
Concept explainers
The range of the values of the mass m2 so that the two connected blocks resting on two inclined planes are in equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 83QAP
The mass m2 can have values between 3.51 kg and 52.64 kg for the system of masses to be in equilibrium.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Formula used:
From the diagram given, if the value of m2 falls below a certain value, it would slide up the plane and the block of mass m1 would slide down. This gives the value of the minimum mass of m2.
If the value of m2 increases beyond a certain value, the block would slide down the plane and the block of mass m1 would slide up.
By drawing the free body diagrams for each case, and applying the force equations for each case, the range of the values of m2 can be determined.
Explanation and Calculation:
Case 1:
Consider the case when the block 1slides down the plane and the block 2 slides up the plane.
The free body diagram for m1 is shown below:
The block rests on an incline which makes an angle
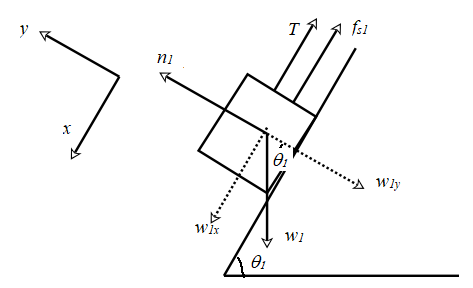
The weight
Resolve the weight w1 into components along the +x and −y directions as shown. The magnitudes of the components are given by,
Write the force equation along the +y direction.
Since the block is in equilibrium,
Therefore,
The force of friction is given by,
The system is in equilibrium along the x direction too. Therefore,
Using equations (1) and (2), in the above equation,
In a similar manner, construct a free body diagram for the block 2.
The block rests on an incline which makes an angle
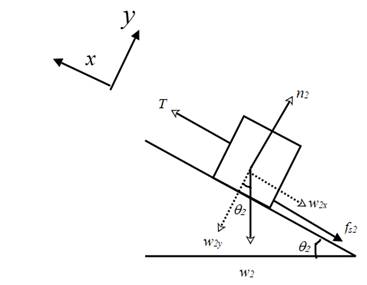
The weight
Resolve the weight w2 into components along the −x and −y directions as shown. The magnitudes of the components are given by,
Write the force equation along the +y direction and apply the condition for equilibrium.
Therefore,
The force of friction is given by,
The system is in equilibrium along the x direction too. Therefore,
Using equations (4) and (6), in the above equation,
Add equations (3) and (7) and write an expression for m2.
Substitute the known values of the variables in the expression and calculate the value of m2.
The minimum value of m2 for which the system is in equilibrium is 3.51 kg.
Case 2:
Consider the case when the block 1slides up the plane and the block 2 slides down the plane.
The free body diagram for m1 is shown below:
Assume the +x direction up the incline and the +y direction perpendicular to the plane. The weight
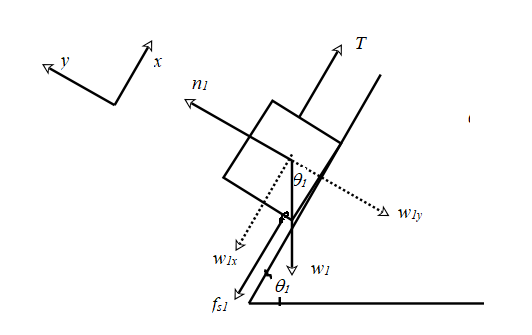
The equations (1) and (2) are applied to this free body diagram too.
Write the condition for equilibrium along the x direction.
Use equations (1) and (2) in the expression.
In a similar manner, construct a free body diagram for the block 2.
. Assume a coordinate system which has the +x direction pointing down the plane and the +y direction perpendicular to the plane away from it. The weight
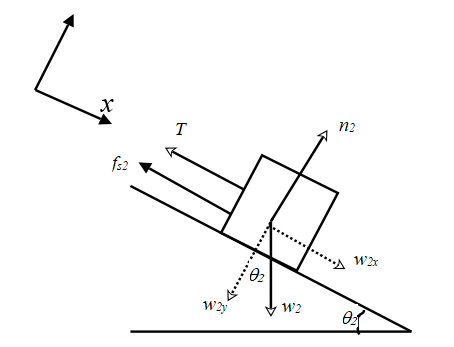
The equations (4), (5) and (6) are valid for this case too.
