
Concept explainers
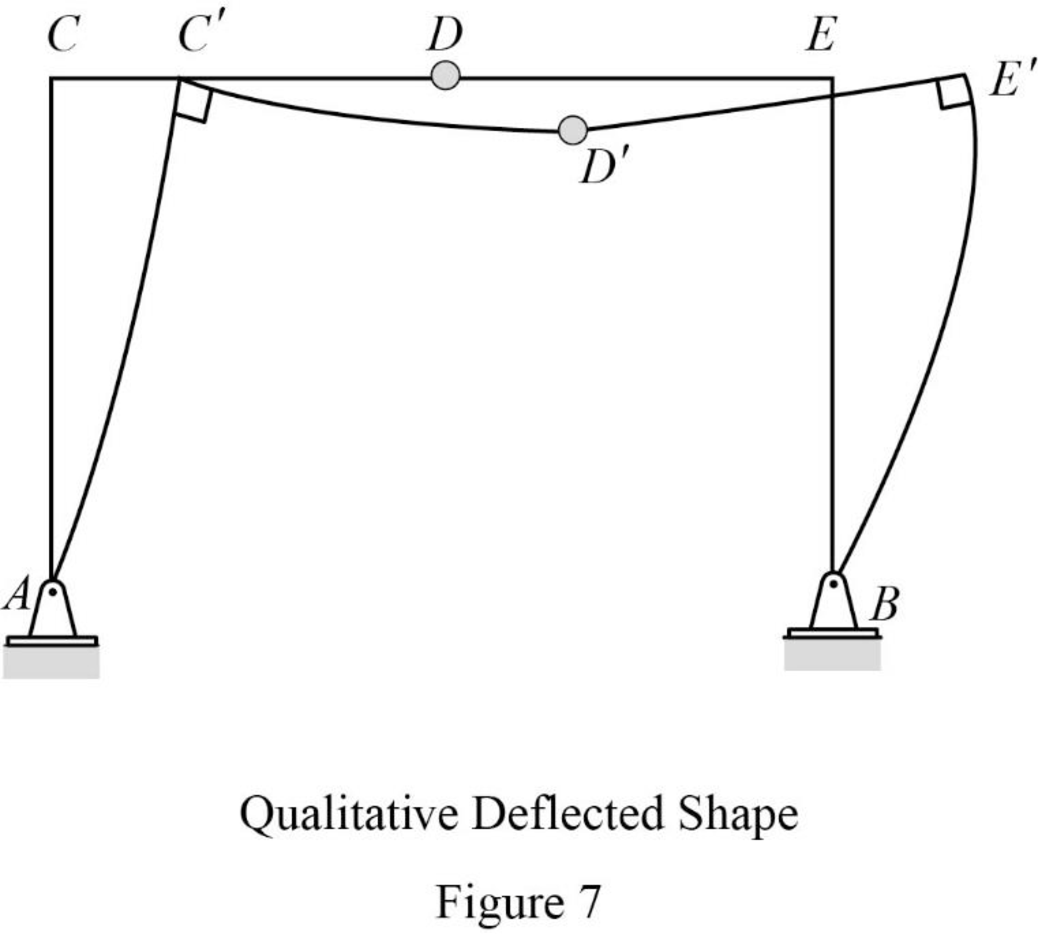
Plot the shear diagram, bending moment diagram, axial force diagram, and the qualitative deflected shape of the frame.
Explanation of Solution
Write the condition for static instability, determinacy and indeterminacy of plane frames as follows:
Here, number of members is m, number of external reactions is r, the number of joints is j, and the number of elastic hinges is
Find the degree of static indeterminacy (i) using the equation;
Refer to the Figure in the question;
The number of members (m) is 3.
The number of external reactions (r) is 4.
The number of joints (j) is 4.
The number of elastic hinges
Substitute the values in Equation (2);
Show the free-body diagram of the entire frame as in Figure 1.
