Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: The relation between the compounds A and B is to be determined.
Concept introduction: Newman projections are drawn to visualize the different conformations of a compound around
The stereochemistry of the compound is determined by prioritizing the groups attached to its stereogenic center. The groups are prioritized on the basis of
Answer to Problem 5.61P
Compounds A and B are identical.
Explanation of Solution
The given Newman projection A is,
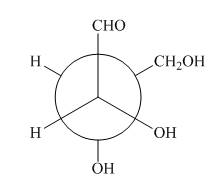
Figure 1
In Newman projection, the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,
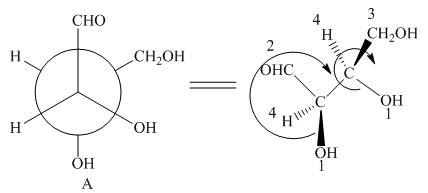
Figure 2
In the given compound,
The given Newman projection B is,
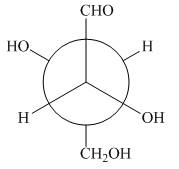
Figure 3
In Newman projection the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,
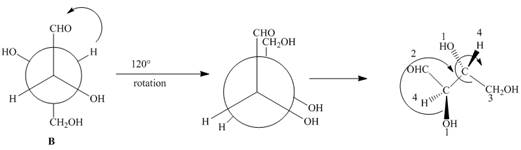
Figure 4
In the given compound,
Both A and B have same configuration around the stereogenic centers. Hence, compounds A and B are identical.
Compounds A and B are identical.
(b)
Interpretation: The relation between the compounds A and C is to be determined.
Concept introduction: Newman projections are drawn to visualize the different conformations of a compound around
The stereochemistry of the compound is determined by prioritizing the groups attached to its stereogenic center. The groups are prioritized on the basis of atomic number of their atoms. The group that contain atom with higher atomic number is given higher priority. Complete the circle in decreasing order of priority from
Answer to Problem 5.61P
Compounds A and C are enantiomers.
Explanation of Solution
The given Newman projection A is,

Figure 1
In Newman projection the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,

Figure 2
In the given compound,
The given Newman projection C is,
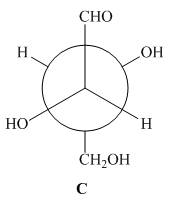
Figure 5
In Newman projection the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,
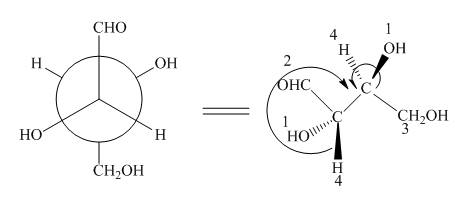
Figure 6
In the given compound,
Both A and C have opposite configuration around the stereogenic centers. Hence, compounds A and C are enantiomers.
Compounds A and C are enantiomers.
(c)
Interpretation: The relation between the compounds A and D is to be determined.
Concept introduction: Newman projections are drawn to visualize the different conformations of a compound around
Enantiomer of a compound has opposite configuration at stereogenic centers. Diastereomers of a compound have at least one stereogenic centre with same configuration and at least one with opposite configuration.
Answer to Problem 5.61P
Compounds A and D are diastereomers.
Explanation of Solution
The given Newman projection A is,

Figure 1
In Newman projection, the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,

Figure 2
In the given compound,
The given Newman projection D is,
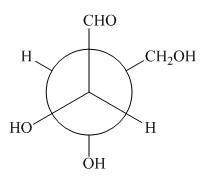
Figure 7
In Newman projection the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,
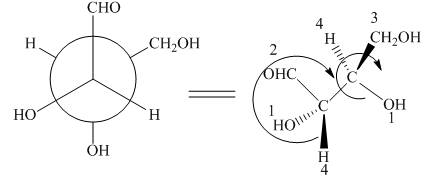
Figure 8
In the given compound,
Both A and D have one stereogenic centre with same configuration and one with opposite configuration. Hence, A and D are diastereomers.
Compounds A and D are diastereomers.
(d)
Interpretation: The relation between the compounds C and D is to be determined.
Concept introduction: Newman projections are drawn to visualize the different conformations of a compound around
Enantiomer of a compound has opposite configuration at stereogenic centers. Diastereomers of a compound have at least one stereogenic centre with same configuration and at least one with opposite configuration.
Answer to Problem 5.61P
Compounds C and D are diastereomers.
Explanation of Solution
The given Newman projection C is,

Figure 5
In Newman projection the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,

Figure 6
In the given compound,
The given Newman projection D is,

Figure 7
In Newman projection the circle represents the back carbon and the dot represents the front carbon. The back carbon is substituted by one hydroxyl, one hydrogen atom and one hydroxymethyl group and the front carbon is substituted by one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group and one formyl group. The skeletal structure for the given projection is,

Figure 8
In the given compound,
Both C and D have one stereogenic centre with same configuration and one with opposite configuration. Hence, compounds C and D are diastereomers.
Compounds C and D are diastereomers.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
PKG ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Complete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forward
- Just try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers. Something that looks reasonable or correct would be sufficient. If you can get many of them correct that would be great!arrow_forwardTake a look at the following molecule, and then answer the questions in the table below it. (You can click the other tab to see the molecule without the colored regions.) with colored region plain 0= CH2-0-C-(CH2)16-CH3 =0 CH-O-C (CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)5-CH3 D CH3 | + OMPLO CH3-N-CH2-CH2-0-P-O-CH2 B CH3 A Try again * 000 Ar 8 0 ?arrow_forwardShow your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward
- Show your work and do something that is reasonable. It does not have to be 100% correct. Just show something that looks good or pretty good as acceptable answers.arrow_forward= 1 = 2 3 4 5 6 ✓ 7 8 ✓ 9 =10 Devise a synthesis to prepare the product from the given starting material. Complete the following reaction scheme. Part 1 of 3 -Br Draw the structure for compound A. Check Step 1 Step 2 A Click and drag to start drawing a structure. × ↓m + OH Save For Later S 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privaarrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reduction: 田 Check AP + + H2 Lindlar catalyst Click an drawing 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rigarrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning




