
Concept explainers
The account balances of Miss Beverly’s Tutoring Service as of June 30, the end of the current fiscal year, are as follows:
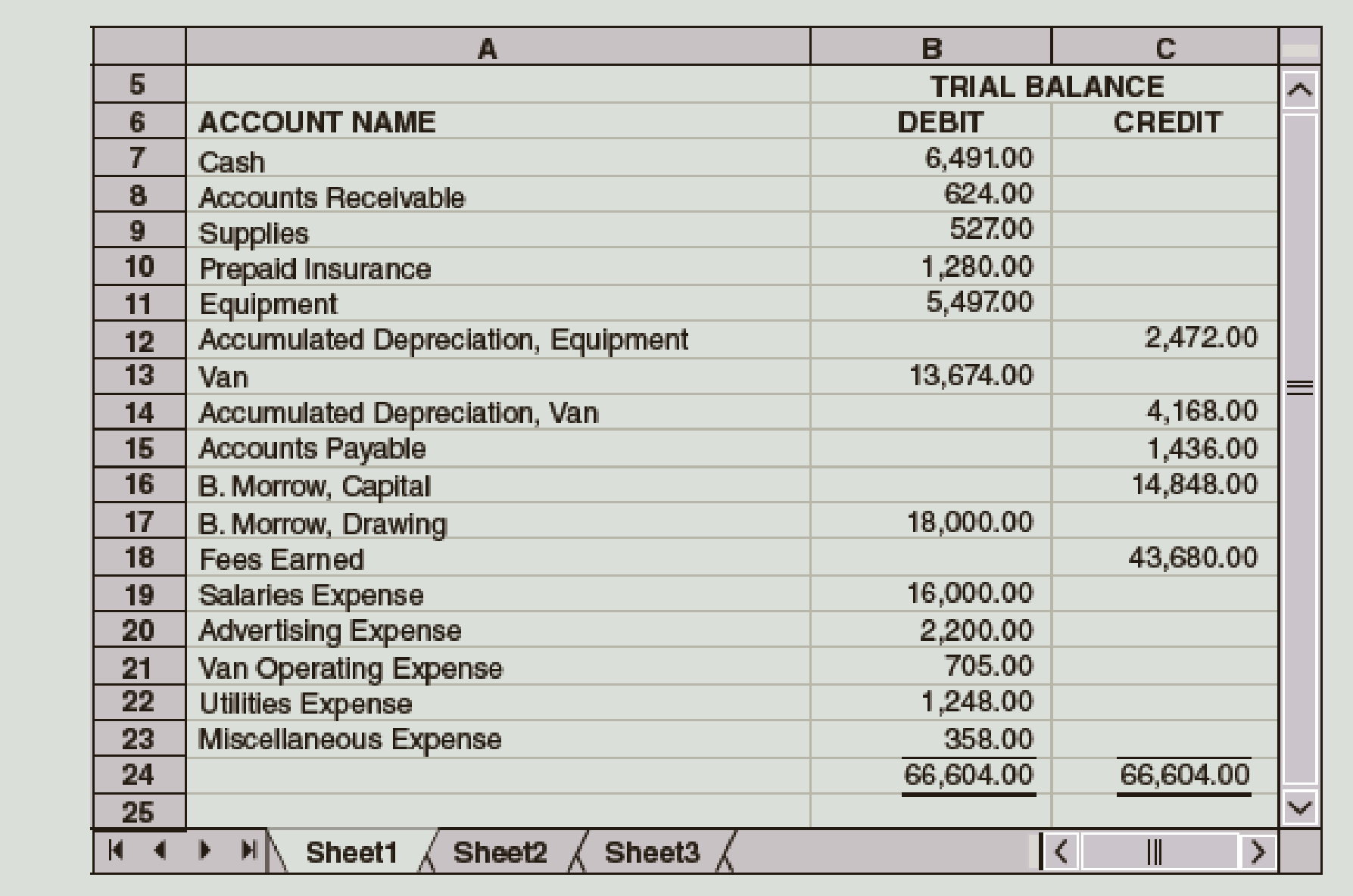
Required
- 1. Data for the adjustments are as follows:
- a. Expired or used up insurance, $470.