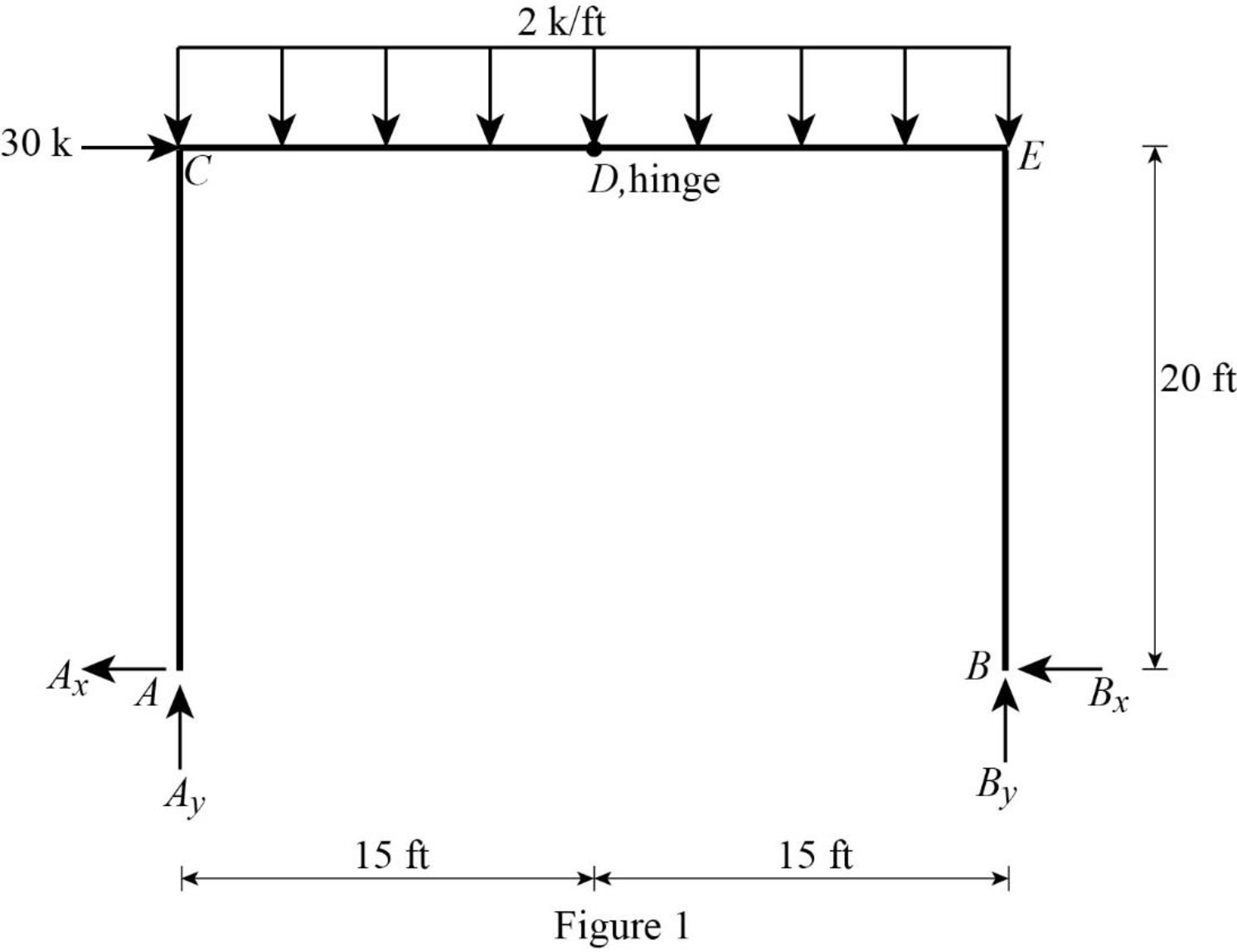
Refer Figure 1,
Consider entire frame.
Take moment about point A.
Find the vertical reaction at point A by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Find the horizontal reaction at point A by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the section DEB.
Find the horizontal reaction at point B by taking moment about the hinge at D.
Substitute 26.25 k for
Show the free-body diagram of the members and joints of the entire frame as in Figure 2.
