
Concept explainers
Plot the shear diagram, bending moment diagram, axial force diagram, and the qualitative deflected shape of the frame.
Explanation of Solution
Write the condition for static instability, determinacy and indeterminacy of plane frames as follows:
Here, number of members is m, number of external reactions is r, the number of joints is j, and the number of elastic hinges is
Find the degree of static indeterminacy (i) using the equation;
Refer to the Figure in the question;
The number of members (m) is 3.
The number of external reactions (r) is 3.
The number of joints (j) is 4.
The number of elastic hinges
Substitute the values in Equation (2);
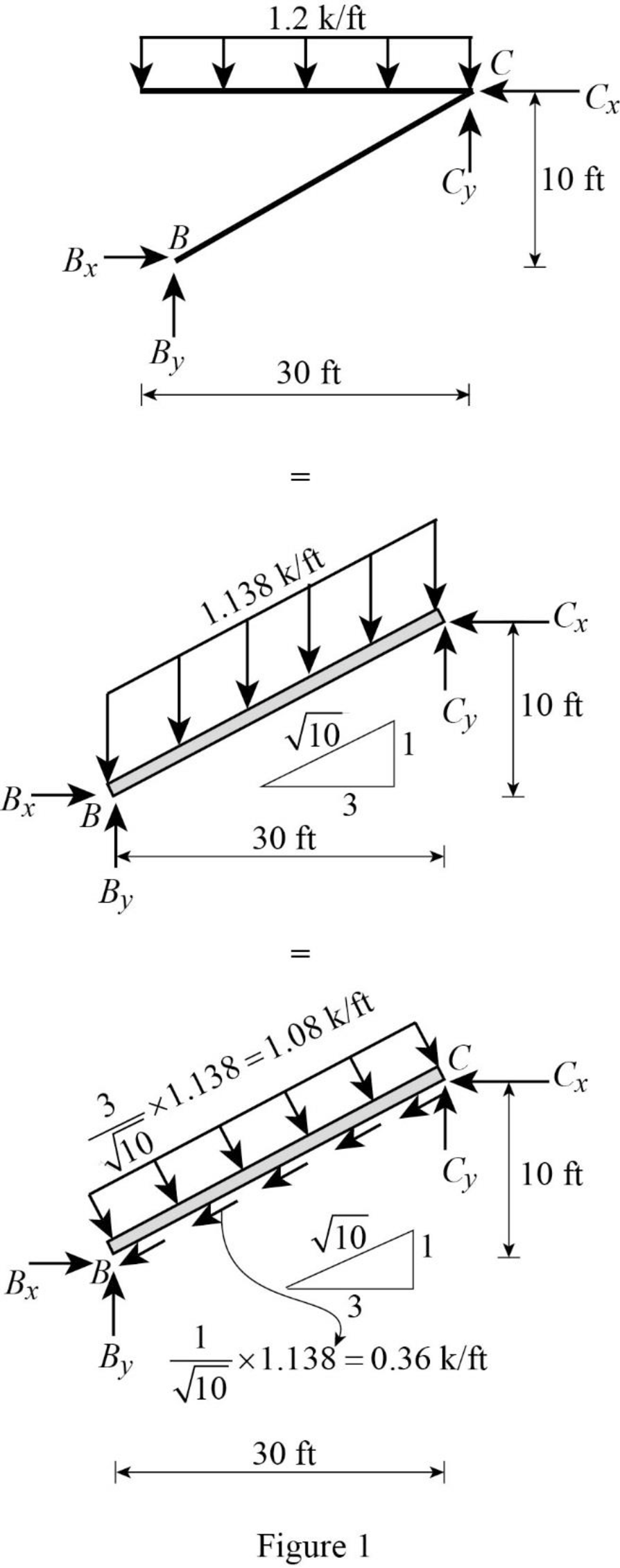
Show the equivalence of uniformly distributed load as in Figure 1.
Show the free-body diagram of the entire frame as in Figure 2.