- b.
Depreciation expense on equipment, $948. - c. Depreciation expense on the van, $1,490.
- d. Salary accrued (earned) since the last payday, $574 (owed and to be paid on the next payday).
- e. Supplies remaining as of June 30, $407.
Your instructor may want you to use a work sheet for these adjustments.
- 2. Journalize the
adjusting entries . - 3. Prepare an income statement.
- 4. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity. Assume that there was an additional investment of $3,000 on June 10.
- 5. Prepare a
balance sheet - 6. Journalize the closing entries using the four steps in the proper sequence.
Check Figure
Net income, $19,567
1.
Indicate the given adjustments and complete the worksheet for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: Worksheet is an accounting tool that helps accountants to record adjustments and up-date balances required to prepare financial statements. Worksheet is a central place where trial balance, adjustments, adjusted trial balance, income statement, and balance sheet are presented.
Indicate the given adjustments and complete the worksheet for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
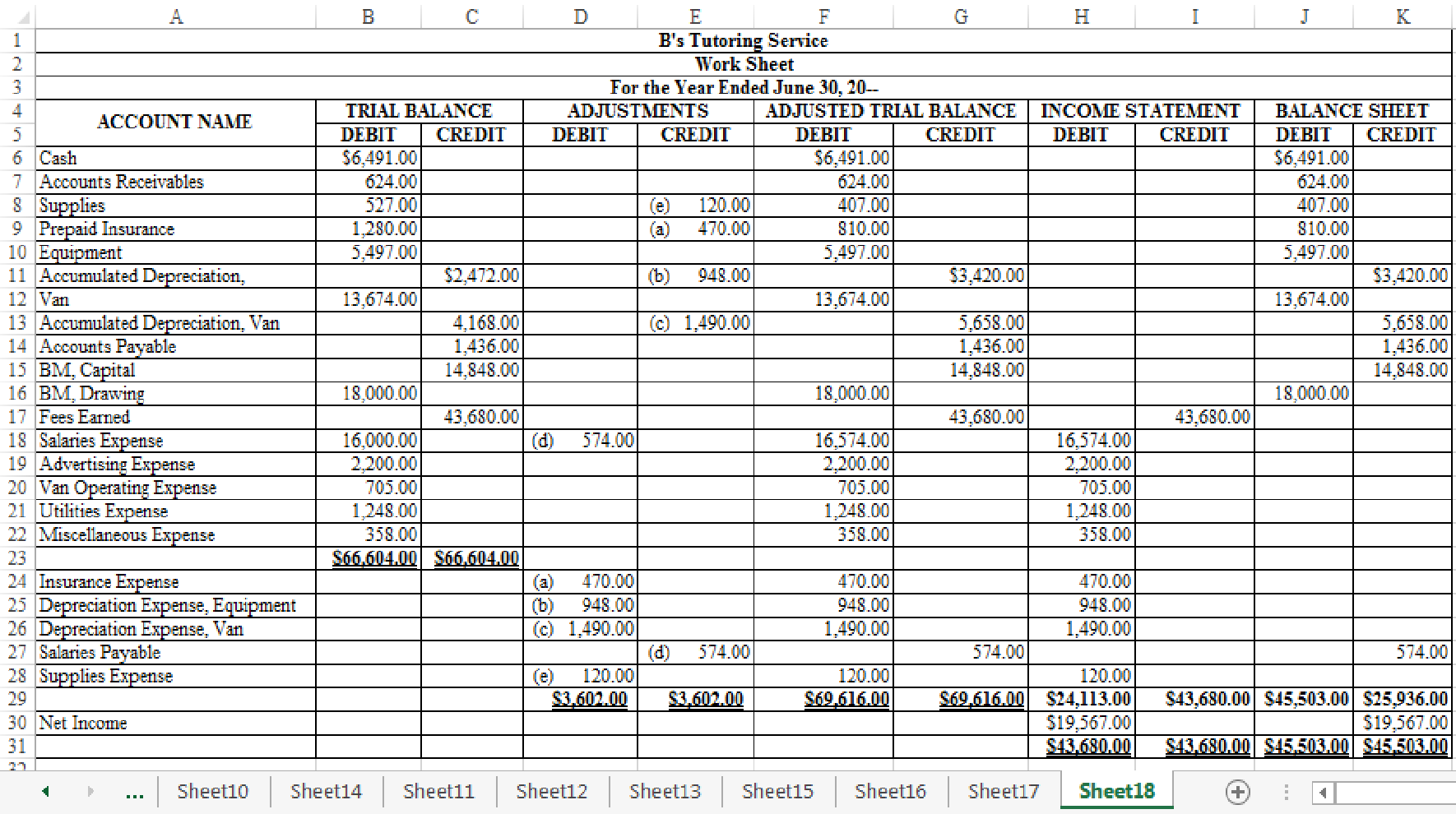
Figure-(1)
2.
