
Concept explainers
(a)
If the crate resting on the bed of a decelerating truck would slide during the braking period.
Answer to Problem 77QAP
The crate will not slide, since the acceleration it experiences due to the truck's deceleration is less than the acceleration it experiences due to the force of static friction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of the crate
Initial velocity of the truck
Final velocity of the truck
Time during which the truck comes to a stop
Coefficient of static friction between the truck and the crate
Formula used:
To find if the crate would slide or not, a free body diagram is drawn for the crate and the force equations for equilibrium and for motion of the crate are determined.
The free body diagram for the crate is shown below:
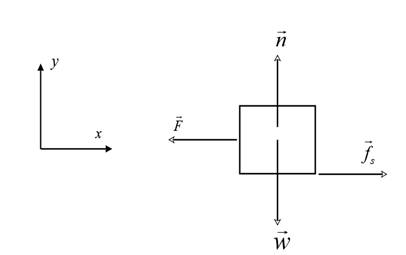
The weight of the block
The block is in equilibrium along the vertical ( y ) direction.
Therefore,
Since,
Therefore,
If
If the force of friction produces an acceleration,
Write an expression for the acceleration due to the force of friction using equations (1) and (2).
The expression for the acceleration produced by the truck is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration
Express the initial velocity of the crate in m/s.
Calculate the acceleration a experienced by the crate due to the truck's decoration by substituting the values of the variables in equation (4).
This acceleration acts along the −x direction.
The crate slides if a >af.
Conclusion:
It can be seen that the acceleration in the +x direction is 6.419 m/s2 and that along the −x direction is 1.158 m/s2. Since
(b)
The minimum stopping time for the truck, that prevents the crate from sliding.
Answer to Problem 77QAP
For the crate to not slide on the bed of the truck, the minimum stopping time of the truck is 2.16 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Acceleration produced by the
Initial velocity of the truck
Final velocity of the truck
Formula used:
The crate will just remain in equilibrium, if the acceleration acting on it along the −x direction due to the truck's deceleration is equal to the acceleration along the +x direction due to the force of friction.
Calculation:
Rewrite the expression for
Substitute the values of the variables in the equation and solve for
Conclusion:
Thus, for the crate to not slide on the bed of the truck, the minimum stopping time of the truck is 2.16 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS,VOLUME 1
- ) Graph the feasible region subject to the following constraints. x + y ≤ 6 y ≤ 2x x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 P + xarrow_forwardSolve the following system of equations: 50x+20y=1800 10x+3y=300arrow_forward> > > we are hiring Salesforce Admin Location: Remote Key Responsibilities: Administer Salesforce Sales & Revenue Cloud (CPQ & Billing) Configure workflows, validation rules & dashboards Automate processes using Flows & Process Builder Collaborate with Sales, Finance & Marketing teams Manage user roles & security Apply: Hr@forcecraver.comarrow_forward
- Answer this questionarrow_forward1. vector projection. Assume, ER1001 and you know the following: ||||=4, 7=-0.5.7. For each of the following, explicitly compute the value. འབ (a) (b) (c) (d) answer. Explicitly compute ||y7||. Explain your answer. Explicitly compute the cosine similarity of and y. Explain your Explicitly compute (x, y). Explain your answer. Find the projection of onto y and the projection of onto .arrow_forward2. Answer the following questions using vectors u and v. --0-0-0 = find the the cosine similarity and the angle between u and v. འརྒྱ (a) (b) find the scalar projection of u onto v. (c) find the projection of u onto v. (d) (e) (f) find the scalar projection of onto u. find the projection of u onto u. find the projection of u onto and the projection of onto . (Hint: find the inner product and verify the orthogonality)arrow_forward
- Using f(x) = log x, what is the x-intercept of g(x) = log (x + 4)? Explain your reasoning. Please type out answerarrow_forwardThe function f(x) = log x is transformed to produce g(x) = log (x) – 3. Identify the type of transformation and describe the change. Please type out answerarrow_forwardEach graph below is the graph of a system of three linear equations in three unknowns of the form Ax = b. Determine whether each system has a solution and, if it does, the number of free variables. A. O free variables ✓ B. no solution C. no solution D. no solution E. 1 free variable F. 1 free variablearrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





