
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The point on the graph corresponds to the reactants has to be given.
The given graph is,
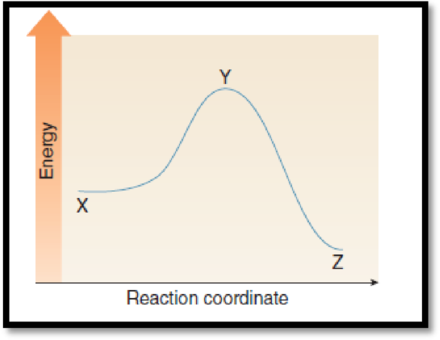
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The point on the graph corresponds to the product has to be given.
The given graph is,
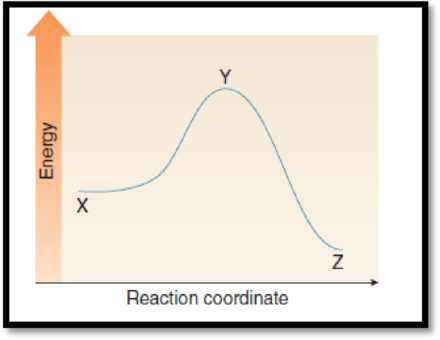
Figure 1
(c)
Interpretation:
The point on the graph corresponds to the transition state has to be given.
The given graph is,
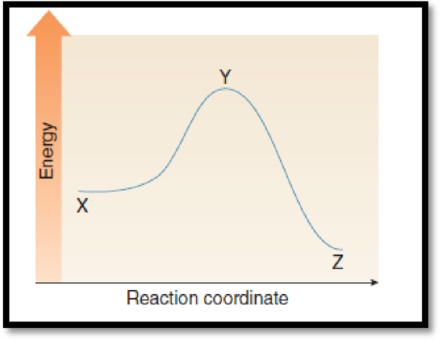
Figure 1
(d)
Interpretation:
The difference in energy between the two points which equals activation energy has to be given.
The given graph is,
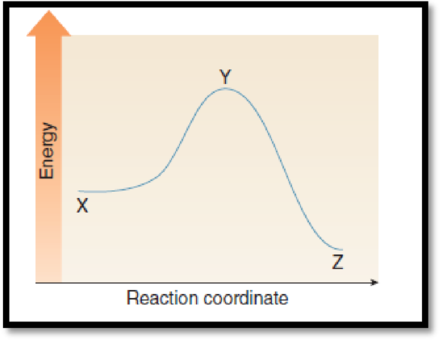
Figure 1
(e)
Interpretation:
The difference in energy between the two points which equals enthalpy has to be given.
The given graph is,
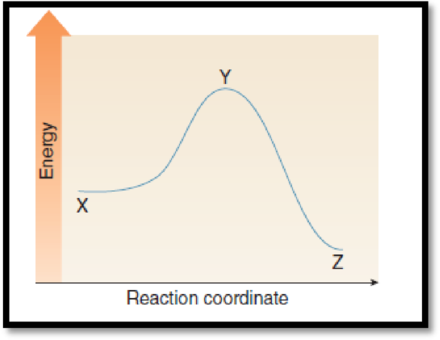
Figure 1
(f)
Interpretation:
The point with highest energy has to be given.
The given graph is,
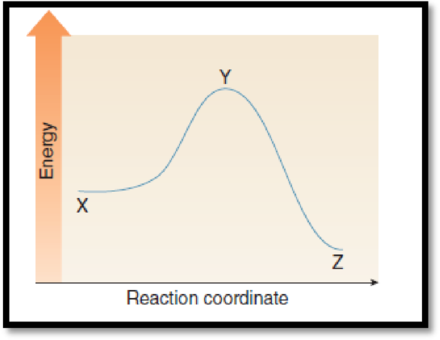
Figure 1
(g)
Interpretation:
The point with lowest energy has to be given.
The given graph is,
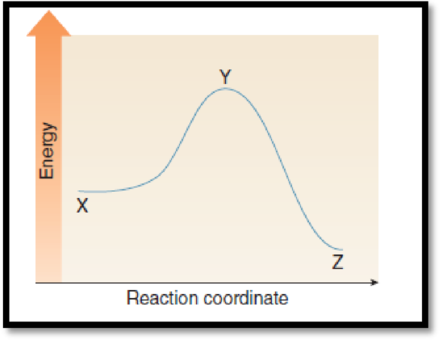
Figure 1
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
- please help i cant find the article to even startarrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardhelp with the rf values i am so confusedarrow_forward
- Predict the organic reactant of X and Y that are involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product for this reaction.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardPlease provide the complete mechanism for the reaction below and include all appropriate arrows, formal charges, and intermediates. Please draw out the answerarrow_forward
 Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781285199023Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