Prepare adjusting journal entries for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and owners’ or stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle and matching concept.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare adjusting journal entries for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
Adjusting entry (a) for the prepaid insurance:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Insurance Expense | 470 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | 470 | |||||
| (Record part of prepaid insurance expired) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Insurance Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is an asset account. Since amount of insurance has expired, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Adjusting entry (b) for the depreciation expense for equipment:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 948 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment | 948 | |||||
| (Record depreciation expense) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Equipment is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
Adjusting entry (c) for the depreciation expense for van:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Depreciation Expense, Van | 1,490 | |||
| Accumulated Depreciation, Van | 1,490 | |||||
| (Record depreciation expense for van) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Van is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Van is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
Adjusting entry (d) for the salaries expense:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Salaries Expense | 574 | |||
| Salaries Payable | 574 | |||||
| (Record accrued salaries expenses) | ||||||
Table (4)
Description:
- Salaries Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Salaries Payable is a liability account. Since amount of payables has increased, liability decreased, and an increase in liability is credited.
Adjusting entry (e) for the supplies expense:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 20-- | ||||||
| June | 30 | Supplies Expense | 120 | |||
| Supplies | 120 | |||||
| (Record part of supplies consumed) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Supplies Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Supplies is an asset account. Since amount of supplies is used, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
3.
Prepare an income statement for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--, based on the account balances from worksheet of Part (1).
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations, and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement of B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
| B’s Tutoring Service | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended June 30, 20-- | ||
| Revenues: | ||
| Fees Earned | $43,680 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salaries Expense | $16,574 | |
| Advertising Expense | 2,200 | |
| Van Operating Expense | 705 | |
| Utilities Expense | 1,248 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 358 | |
| Insurance Expense | 470 | |
| Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 948 | |
| Depreciation Expense, Van | 1,490 | |
| Supplies Expense | 120 | |
| Total expenses | 24,113 | |
| Net income | $19,567 | |
Table (6)
4.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--. (Refer to net income computed in Part (3)).
Explanation of Solution
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to, and drawings is deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the end result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for B’s Tutoring Service for the year ended June 30, 20--.
| B’s Tutoring Service | ||
| Statement of Owners’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended June 30, 20-- | ||
| BM, Capital, June 1, 20-- | $11,848 | |
| Investment on June 10 | $3,000 | |
| Net income for the year | 19,567 | |
| 22,567 | ||
| Less: Withdrawals for June | 18,000 | |
| Increase in capital | 4,567 | |
| BM, Capital, June 30, 20-- | $16,415 | |
Table (7)
5.
Prepare a balance sheet for B’s Tutoring Service, based on the account balances from work sheet in Part (1), and capital of the owner from the statement of owners’ equity prepared in Part (4).
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and owners (owners’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by owners and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet for B’s Tutoring Service as at June 30, 20--.
| B’s Tutoring Service | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| June 30, 20-- | ||
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $6,491 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 624 | |
| Supplies | 407 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 810 | |
| Equipment | $5,497 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation, Equipment | 3,420 | 2,077 |
| Van | 13,674 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation, Van | 5,658 | 8,016 |
| Total Assets | $18,425 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | $1,436 | |
| Salaries Payable | 574 | |
| Total Liabilities | $2,010 | |
| Owners’ Equity | ||
| BM, Capital | 16,415 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners’ Equity | $18,425 | |
Table (8)
6.
Prepare closing entries.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to capital account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and drawing accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Steps in closing procedure:
- 1. Close the revenue accounts to Income Summary account.
- 2. Close the expense accounts to Income Summary account.
- 3. Close the Income Summary account and transfer the net income or net loss balance to the Capital account.
- 4. Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
Prepare closing entries.
Step 1: Close the revenue accounts to Income Summary account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| June | 30 | Fees Earned | 43,680 | |||
| Income Summary | 43,680 | |||||
| (Record closing of revenue to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Fees Earned is a revenue account. Revenue account has a normal credit balance. Since revenue is closed to Income Summary account, the account is debited.
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is credited to hold the transferred balance from revenue account.
Step 2: Close the expense accounts to Income Summary account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Income Summary | 24,113 | |||||
| Salaries Expense | 16,574 | |||||
| Advertising Expense | 2,200 | |||||
| Supplies Expense | 120 | |||||
| Van Operating Expense | 705 | |||||
| Utilities Expense | 1,248 | |||||
| Insurance Expense | 470 | |||||
| Depreciation Expense, Equipment | 948 | |||||
| Depreciation Expense, Van | 1,490 | |||||
| Miscellaneous Expense | 120 | |||||
| (Record closing of expenses to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (10)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is debited to hold the transferred balance from expense accounts.
- Salaries Expense, Advertising Expense, Supplies Expense, Van Operating Expense, Utilities Expense, Insurance Expense, Depreciation Expense-Equipment, Depreciation Expense-Van, and Miscellaneous Expense are expense accounts. Expense account has a normal debit balance. Since expenses are closed to Income Summary account, the accounts are credited.
Step 3: Close the net income to Capital account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| Income Summary | 19,567 | |||||
| BM, Capital | 19,567 | |||||
| (Record closing of net income to capital account) | ||||||
Table (11)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. Since net income is closed, the account is reversed, hence, the Income Summary account is debited.
- BM, Capital is a capital account. Since net income is transferred to the account, the value increased, and an increase in capital is credited.
Step 4: Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| BM, Capital | 18,000 | |||||
| BM, Drawing | 18,000 | |||||
| (Record closing of drawing to capital account) | ||||||
Table (12)
Description:
- BM, Capital is a capital account. Since drawings is transferred to the account, the value decreased, and a decrease in capital is debited.
- BM, Drawing is a capital account. Since drawings is transferred, the account is credited to reverse the previously debited effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Business Essentials (12th Edition) (What's New in Intro to Business)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
- PLEASE HELP ME WITH THIS ACCOUNTING PROBLEMarrow_forwardLet's say that Dr. Tim’s Company purchased a heavy-duty truck on July 1, 2021, for $30,000. It was estimated that it would have a useful life of 10 years and then would have a trade-in value of $6,000. The company uses the straight-line method. It was traded on August 1, 2026, for a similar truck costing $42,000; $16,000 was allowed as trade-in value (also fair value) on the old truck and $26,000 was paid in cash. A comparison of expected cash flows for the trucks includes the exchange lacks commercial substance. What is the entry to record the trade-in? Truck (new) $42,000 Accumulated Depreciation $12,200 ($30,000 - $6,000) x (61 months / 120 months) Loss on Disposal of Trucks $1,800 ($30,000 - $12,200 - $16,000 [trade-in] Trucks (old)…arrow_forward16. Candy Company projects the following sales: BB (Click on the icon to view the projected sales.) Candy collects sales on account in the month after the sale. The Accounts Receivable balance on January 1 is $12,300, which represents December's sales on account. Candy projects the following cash receipts from customers: BEE (Click on the icon to view the cash receipts from customers.) Recalculate cash receipts from customers if total sales remain the same but cash sales are only 5% of the total. Begin by computing the cash sales and sales on account for each month if cash sales are only 5% of the total. January February March Cash sales (5%) Sales on account (95%) Total sales $ 31,000 $ 27,000 $ 33,000 Data table X I Data table - X January February March January February March Cash sales (10%) $ 3,100 $ 27,900 Sales on account (90%) 2,700 $ 24,300 3,300 29,700 Cash receipts from cash sales Cash receipts from sales on account $ 3,100 $ 2,700 $ 12,300 27,900 3,300 24,300 $ 31,000 $…arrow_forward