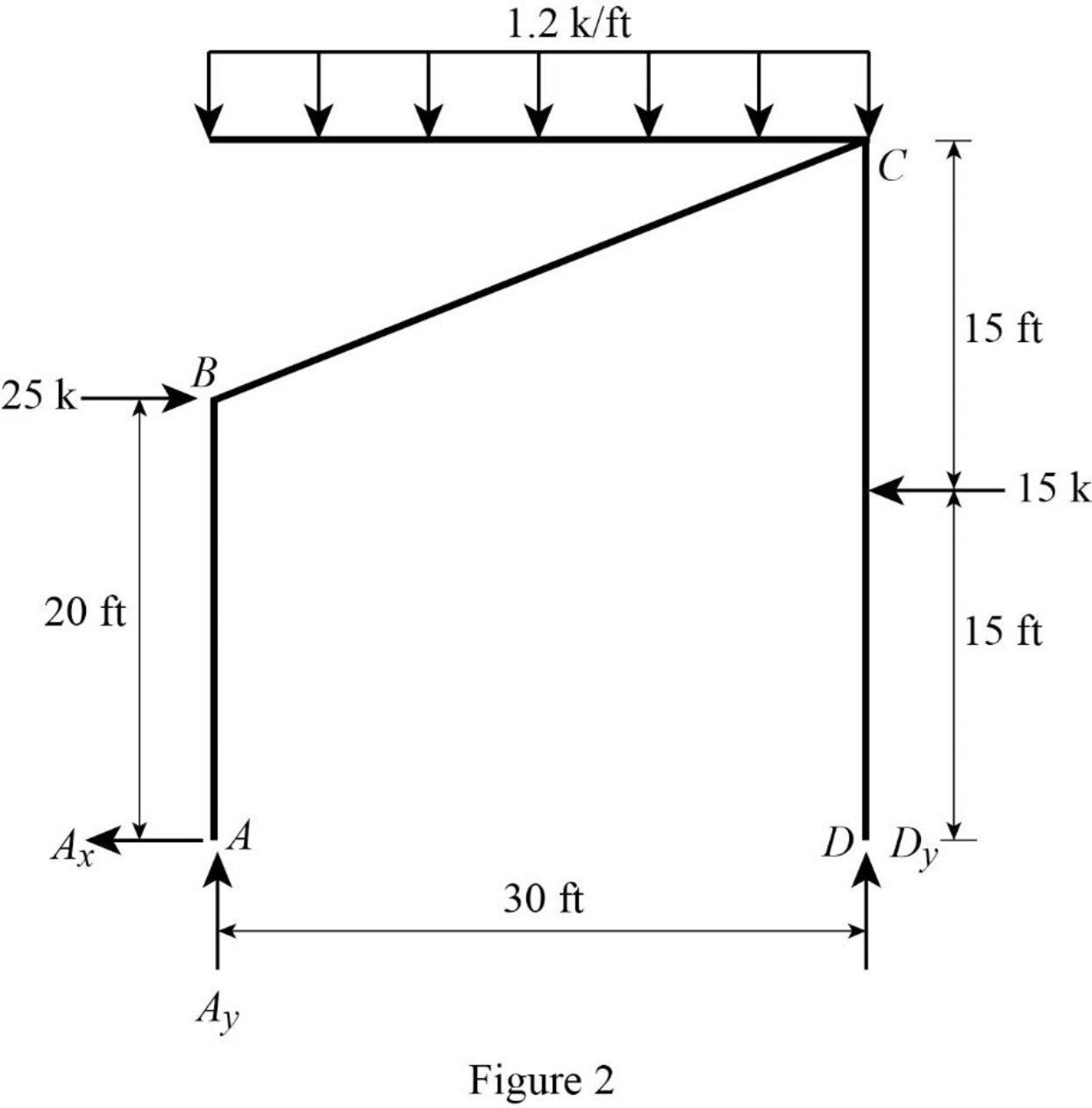
Find the horizontal reaction at point A by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Find the vertical reaction at point D by taking moment about point A.
Find the vertical reaction at point A by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Show the free-body diagram of the members and joints of the entire frame as in Figure 3.
