
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780134605180
Author: Gerard J. Tortora, Berdell R. Funke, Christine L. Case, Derek Weber, Warner Bair
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5R
There are three mechanisms for the phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP. Write the name of the mechanism that describes each of the reactions in the following table.
| ATP Generated by | Reaction |
| a. ______ | An electron, liberated from chlorophyll by light, is passed down an electron transport chain. |
| b. ______ | Cytochrome c passes two electrons to cytochrome a. |
| c. ______ | 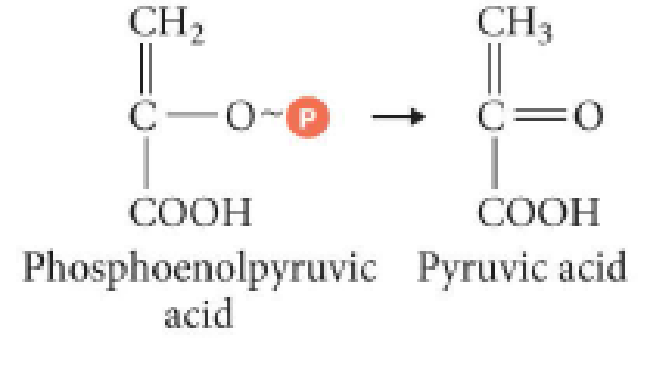 |
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Different species or organisms research for ecology
What is the result of the following gram stain:
positive
○ capsulated
○ acid-fast
○ negative
What
type
of stain is the image below:
capsule stain
endospore stain
gram stain
negative stain
ASM MicrobeLibrary.org Keplinger
Chapter 5 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Ch. 5 - Prob. 1RCh. 5 - DRAW ITUsing the diagrams below, show each of the...Ch. 5 - DRAW IT An enzyme and substrate are combined. The...Ch. 5 - Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the...Ch. 5 - There are three mechanisms for the phosphorylation...Ch. 5 - All of the energy-producing biochemical reactions...Ch. 5 - Fill in the following table with the carbon source...Ch. 5 - Write your own definition of the chemiosmotic...Ch. 5 - Why must NADH be reoxidized? How does this happen...Ch. 5 - NAME IT What nutritional type is a colorless...
Ch. 5 - Which substance in the following reaction is being...Ch. 5 - Which of the following reactions produces the most...Ch. 5 - Prob. 3MCQCh. 5 - Which of the following compounds has the greatest...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5MCQCh. 5 - Prob. 6MCQCh. 5 - Which culture produces the most lactic acid? Use...Ch. 5 - Which culture produces the most ATP? Use the...Ch. 5 - Which culture uses NAD+? Use the following choices...Ch. 5 - Which culture uses the most glucose? Use the...Ch. 5 - Explain why, even under ideal conditions,...Ch. 5 - The following graph shows the normal rate of...Ch. 5 - Compare and contrast carbohydrate catabolism and...Ch. 5 - How much ATP could be obtained from the complete...Ch. 5 - The chemoautotroph Acidithiobacillus can obtain...Ch. 5 - Haemophilus influenzae requires hemin (X factor)...Ch. 5 - The drug Hivid, also called ddC, inhibits DNA...Ch. 5 - The bacterial enzyme streptokinase is used to...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. If Earth were twice as far as it actua...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
How could you separate a mixture of the following compounds? The reagents available to you are water, either, 1...
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the result of the acid-fast stain below: Stock Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Image Getty Images St Soy Getty Images by Getty Images by Getty Images Joy Getty encapsulated O endosporulating negative ○ positivearrow_forwardYou have a stock vial of diligence 75mg in 3ml and need to draw up a dose of 50mg for your patient.how many mls should you draw up to give this dosearrow_forwardYou are recquired to administer 150mg hydrocortisone intravenously,how many mls should you give?(stock =hydrocortisone 100mg in 2mls)arrow_forward
- If someone was working with a 50 MBq F-18 source, what would be the internal and external dose consequences?arrow_forwardWe will be starting a group project next week where you and your group will research and ultimately present on a current research article related to the biology of a pathogen that infects humans. The article could be about the pathogen itself, the disease process related to the pathogen, the immune response to the pathogen, vaccines or treatments that affect the pathogen, or other biology-related study about the pathogen. I recommend that you choose a pathogen that is currently interesting to researchers, so that you will be able to find plenty of articles about it. Avoid choosing a historical disease that no longer circulates. List 3 possible pathogens or diseases that you might want to do for your group project.arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forward
- DNK dagi nukleotidlar va undan sintezlangan oqsildagi peptid boglar farqi 901 taga teng bo'lib undagi A jami H boglardan 6,5 marta kam bo'lsa DNK dagi jami H bog‘lar sonini topingarrow_forwardOne of the ways for a cell to generate ATP is through the oxidative phosphorylation. In oxidative phosphorylation 3 ATP are produced from every one NADH molecule. In respiration, every glucose molecule produces 10 NADH molecules. If a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forwardIf a cell is growing on 5 glucose molecules, how much ATP can be produced using oxidative phosphorylation/aerobic respiration?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning


Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Photosynthesis & Respiration | Reactions | Chemistry | FuseSchool; Author: FuseSchool - Global Education;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3XIyweZg6Sw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY