
Concept explainers
Label each stereogenic center as
a. 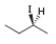 c.
c. 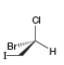 e.
e. 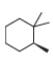 g.
g.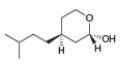
b. 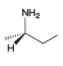 d.
d. 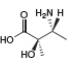 f.
f. 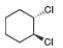 h.
h. 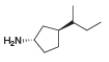
(a)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
The stereogenic center has
Explanation of Solution
The
(1) Assign numbering to the groups which are bonded to the chiral carbon based on the molecular weight and electronegativity.
(2) If the sequence of the numbering follows clockwise direction, the chiral atom is assigned
(3) If the sequence of the numbering follows anticlockwise direction, the chiral atom is assigned
(4) If the rotation is clock-wise and the least priority group is above the plane, then the configuration is inverted to the obtained configuration from the above CIP rule which means
In the given compound, the increasing order of priority assigned to the groups attached to chiral center is,
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
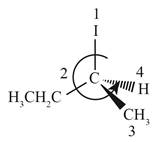
Figure 1
The rotation in the above compound is in anticlockwise direction. Hence, the stereogenic center has
(b)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
The stereogenic center has
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, the increasing order of priority assigned to the groups attached to chiral center is,
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
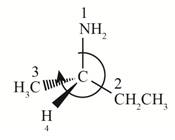
Figure 2
The rotation in the above compound is in clockwise direction and the least priority group is above the plane, then the configuration is inverted. Hence, the stereogenic center has
(c)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
The stereogenic center has
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, the increasing order of priority assigned to the groups attached to chiral center is,
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
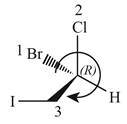
Figure 3
The rotation in the above compound is in clockwise direction. Hence, the stereogenic center has
(d)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
Both the stereogenic centers has
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, two chiral centers are present.
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
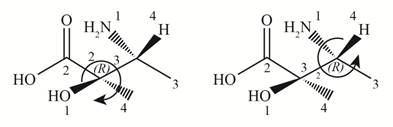
Figure 4
The rotation of first chiral center in the above compound is in clockwise direction and second chiral center shows anticlockwise rotation. In second chiral center, the least priority group is above the plane, and then the configuration is inverted. Hence, both the stereogenic centers has
(e)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
The stereogenic center has
Explanation of Solution
The groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
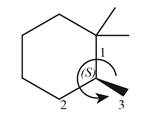
Figure 5
The rotation in the above compound is in anticlockwise direction and the least priority group is below the plane. Hence, the stereogenic center has
(f)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
Both the stereogenic centers has
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, two chiral centers are present.
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
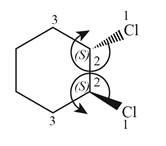
Figure 6
The rotation of first chiral center in the above compound is in clockwise direction and second chiral center shows anticlockwise rotation. In first chiral center, the highest priority group is below the plane, and then the configuration is inverted to
(g)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
Both the stereogenic centers has
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, two chiral centers are present.
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
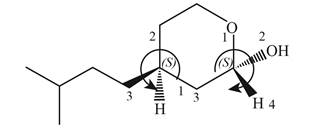
Figure 7
The rotation of first chiral center in the above compound is in clockwise direction and second chiral center shows anticlockwise rotation. In first chiral center, the highest priority group is below the plane, and then the configuration is inverted to
(h)
Interpretation: The stereogenic center in the given compound is to be labeled as
Concept introduction: A carbon atom that has four nonequivalent atoms or groups attached to it is known as chiral carbon atom. Chiral carbon centers are also called as asymmetric or stereogenic centers.
The naming of chiral center and geometric isomers are based on Cahn-Ingold-Prelog priority rules. If the priority assigned to each group attached to the chirality center in a molecule is in a clockwise direction, then it is the R-stereoisomer, and if this is counter-clockwise, then it is the S-stereoisomer. R and S-stereoisomer are mirror images of each other.
Answer to Problem 5.47P
The configurations of three stereogenic centers are
Explanation of Solution
In the given compound, three chiral centers are present.
Therefore, the groups in the given compound are numbered as shown below.
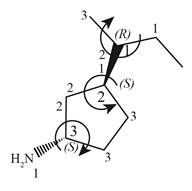
Figure 8
The rotation of first chiral center in the above compound is in clockwise direction. Thus, it has
(a) The stereogenic center has
(b) The stereogenic center has
(c) The stereogenic center has
(d) Both the stereogenic centers has
(e) Both the stereogenic centers has
(f) Both the stereogenic centers has
(g) Both the stereogenic centers has
(h) The configurations of three stereogenic centers are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
- Identify any polar covalent bonds in epichlorohydrin with S+ and 8- symbols in the appropriate locations. Choose the correct answer below. Η H's+ 6Η Η Η Η Η Ηδ Η Ο Ο HH +Η Η +Η Η Η -8+ CIarrow_forwardH H:O::::H H H HH H::O:D:D:H HH HH H:O:D:D:H .. HH H:O:D:D:H H H Select the correct Lewis dot structure for the following compound: CH3CH2OHarrow_forwardRank the following compounds in order of decreasing boiling point. ннннн -С-С-Н . н-с- ННННН H ΗΤΗ НННН TTTĪ н-с-с-с-с-о-н НННН НН C' Н н-с-с-с-с-н НН || Ш НННН H-C-C-C-C-N-H ННННН IVarrow_forward
- Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing dipole moment. |>||>||| ||>|||>| |>|||>|| |||>||>| O ||>>||| H F H F H c=c || H c=c F F IIIarrow_forwardchoose the description that best describes the geometry for the following charged species ch3-arrow_forwardWhy isn't the ketone in this compound converted to an acetal or hemiacetal by the alcohol and acid?arrow_forward
- What is the approximate bond angle around the nitrogen atom? HNH H Harrow_forwardOH 1. NaOCH2CH3 Q 2. CH3CH2Br (1 equiv) H3O+ Select to Draw 1. NaOCH2 CH3 2. CH3Br (1 equiv) heat Select to Edit Select to Drawarrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in acidic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. S₂O₃²⁻(aq) → S₄O₆²⁻(aq)arrow_forward
- Q Select to Edit NH3 (CH3)2CHCI (1 equiv) AICI 3 Select to Draw cat. H2SO4 SO3 (1 equiv) HO SOCl2 pyridine Select to Edit >arrow_forwardComplete and balance the following half-reaction in basic solution. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. Zn(s) → Zn(OH)₄²⁻(aq)arrow_forwardb. ὋΗ CH3CH2OH H2SO4arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