- 11. Kapper Company projects 2025 first quarter sales to be $35,000 and increase by 15% per quarter. Determine the projected sales for 2025 by quarter and in total. Round answers to the nearest dollar. 12. Fagg Company manufactures and sells bicycles. A popular model is the XC. The company expects to sell 2,100 XCs in 2024 and 2,000 XCs in 2025. At the beginning of 2024, Friedman has 380 XCs in Finished Goods Inventory and desires to h of the next year's sales available at the end of the year. How many XCs will Fagg need to produce in 2024? 11. Kapper Company projects 2025 first quarter sales to be $35,000 and increase by 15% per quarter. Determine the projected sales for 2025 by quarter and in total. Round answers to the nearest dollar. Determine the projected sales for each quarter, then compute the projected sales for 2025. Base sale amount Quarter 1 Multiplier for sales increase = Projected sales for the quarter Larrow_forward15. Callarman Company began operations on January 1 and has projected the following selling and administrative expenses: (Click on the icon to view the selling and administrative expenses.) Determine the cash payments for selling and administrative expenses for the first three months of operations. (Complete all answer boxes. Enter a "0" for zero amounts.) Rent Expense Utilities Expense Depreciation Expense Insurance Expense Total cash payments for selling and administrative expenses Data tables January February March Rent Expense Utilities Expense Depreciation Expense Insurance Expense $1,400 per month, paid as incurred 800 per month, paid in month after incurred 1,000 per month 50 per month, 9 months prepaid on January 1 Print Donearrow_forwardMatch the budget types to the definitions. Budget Types 5. Financial 6. Flexible 7. Operating 8. Operational 9. Static 10. Strategic Definitions a. Includes sales, production, and cost of goods sold budgets b. Long-term budgets c. Includes only one level of sales volume d. Includes various levels of sales volumes e. Short-term budgets f. Includes the budgeted financial statementsarrow_forward
- 14. Cain Company is a sporting goods store. The company sells a tent that sleeps six people. The store expects to sell 280 tents in 2024 and 360 tents in 2025. At the beginning of 2024, Cain Company has 30 tents in Merchandise Inventory and desires to have 60% of the next year's sales available at the end of the year. How many tents will Cain Company need to purchase in 2024? Begin by selecting the labels, then enter the amounts to compute the budgeted tents to be purchased. Plus: Total tents needed Less: Budgetec Budgeted tents returned Budgeted tents to be sold Desired tents in ending inventory Tents in beginning inventory Zarrow_forwardCalculate Airbnb inventory turnover for the year 2024. ( (COGS) was $1.829 billion for the previous 12 months)(average inventory for 2024 is showing a significant increase, with the company reporting over $491 million) What does inventory turnover tells an investor?arrow_forwardCariman Company manufactures and sells three styles of door Handles: Gold, Bronze and Silver. Production takes 50, 50, and 20 machine hours to manufacture 1,000-unit batches of Gold, Bronze, and Silver Handles, respectively. The following additional data apply: Projected sales in units Per Unit data: Gold Bronze Silver 60,000 100,000 80,000 2. Determine the activity cost driver rate for setup costs and inspection costs? 3. Using the ABC system, for the Gold style of Handle: a. Calculate the estimated overhead costs per unit? b. Calculate the estimated operating profit per unit? 4. Explain the difference between the profits obtained from the traditional system and the ABC system. Which system provides a better estimate of profitability? Selling price $80 $40 $60 Direct materials $16 $8 $16 Direct labour $30 $6 $18 Overhead cost based on direct labour hours (traditional system) $24 $6 $18 Hours per 1,000-unit batch: Direct labour hours Machine hours Setup hours Inspection hours 80 20 60…arrow_forward
- I need some help with problem B. I have done the work, but I'd like to make sure if I have done the calculations correctly. If you see anything else that is wrong, please let me know.arrow_forwardModule 6 Discussion Discuss the significance of recognizing the time value of money in the long-term impact of the capital budgeting decision. 60 Replies, 59 Unread Σarrow_forwardHow many weeks of supply does summit logistics Inc. Hold ?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub  Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





