
Concept explainers
(a)
The effect of weight of the book when reduce the applying force to the book in the same spot on the wall.
Answer to Problem 5QAP
The weight of the book is not changed.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The book is pressed against on the wall. When we reduce the applying force to the book, the book remains in the same spot on the wall.
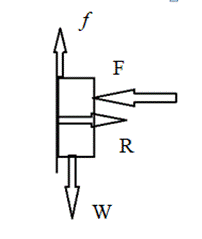
So the magnitude remains constant. Therefore weight stays the same.
Conclusion:
The weight stays the same.
(b)
The effect of the normal force of the wall on the book when reduce the applying force to the book in the same spot on the wall.
Answer to Problem 5QAP
The normal force of the wall on the book decreases.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The book is pressed against on the wall. When we reduce the applying force to the book, the book remains in the same spot on the wall.
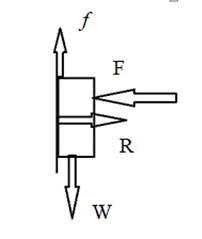
When applied force is reduced the normal force decreases.
Conclusion:
The normal force of the wall on the book decreases.
(c)
The effect of the frictional force of the wall on the book when reduce the applying force to the book in the same spot on the wall.
Answer to Problem 5QAP
The frictional force of the wall on the book is not changed.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The book is pressed against on the wall. When we reduce the applying force to the book, the book remains in the same spot on the wall.
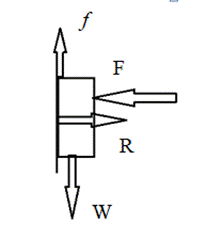
So the weight of the book is constant. Therefore the frictional force of the wall on the book stays same.
Conclusion:
The frictional force of the wall on the book stays same.
(d)
The effect of the maximum static frictional force of the wall on the book when reduce the applying force to the book in the same spot on the wall.
Answer to Problem 5QAP
The maximum static frictional force of the wall on the book deceases.
Explanation of Solution
Introduction:
The book is pressed against on the wall. When we reduce the applying force to the book, the book remains in the same spot on the wall.
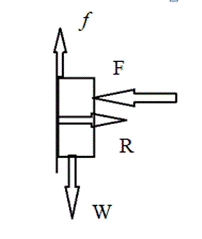
When F reduces R decreases. Since
Conclusion:
The maximum static frictional force of the wall on the book deceases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS,VOLUME 1
- The drawing shows a crystalline slab (refractive index 1.995) with a rectangular cross section. A ray of light strikes the slab at an incident angle of 01 = 35.0°, enters the slab, and travels to point P. This slab is surrounded by a fluid with a refractive index n. What is the maximum value of n such that total internal reflection occurs at point P? Ме Buarrow_forwardWhat is the amount of M112 needed to breach a 5-foot thick dense concrete wall utilizing an internal charge placed in the center of the target?arrow_forwardA small postage stamp is placed in front of a concave mirror (radius = 1.1 m), such that the image distance equals the object distance. (a) What is the object distance? (b) What is the magnification of the mirror (with the proper sign)?arrow_forward
- Calculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers. Record these values in Data Table 5. Ruler = 11.56 g, small washer = 1.85 g, large washer = 24.30 g. Calculate the % Difference in the Torques and record the values in Data Table 5. Is ΣAnticlockwise torque and Anticlockwise torque the same thing, are they solved in the same way?arrow_forwardA window washer stands on a uniform plank of mass M = 142 kg and length l = 2.80 m supported by 2 ropes attached at the ends of the plank. The window washer has a mass m = 68.0 kg. What is the tension in each of the ropes, T1 and T2, if the window washer's displacement from the center of mass of the plank is x = 0.930 m as shown in Figure 1: Window Washer Problem?arrow_forwardA man holds a double-sided spherical mirror so that he is looking directly into its convex surface, 33 cm from his face. The magnification of the image of his face is +0.17. What will be the image distance when he reverses the mirror (looking into its concave surface), maintaining the same distance between the mirror and his face? Be sure to include the algebraic sign (+ or -) with your answer.arrow_forward
- How do you draw a diagram of the ruler and mass system in equilibrium identifying the anti-clockwise torque and clockwise torque? How do I calculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers, does it come from the data in table 4? Please help, thank you!arrow_forwardExample Double pane windows have two panes of glass (n = 1.5), with a layer of air sandwiched between them. If light from outside enters the first pane at an angle of 25° from the surface normal, what angle does it enter the house at? ☑ 3 5arrow_forwardDid your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. What does this Σ mean? My results do not show they are equal to each other, what does this mean then, and what does the data show? Thanks!arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning