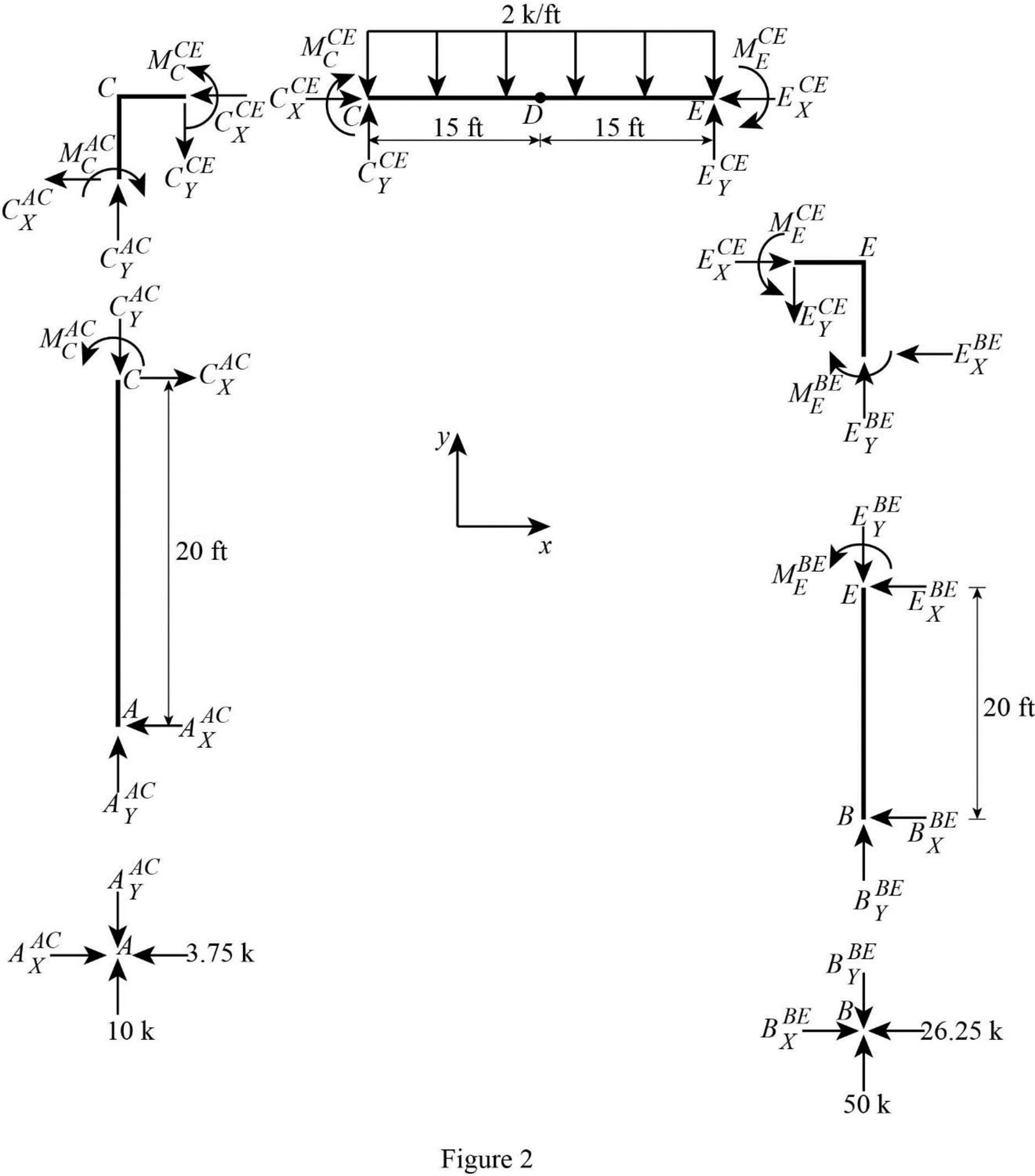
Consider point A:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the member AC:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point C.
Consider the point C:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point C.
Consider the member CDE:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point E.
Consider the point E:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point E.
Consider the point B:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Plot the moment end forces of the frame as in Figure 3.