Write the equation for equilibrium along the x direction.
Using equations (4) and (6) in the expression,
Add equations (8) and (9) and write an expression for m2.
Substitute the known values of the variables in the expression.
The maximum value of m2 for the system to be in equilibrium is 52.64 kg.
Conclusion:
Thus, the mass m2 can have values between 3.51 kg and 52.64 kg for the system of masses to be in equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS,VOLUME 1
- A circular loop of wire with radius 0.0480 m and resistance 0.163 Ω is in a region of spatially uniform magnetic field, as shown in the following figure (Figure 1). The magnetic field is directed out of the plane of the figure. The magnetic field has an initial value of 7.88 T and is decreasing at a rate of -0.696 T/s . Is the induced current in the loop clockwise or counterclockwise? What is the rate at which electrical energy is being dissipated by the resistance of the loop? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA 0.333 m long metal bar is pulled to the left by an applied force F and moves to the left at a constant speed of 5.90 m/s. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 46.7 Ω resistor, as shown in (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. You can ignore the resistance of the bar and rails. The circuit is in a uniform 0.625 T magnetic field that is directed out of the plane of the figure. Is the induced current in the circuit clockwise or counterclockwise? What is the rate at which the applied force is doing work on the bar? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardA 0.850-m-long metal bar is pulled to the right at a steady 5.0 m/s perpendicular to a uniform, 0.650-T magnetic field. The bar rides on parallel metal rails connected through a 25-Ω, resistor (Figure 1), so the apparatus makes a complete circuit. Ignore the resistance of the bar and the rails. Calculate the magnitude of the emf induced in the circuit. Find the direction of the current induced in the circuit. Calculate the current through the resistor.arrow_forward
- In the figure, a conducting rod with length L = 29.0 cm moves in a magnetic field B→ of magnitude 0.510 T directed into the plane of the figure. The rod moves with speed v = 5.00 m/s in the direction shown. When the charges in the rod are in equilibrium, which point, a or b, has an excess of positive charge and where does the electric field point? What is the magnitude E of the electric field within the rod, the potential difference between the ends of the rod, and the magnitude E of the motional emf induced in the rod? Which point has a higher potential? Please explain all stepsarrow_forwardExamine the data and % error values in Data Table 2 where the mass of the pendulum bob increased but the angular displacement and length of the simple pendulum remained constant. Describe whether or not your data shows that the period of the pendulum depends on the mass of the pendulum bob, to within a reasonable percent error.arrow_forwardPlease graph, my software isn't working - Data Table 4 of Period, T vs √L . (Note: variables are identified for graphing as y vs x.) On the graph insert a best fit line or curve and display the equation on the graph. Thank you!arrow_forward
- I need help with problems 93 and 94arrow_forwardSince the instruction says to use SI units with the correct sig-fig, should I only have 2 s for each trial in the Period column? Determine the theoretical period of the pendulum using the equation T= 2π √L/g using the pendulum length, L, from Data Table 2. Calculate the % error in the periods measured for each trial in Data Table 2 then recordarrow_forwardA radiography contingent are carrying out industrial radiography. A worker accidentally crossed a barrier exposing themselves for 15 seconds at a distance of 2 metres from an Ir-192 source of approximately 200 Bq worth of activity. What dose would they have received during the time they were exposed?arrow_forward
- In the following figure the circuit to the left has a switch thatat t = 0 s is switched and disconnects the battery from the circuit. The state depicted on thefigure is right after the switch, still t = 0. As the current decreases over time, the magneticflux through the circuit on the right (due to the long cable of the circuit on the left) changesand induces an EMF on the right circuit. How much power is consumed by R2 as a functionof time.The distance between the wire on the left and the closest wire on the right is r = 2.0 cm.The size of the circuit on the right is noted on the figure.arrow_forwardsingly A samply ionized helium atom is in the ground state. It absorbs energy and makes a transition to the n=7 excited state. The ion returns to wo the wavelength the ground state by emitting SIX photons ONLY. What is the of the second highest energy photon ?arrow_forwardAn electron, traveling at a speed of 5.60x10° m/s, strikes the target of an X-ray tube. Upon impart, the eletion decelerates to one-third of it's original speed, with an X-ray photon being emitted in the process. What is the wavelength of the photon? m.arrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





