
Concept explainers
(a)
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.100.
Answer to Problem 81QAP
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.100 is 8.12 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length of the ski slope
The angle made by the slope to the horizontal
Initial speed of the ski
Coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and snow
Formula used:
A free body diagram of the ski is drawn to analyze its motion.
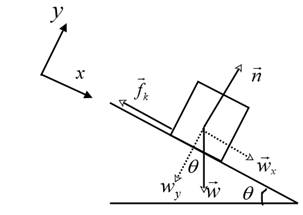
Assume a coordinate system, with the +x directed downwards along the incline and +y directed upwards, perpendicular to the incline. The weight
Resolve the weight
The ski is in equilibrium along the y direction.
Therefore,
Therefore, using equation (1),
The force of kinetic friction and the normal force are related according to the following equation:
From equation (2)
Write the force equation along the +x direction.
Use the values of wx and fk from equations (2) and (3) in the expression,
Simplify and write an expression for ax.
Use the following equation of motion to obtain the value of the time t.
Calculation:
Substitute the values of the variables in equation (4) and calculate the value of the acceleration.
Use the calculated value of ax and the values of v0 and
Solve the quadratic equation.
Taking the positive root,
Conclusion:
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.100 is 8.12 s.
(b)
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.150.
Answer to Problem 81QAP
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.150 is 8.39 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The length of the ski slope
The angle made by the slope to the horizontal
Initial speed of the ski
Coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and snow
Formula used:
The acceleration of the ski down the slope is given by
The time taken to reach the bottom of the slope is calculated using the expression,
Calculation:
Substitute the values of the variables in equation for acceleration and calculate the value of the acceleration.
Use the calculated value of ax and the values of v0 and
Solve the quadratic equation.
Taking the positive root,
Conclusion:
The time taken by the runaway ski to slide down a 250-m long slope when the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ski and the snow is 0.150 is 8.39 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS,VOLUME 1
- Rod AB is fixed to a smooth collar D, which slides freely along the vertical guide shown in (Figure 1). Point C is located just to the left of the concentrated load P = 70 lb. Suppose that w= 17 lb/ft. Follow the sign convention. Part A Figure 3 ft -1.5 ft √30° 1 of 1 Determine the normal force at point C. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Η vec Nc= Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the shear force at point C. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. VC= ΜΕ ΑΣΦΗ vec Submit Request Answer Part C Determine the moment at point C. Express your answer in pound-feet to three significant figures. Mc= Ο ΑΣΦ Η vec Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback ? ? lb lb ? lb-ftarrow_forwardConsider a uniformly charged ring of radius R with total charge Q, centered at the origin inthe xy-plane. Find the electric field (as a vector) at a point on the z-axis at a distance z above thecenter of the ring. Assume the charge density is constant along the ring.arrow_forward3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wx fuc, then use equation Vs VA + Ve/athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) 0.5 m B 1 m 60° A 45° vc = 3 m/sarrow_forward
- 3) If the slider block C is moving at 3m/s, determine the angular velocity of BC and the crank AB at the instant shown. (Use equation Vs Vc wxf, then use equation V, VA + Va/Athen write it in terms of w and the appropriate r equate the two and solve) f-3marrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- 14. A boy is out walking his dog. From his house, he walks 30 m North, then 23 m East, then 120 cm South, then 95 m West, and finally 10 m East. Draw a diagram showing the path that the boy walked, his total displacement, and then determine the magnitude and direction of his total displacement.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forward12. A motorboat traveling 6 m/s, West encounters a water current travelling 3.5 m/s, South. a) Draw a vector diagram showing the resultant velocity, then determine the resultant velocity of the motorboat. b) If the width of the river is 112 m wide, then how much time does it take for the boat to travel shore to shore? c) What distance downstream does the boat reach the opposite shore?arrow_forward
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