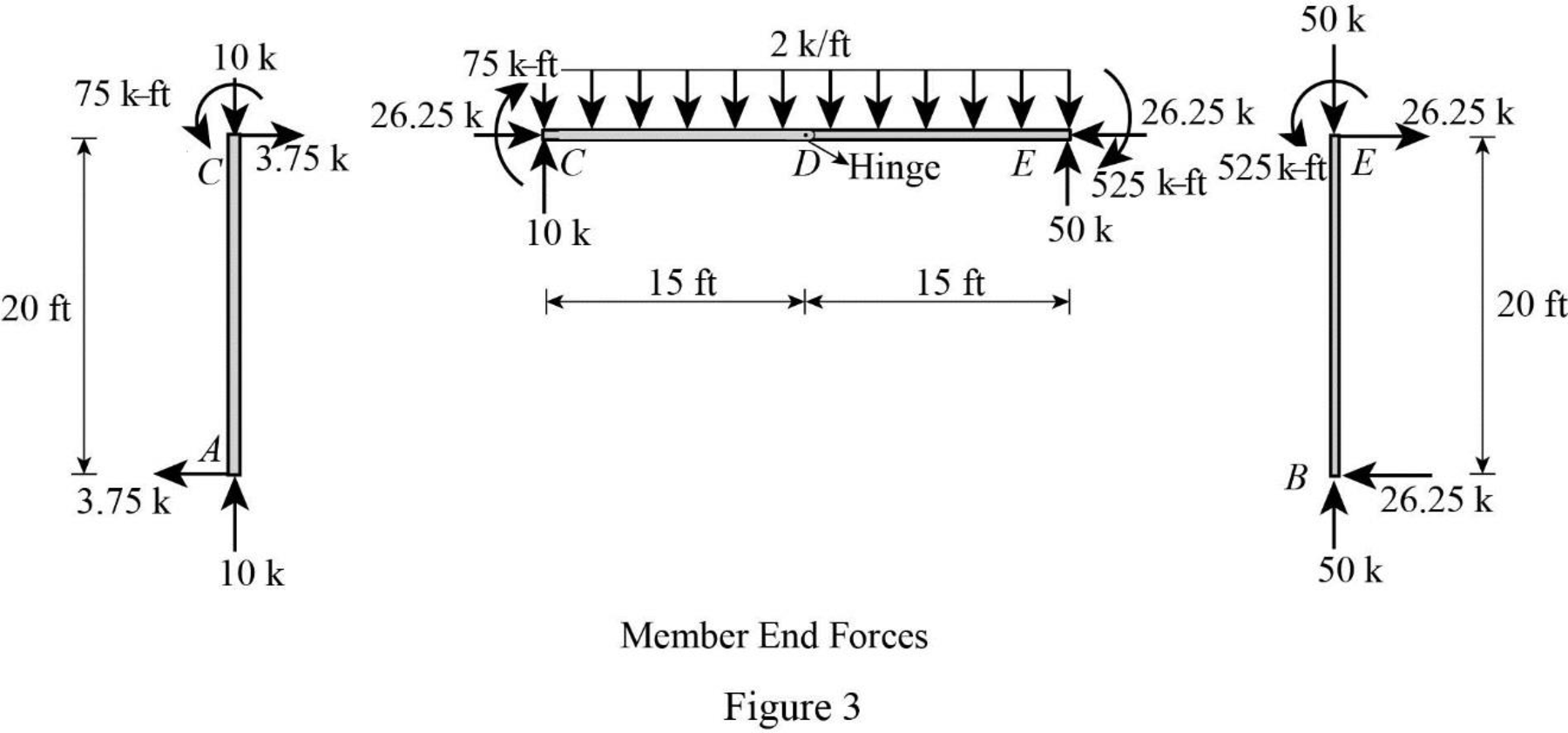
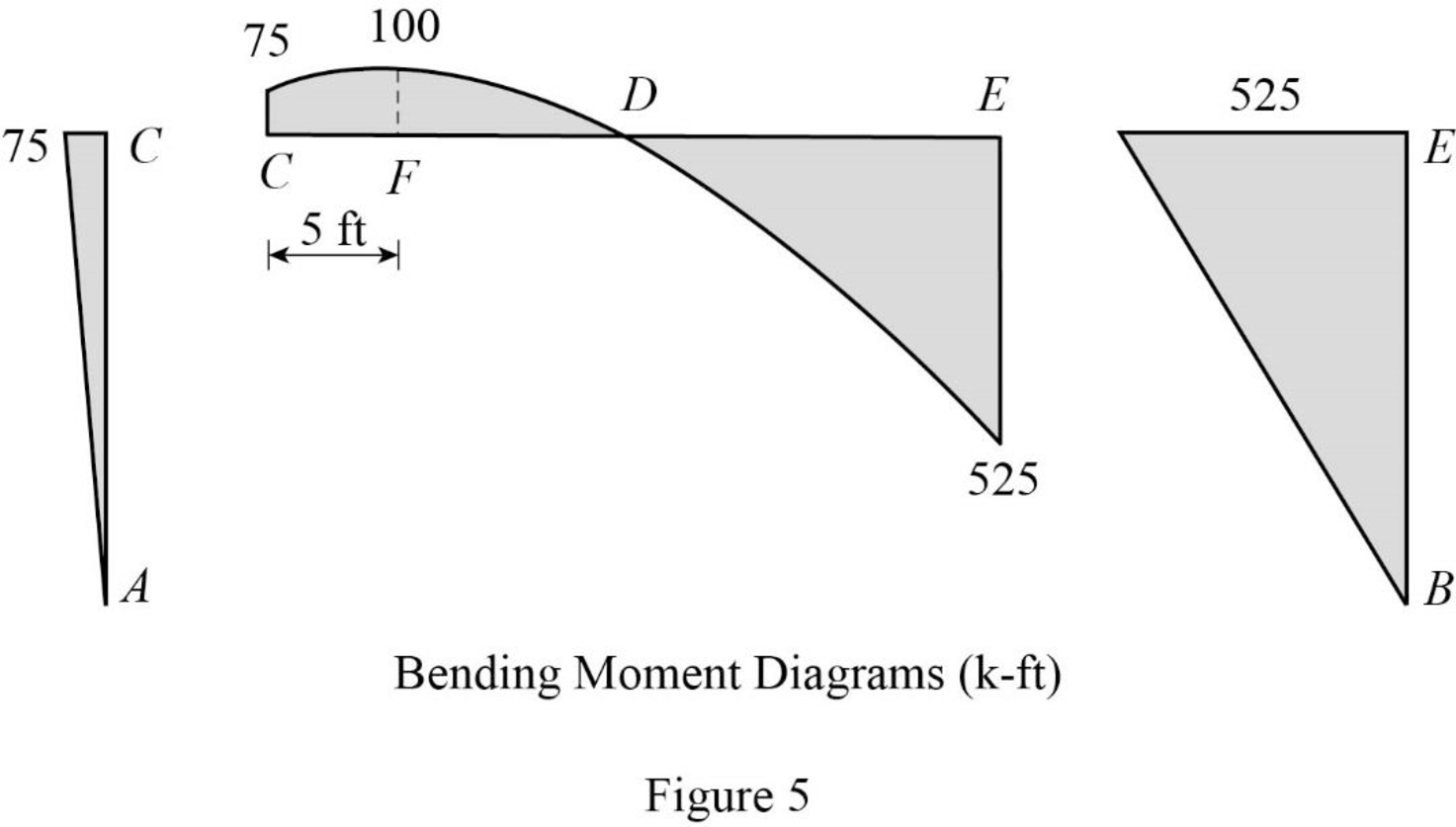
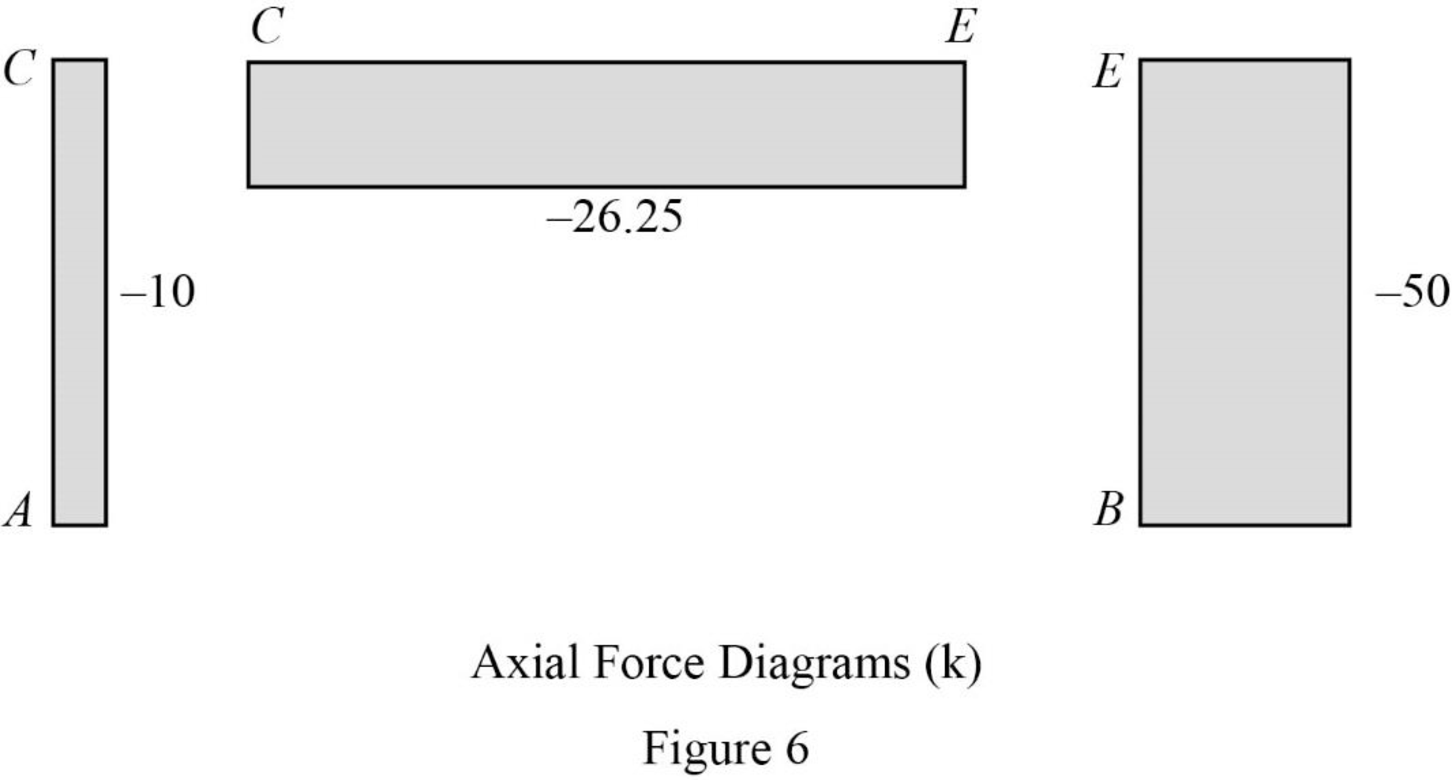
Refer to the moment end force diagram plot the shear diagram, bending moment diagram, and the axial force diagrams.
Plot the shear force diagram as in Figure 4.
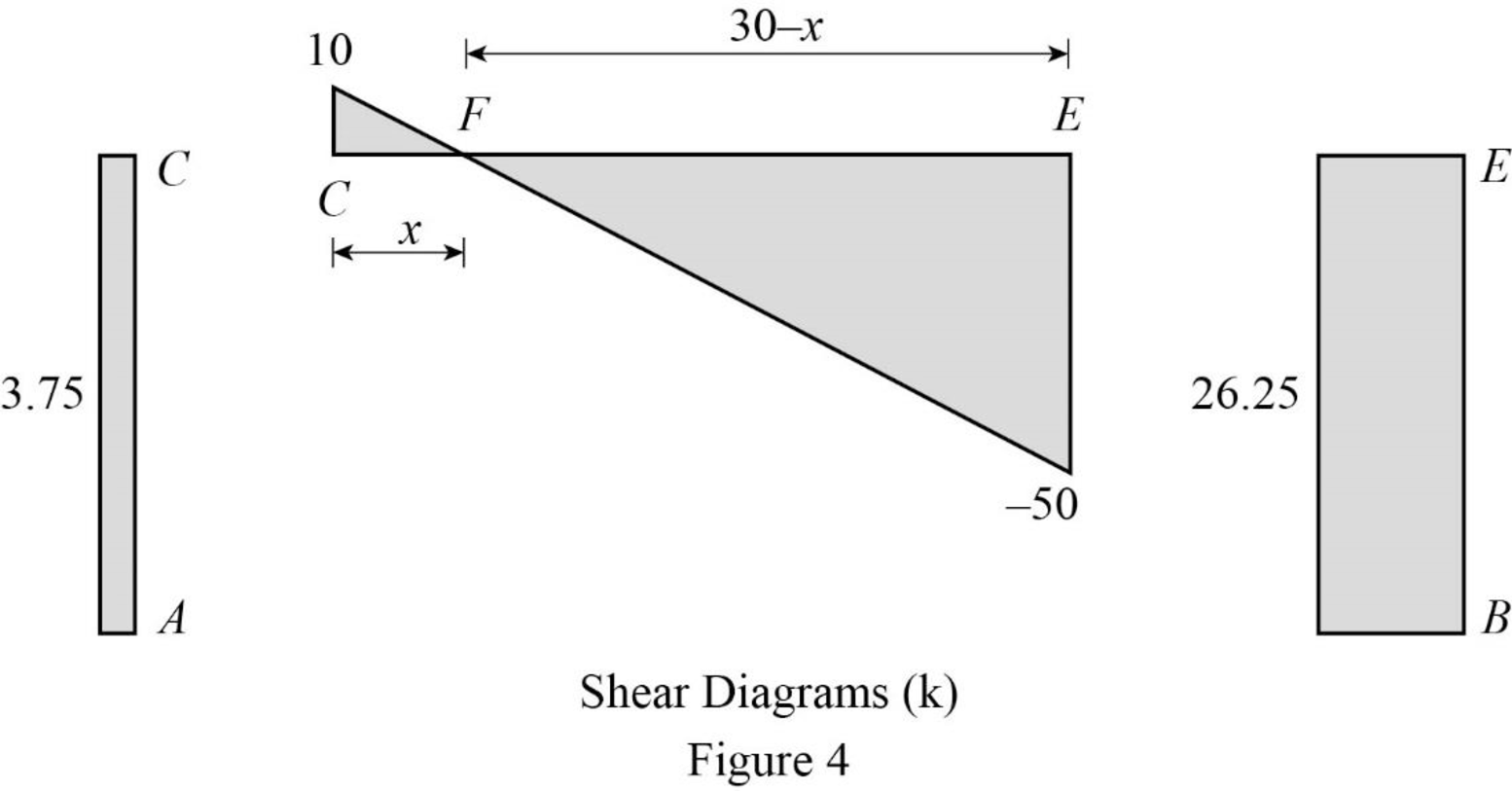
Refer to the shear force diagram, the maximum bending moment occurs at point F where the shear force changes sign.
Use similar triangle concept for the region CE:
Plot the bending moment diagram as in Figure 5.
Plot the axial force diagram as in Figure 6.
Plot the qualitative deflected shape as in Figure 7.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Structural Analysis
- solve pleasearrow_forwardA mechanism for pushing small boxes from an assembly line onto a conveyor belt is shown with arm OD and crank CB in their vertical positions. For the configuration shown, crank CB has a constant clockwise angular velocity of 0.6π rad/s. Determine the acceleration QE of E (positive if to the right, negative if down). 450 mm 215 mm 565 mm A 185 mm 105 mm 110185. mm mm Answer: a = i B 40 mm E m/s²arrow_forwardPlease answer the following questions in the picture, use the second picture to answer some of the questions. I appreciate your help! Explain step by step, thank you!arrow_forward
- Question 5. Three pipes A, B, and C are interconnected as in Fig. 2. The pipe characteristics are given below. Find the rate at which water will flow in each pipe. Find also the pressure at point P. (Neglect minor losses) Pipe D (in) L (ft) f A 6 2000 0.020 B 4 1600 0.032 C 8 3000 0.02 -El. 200 ft P -El. 120 ft B Fig. 2 -El. 50 ft.arrow_forwardcalculate all nodal displacementts and all the member forces of the trussarrow_forwardNOTE: Use areal methods only for V,M,N diagrams(Do NOT use the equations) (also draw the N diagram(s) for the entire structure)arrow_forward
- The figure below shows a foundation of 10 ft x 6.25 ft resting on a sand deposit. The net load per unit area at the level of the foundation, qo, is 2100 lb/ft². For the sand, μs = 0.3, E, = 3200 lb/in.², Dƒ = 2.5 ft, and H = 32 ft. Foundation BX L Rigid foundation settlement Flexible foundation settlement H μ, Poisson's ratio E, = Modulus of elasticity Soil Rock Elastic settlement of flexible and rigid foundations Table 1 Variation of F₁ with m' and n' m' n' 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0 2.5 3.0 0.25 0.014 0.013 0.012 0.011 0.011 0.011 0.010 0.010 0.50 0.049 0.046 