the price and the annual volume. It is given that the price is $21 for the volume up to 1,000 and $19 for the additional volume. Thus, price is $21 for the 1,000 units and $19 for additional 19,000 units. Hence, the total cost for Vendor C is $382,000.
At the annual volume of 20,000 units, Vendor B has the lowest total cost of ($360,000). Hence, it should be chosen from a cost standpoint.
b)
To determine: The range of the best alternative.
Introduction:Decision-making is the process that helps to make decision. It is the process of choosing a best alternative by evaluating many alternatives.
Answer to Problem 8P
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
A manager has to decide whether to purchase a product or produce it internally. Internal production consists of two processes. Variable cost and fixed cost of the first process is $17 and $200,000 respectively. Variable cost and fixed cost of the second process is $14 and $240,000 respectively.
There are three vendors available to purchase a product. Vendor A has a price of $20 per unit up to 30,000 units. Vendor B has a price of $22 per unit if the demand is 1,000 units or less and $18 for larger volumes. Vendor C has a price of $21 per unit for first 1,000 units and $19 per unit for additional units.
Cost function for each alternative if the annual volume is 1-1,000 units:
First internal process:
Second internal process:
Vendor A:
Vendor B:
Vendor C:
When considering the cost functions, Vendor A would exhibit less cost when compare to Vendor B and Vendor C. Vendor A should be preferred over other alternatives. The graph is as follows:

Cost function for each alternative if the annual volume is more than 1,000 units:
First internal process:
Second internal process:
Vendor A:
Vendor B:
Vendor C:
When considering the cost functions, Vendor B would dominate Vendor A and Vendor C. Hence, Vendor A and Vendor C should be eliminated. The graph considering two internal processes and Vendor B is as follows:
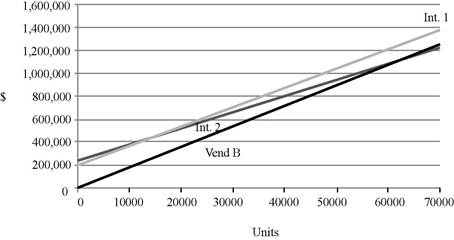
Determine the value of Q by equaling two cost equations:
Equal the cost function of second internal process and Vendor B to determine the value of Q.
Calculate the total cost of first internal process:
Substitute the value Q in the cost equation of first internal process. Hence, the total cost is $1,220,000.
Calculate the total cost of second internal process:
Substitute the value Q in the cost equation of second internal process. Hence, the total cost is $1,080,000.
Calculate the total cost of Vendor A:
Substitute the value Q in the cost equation of Vendor A. Hence, the total cost is $1,200,000.
Calculate the total cost of Vendor B:
Substitute the value Q in the cost equation of Vendor B. Hence, the total cost is $1,080,000.
Calculate the total cost of Vendor C:
Substitute the value Q in the cost equation of Vendor C. Hence, the total cost is $1,142,000.
Inference:
- Vendor A should be preferred when the purchasing quantity ranges from 1 to 1,000 units.
- Vendor B should be preferred when the purchasing quantity ranges from 1,001 to 59,999 units.
- There would indifferent between Vendor B and second internal process if the quantity is 60,000 units.
- Second internal process should be preferred if the quantity is more than 60,000 units.
First internal process and Vendor C are never best.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Operations Management
- PepsiCo South Africa says the incident where a woman discovered part of a rodent in her loaf of bread, is anisolated occurrence.Durban woman, Nombulelo Mkumla, took to social media last week to share how she discovered the rodent.In a lengthy Facebook post, she said she purchased the loaf of bread from a local shop after work on August 27.For the next days, Mkumla proceeded to use slices of bread from the load to make toast."Then, on the morning of August 31, I took the bread out of the fridge to make toast and noticed something disgusting andscary. I took a picture and sent it to my friends, and one of them said, 'Yi mpuku leyo tshomi' [That's a rat friend]“."I was in denial and suggested it might be something else, but the rat scenario made sense - it's possible the rat got into thebread at the factory, and no one noticed," Mkumla said.She went back to the shop she'd bought the bread from and was told to lay a complaint directly with the supplier.She sent an email with a video and…arrow_forwardThe deaths are included in the discharges; this includes deaths occurring in less than 48 hours and postoperative deaths. Rehabilitation had 362 discharges, 22 deaths, 1<48 hours, 0 Postoperative. what is the gross death rate for the rehabilitation service?arrow_forwardA copy machine is available 24 hours a day. On a typical day, the machine produces 100 jobs. Each job takes about 3 minutes on the machine, 2 minutes of which is processing time and 1 minute is setup time (logging in, defining the job). About 20 percent of the jobs need to be reworked, in which case the setup time and the processing time have to be repeated. The remainder of the time, the equipment is idle. What is the OEE of the equipment?arrow_forward
- How do you think we can keep updating Toyota's ideas as new technologies come out and what customers want keeps changing?arrow_forwardGiven how TPS has helped change things in so many fields, do you think there are parts of it that might be hard to use in areas that aren’t about making things, like in healthcare or services? If so, why do you think that might be?arrow_forwardDo you feel there is anything positive about rework?arrow_forward
- Do you think technology can achieve faster setup times? How would it be implemented in the hospital workforce?arrow_forwardIn your experience or opinion, do you think process changes like organizing workspaces make a bigger difference, or is investing in technology usually the better solution for faster setups?arrow_forwardHave you seen rework done in your business, and what was done to prevent that from occurring again?arrow_forward
- Research a company different than case studies examined and search the internet and find an example of a business that had to rework a process. How was the organization affected to rework a process in order to restore a good flow unit? Did rework hurt a process or improve the organization's operational efficiency? • Note: Include a reference with supportive citations in the discussion reply in your post.arrow_forwardSetup time is very important in affecting a process and the capacity of a process. How do you reduce setup time? Give examples of reducing setup time. Please Provide a referenecearrow_forwardDo you think TPS was successful? If so, how? Are there other companies that have used TPS? If so, give examples. Please provide a referencearrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning