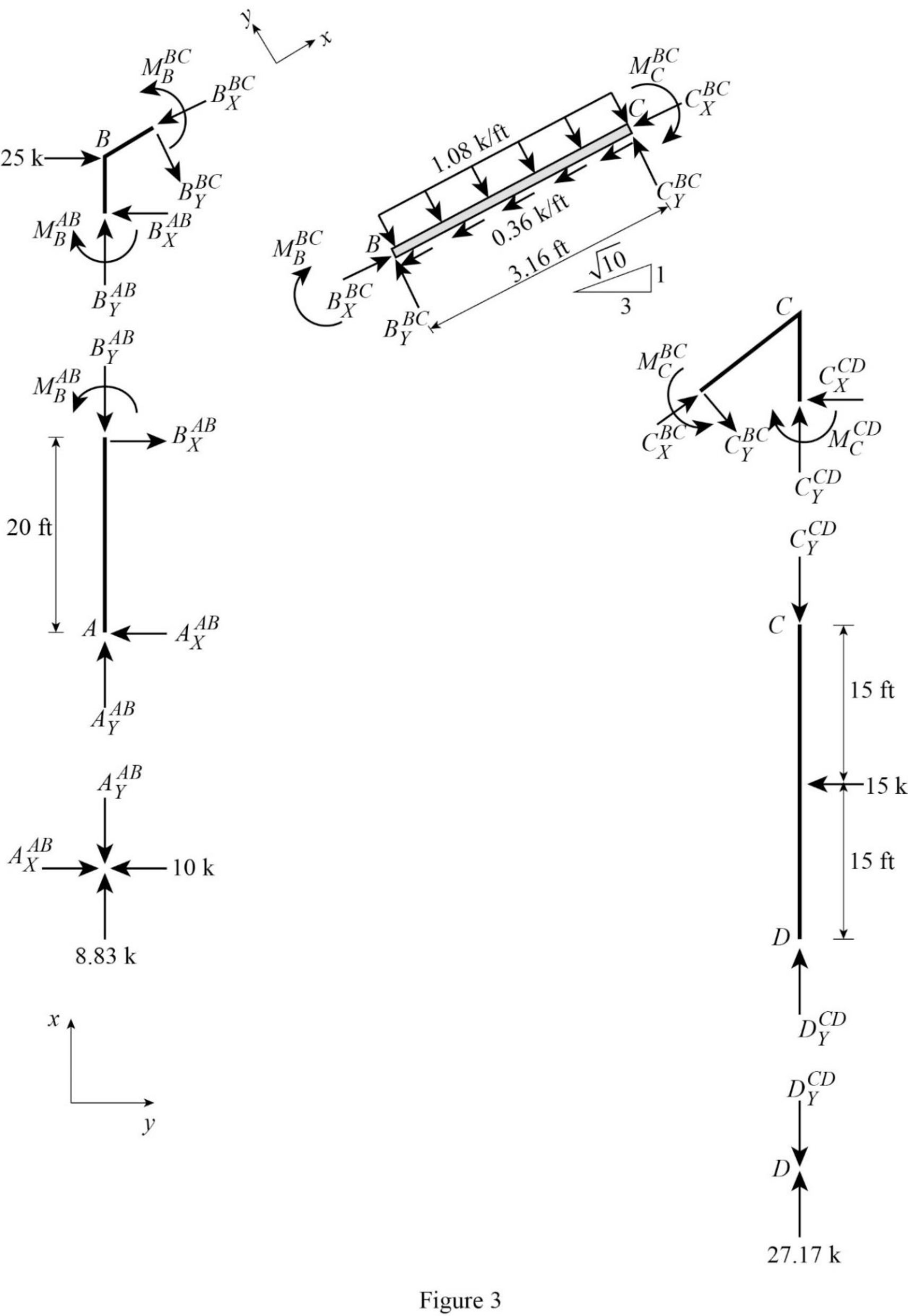
Consider point A:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the member AB:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Take moment about the point B.
Consider the point D:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Consider the member CD:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Take moment about the point C.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the point C:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about the point C.
Consider the section BC:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Take moment about point B:
Plot the moment end forces of the frame as in Figure 4.
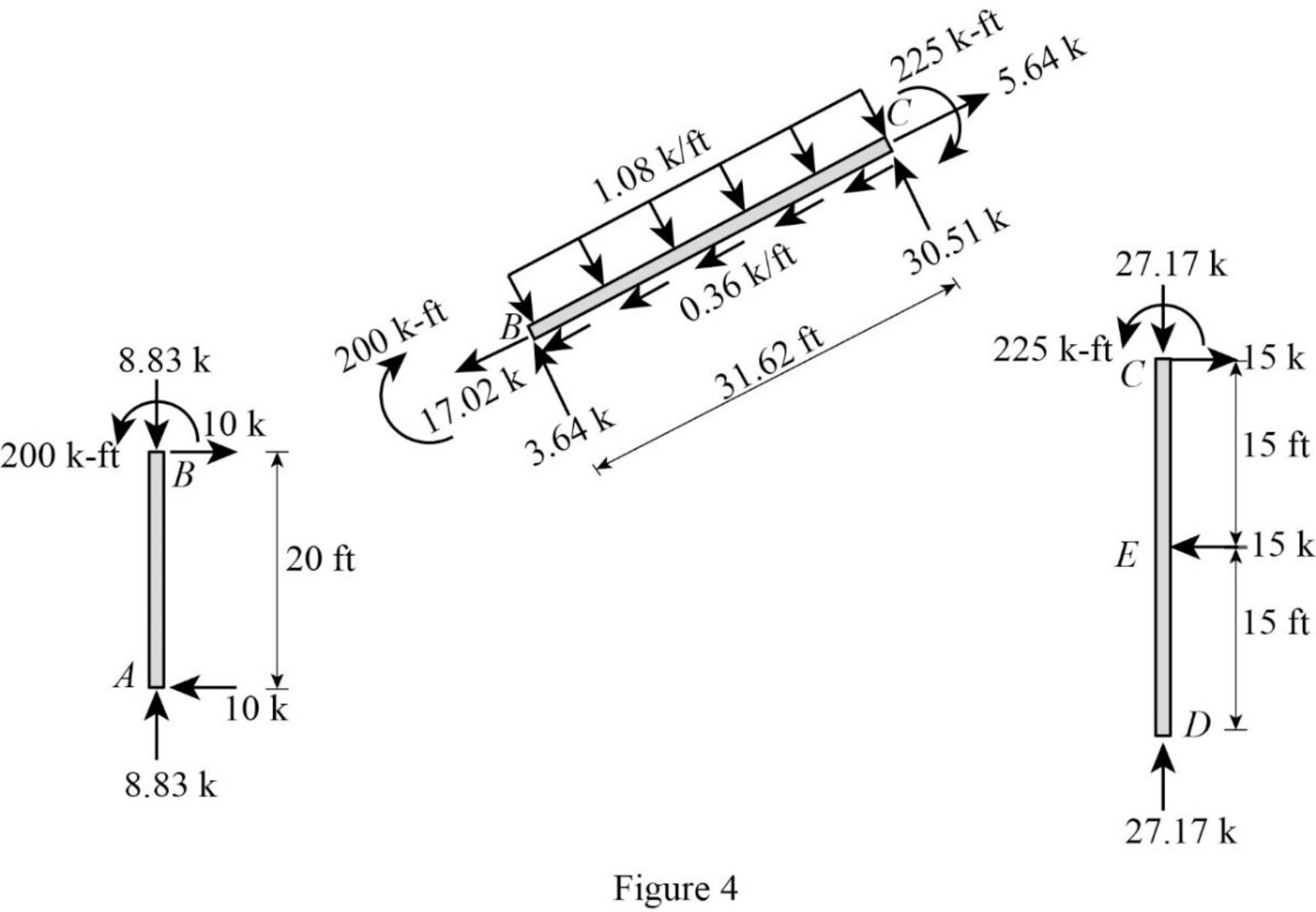
Refer to the moment end force diagram plot the shear diagram, bending moment diagram, and the axial force diagrams.
Plot the shear force diagram as in Figure 5.
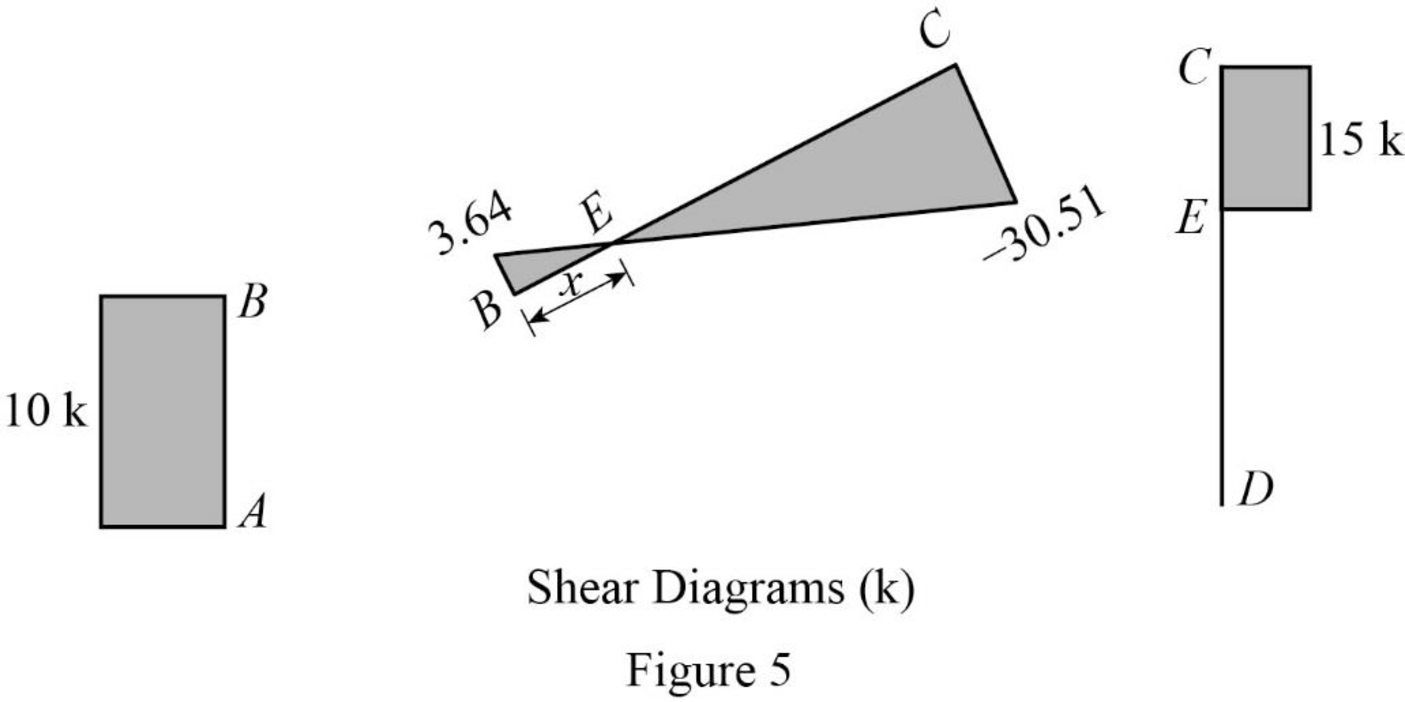
The maximum bending moment occurs where the shear force changes sign.
Consider the section BEC, use the similar triangle concept.
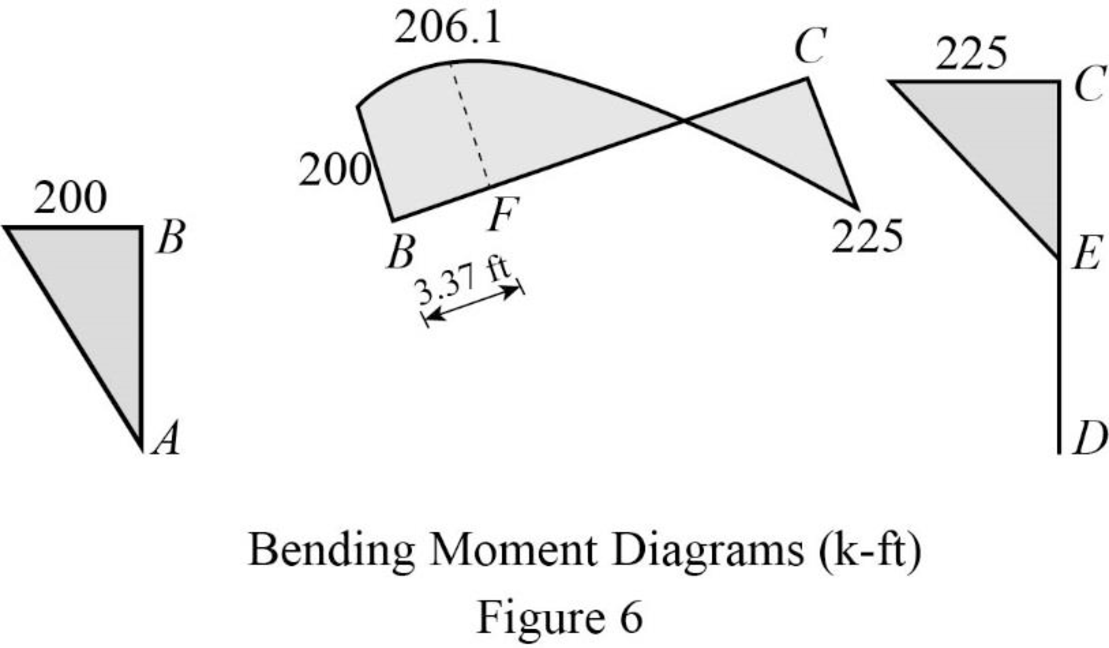
Plot the bending moment diagram as in Figure 6.
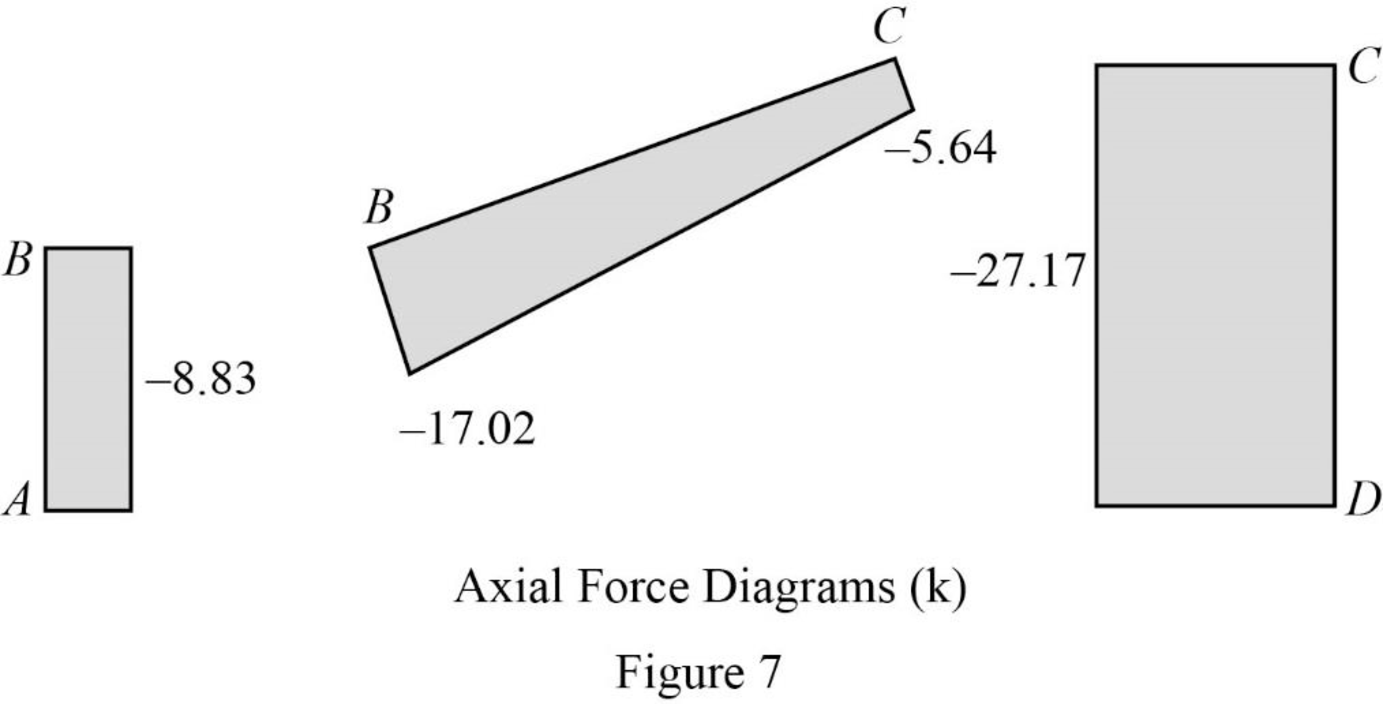
Plot the axial force diagram as in Figure 7.
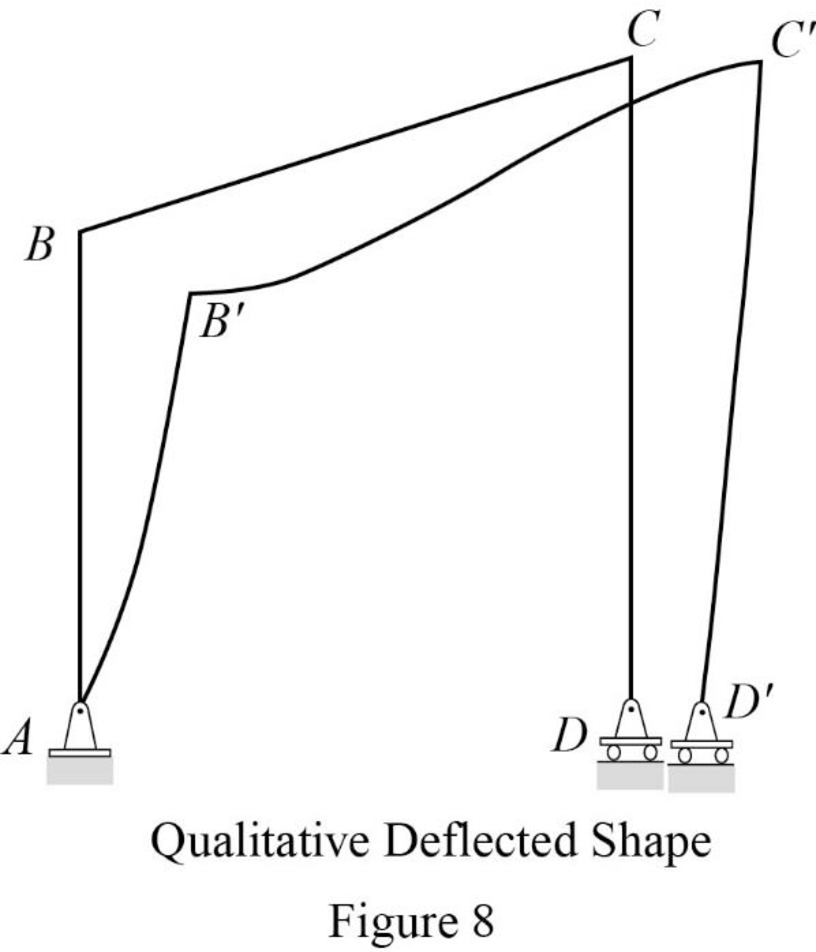
Plot the qualitative deflected shape as in Figure 8.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Structural Analysis
- I dont understand how to do the hand calculations help pls A multi-cell box beam, 1800 mm long, is subject to a vertical shear load of 6 kN applied in a vertical plane. Points 1-8 mark the boom elements on the beam. Calculate the shear flow in each web and locate the shear centre using hand calculations. The results, including mesh convergence, shear flow, stress distribution, deformation, and shear centre location, will then be compared with findings from Abaqus FEA. The material properties are: Young's modulus (E) is 72 GPa, and Poisson's ratio (ν) is 0.3.arrow_forwardfind the following (show all work) Seepage velocity vs (m/sec) Discharge velocity v (m/sec) Hydraulic Conductivity k (m/sec) given : length of specimen 0.25 m , Diameter of specimen 0.10 m , Head difference 0.50 m , water collected in 2 minutes, 50 ml, the void ratio of soil 0.46arrow_forwarddraw sketches to comment the different components of the total head (Bernoulli's equation) Define head loss Explain the differences between a seepage and a discharge velocities in soil. Are they related if so in what way.arrow_forward
- Q1: Determine the duration of project for the activities shown below, and find the critical path by using (A-0- Diagram) ABC DEFOHIJKMN R 4 5 6 8 3 7 8 11 3 8 3 7 8 11 3 8 489 4 Activity Duration (Weeks) Followed C,D D,F JJHOK MIK NMR- by E 1arrow_forwardI dont understand how to do the hand calculations help pls A multi-cell box beam, 1800 mm long, is subject to a vertical shear load of 6 kN applied in a vertical plane. Points 1-8 mark the boom elements on the beam. Calculate the shear flow in each web and locate the shear centre using hand calculations. The results, including mesh convergence, shear flow, stress distribution, deformation, and shear centre location, will then be compared with findings from Abaqus FEA. The material properties are: Young's modulus (E) is 72 GPa, and Poisson's ratio (ν) is 0.3.arrow_forward2. Vertical highway curve: Given PVI at 65 + 00, L = 800 ft, g1 = +4%, g2 = -3%, and PVI elevation = 264.2 ft, compute the elevations of the curve high point and for all of the full stations until reaching the end of the curve as well as for the beginning and end of the curve.arrow_forward
- 1. Horizontal highway curve: Given Pl at 65 + 78.20, A = 22°00', and D = 6°00', compute the deflections to the nearest second for the full stations (means stations 65+00, 66+00, etc.) as well as for the beginning and end of the curve.arrow_forwardWater flows uniformly in a channel with a bottom slope of 0.002 and a compound cross-section: Section 1 has concrete sides and bottom. Section 2 is vegetated with light brush. Manning coefficients and dimensions (in meters) are shown below: Calculate: a. The composite Manning roughness coefficient for the channel b. The flow rate in cubic meters per second (cms) for the water levels shownarrow_forwardQ2: For the activities shown in the table below, it is required to reduce the total duration of the project four days by using crash program and network diagram, If you knew that indirect costs is 150 S/day and the delay fine is 100 S/day after the 14th day. Find new cost after crashing the project four days? Activity Preceding Normal Program Crash Program activity Duration (days) Direct Cost (S) Duration (days) Direct Cost (S) A 5 600 3 950 B 4 200 3 500 C A 5 300 4 500 D A 2 600 1 615 E B 6 900 5 1025 800 F C 4 700 3 450 400 G D 4 700 700 3 1400 H E 600 I F,G,H 5000 Σ (40 p (good luck)arrow_forward
- The Figure below shows a frame subjected to a uniform load 1kN/m.EI is constant.Compute horizontal displacement and rotation at C. (15Marks) A 3m 5-83m 4m 5m 1kN/m Barrow_forwardI need detailed help solving this exercise from homework of Engineering Mathematics II.I do not really understand how to do, please do it step by step, not that long but clear. Thank you!P.S.: Please do not use AI, thanks!arrow_forwardI need detailed help solving this exercise from homework of Engineering Mathematics II.I do not really understand how to do, please do it step by step, not that long but clear. Thank you!P.S.: Please do not use AI, thanks!arrow_forward