0.044 0.042 0.041 0.040 0.038 0.038 1.00 0.142 0.138 0.134 0.130 0.127 0.125 0.121 0.118 2.00 0.285 0.290 0.292 0.292 0.291 0.289 0.284 0.279 5.00 0.437 0.465 0.487 0.503 0.516 0.526 0.543 0.551 10.00 0.498 0.537 0.570 0.597 0.621 0.641 0.679 0.707 20.00 0.529 0.575 0.614 0.647 0.677 0.702 0.756 0.797 50.00 0.548 0.598 0.640 0.678 0.711 0.740 0.803 0.853 100.00 0.555 0.605 0.649 0.688 0.722 0.753 0.819 0.872 Table 2 Variation of F2…arrow_forward= == An 8 m high retaining wall supports a 5.5 m deep sand (Ya 18.5 kN/m³, q = 34°) overlying a saturated sandy clay (y_sat = 20.3 kN/m³, q = 28°, c = 17 kPa). The groundwater level is located at the interface of two layers. Sketch the lateral stress distribution up to a depth of 8 m for an active condition. Also, determine the line of action of the resultant. 5.5 m Sand |Y=18.5 kN/m³ |₁ =34° Sandy : clay 2.5 m |c=17 kPa Ysat 20.3 kN/m³ 2=28°arrow_forward3. What is the maximum allowable load that can be applied to the pile shown below? : Qall = ? G.W.T. 45' Soft Clay: Ysat 100 pcf Cu = 500 psf, ou = 0° Clay Shale: Qu(lab) 24,000 psi o' = 15° Driven Steel H-Pile: 1/2" thick steel web & flanges (soil plugged) -10". I Note: Pile & soil profile are not drawn to scale Please use the approach outlined in Das 12.16 and an Allowable Stress Design (ASD) approach for your analysis. Use a factor of safety = 3 for design, neglect any effect that shaft resistance has on pile capacity, and neglect the effect of the weight of the pile in your analysis.arrow_forward
- 2. Calculate the ultimate load carrying capacity of the pile tip driven into the soil profile shown below: G.W.T. Qapp 40' Soft Clay: Ysat 100 pcf Cu 500 psf, ₁ = 0° 4c+4 Poorly Graded Sand (SP): Ysat = 125 pcf Q₁ = ? c' = 0, ' = 35° Driven Steel Pipe Pile: Outside Diameter = 2' Inside Diameter = 1'11" Hollow (soil plugged) Note: Pile & soil profile are not drawn to scale For this problem, please calculate N₁* using both the bearing capacity theory approach and using standard design charts. Compare the values that result from these two approaches. Please use only the Nq* from bearing capacity theory for the remainder of your calculations.arrow_forwardDesign a fully restrained BFP moment connection to support the factored bending moment of 1,200 kN·m and factored shear force of 95 kN due to wind and gravity loads. Use 90mm spacing between the bolts, and 40mm edge spacing. The steel grade is A992 for the W920 × 201 beam and W840 × 359 column and A36 for the steel plate (30 mm thick). Use FEXX = 450 MPa electrodes and 20mm A490 bolts (threads included) for the flange plate (Fr= 457 MPa), 16mm A307 bolts for the shear tab (Fnv = 165 MPa). Steel Section Properties W920 × 201 W840 × 359 D₁ = 904 mm bf = 305 mm tf = 20.1 mm tw = 15.2 mm d = 869 mm bf = 404 mm tf = 35.6 mm tw = 21.1 mm Summary of answer: Flange Plate: bPL = tPL = No. of Bolts: Flange bolt = Thickness of fillet weld on shear tab:. Shear tab =arrow_forwardA6.1- A simply supported beam, as shown in Figure 3, is subjected to factored point load Pr= 1250 kN. The beam is designed to have 6-30M bars to resist the maximum bending moment, Mat the section 900 mm away from the centerline of the support. Determine the required development length for the reinforcement at the section with the maximum bending moment. If it is not possible to provide straight bar anchorage into the left support, design the hooked anchorage. Given: Concrete: Normal density with f'c = 25 MPa Reinforcement: Uncoated rebars with fy = 400 MPa Shear reinforcement is in excess of CSA 23.3 minimum requirement: 10M Clear cover to the stirrups: 30 mm Column: 200mm x 500mm m + 1 b=500 mm 200mm Σ Mf 6-30M Figure 3 10 m 200mm h=1000 mm + As = 6-30M Cross-sectionarrow_forward
