
Concept explainers
Biofuels
A lot of energy is locked up in the
Corn, soy, sugarcane, and other food crops are rich in oils, starches, and sugars that can be easily converted to biofuels. The starch in corn kernels, for example, can be enzymatically broken down to glucose, which is fermented to ethanol by bacteria or yeast. However, growing food crops for biofuel production typically requires a lot of energy (in the form of fossil fuels) and it damages the environment. Making biofuels from other plant matter such as weeds or agricultural waste requires additional steps, because these materials contain a higher proportion of cellulose. Breaking down this tough carbohydrate to its glucose monomers adds cost to the biofuel product.
In 2006, David Tilman and his colleagues published the results of a 10-year study comparing the net energy output of various biofuels. The researchers made biofuel from a mixture of native perennial grasses grown without irrigation, fertilizer, pesticides, or herbicides, in sandy soil that was so depleted by intensive agriculture that it had been abandoned. The energy content of this biofuel and the energy it took to produce it were measured and compared with that of biofuels made from food crops (Figure 5.16).
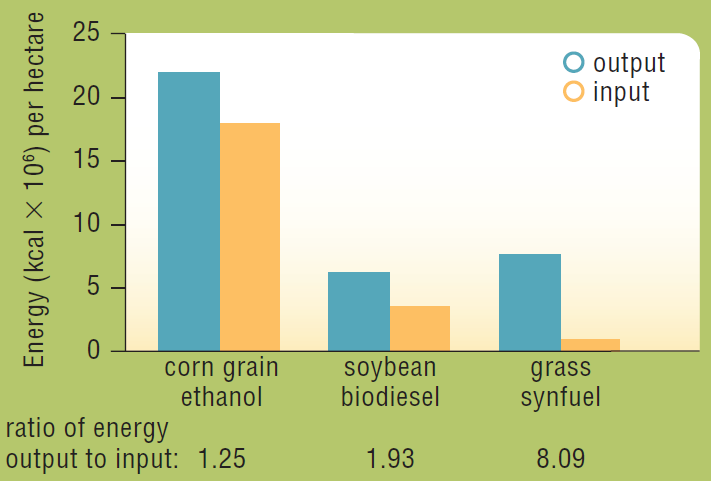
The production of which biofuel was most efficient (which had the highest ratio of energy output to energy input)?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK BIOLOGY TODAY AND TOMORROW WITHOUT
- What is a gain of function mutation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question: Please help. Thank you Is Southern hybridization's purpose detecting specific nucleotide sequences? How so?arrow_forwardUse the following information to answer the question(s) below. Martin Wikelski and L. Michael Romero (Body size, performance and fitness in Galápagos marine iguanas, Integrative and Comparative Biology 43 [2003]:376-86) measured the snout-to-vent (anus) length of Galápagos marine iguanas and observed the percent survival of different-sized animals, all of the same age. The graph shows the log snout-vent length (SVL, a measure of overall body size) plotted against the percent survival of these different size classes for males and females. Survival (%) 100- 80- 60- 40- 20- 0+ 1.9 T 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Log SVL (mm) 19) Examine the figure above. What type of selection for body size appears to be occurring in these marine iguanas? A) directional selection B) stabilizing selection C) disruptive selection D) You cannot determine the type of selection from the above information. 3arrow_forward
- 24) Use the following information to answer the question below. Researchers studying a small milkweed population note that some plants produce a toxin and other plants do not. They identify the gene responsible for toxin production. The dominant allele (T) codes for an enzyme that makes the toxin, and the recessive allele (t) codes for a nonfunctional enzyme that cannot produce the toxin. Heterozygotes produce an intermediate amount of toxin. The genotypes of all individuals in the population are determined (see table) and used to determine the actual allele frequencies in the population. TT 0.49 Tt 0.42 tt 0.09 Refer to the table above. Is this population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Yes. C) No; there are more homozygotes than expected. B) No; there are more heterozygotes than expected. D) It is impossible to tell.arrow_forward30) A B CDEFG Refer to the accompanying figure. Which of the following forms a monophyletic group? A) A, B, C, and D B) C and D C) D, E, and F D) E, F, and Garrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question. Please help with step solution and explanation. Thank you: The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) reaction consists of three steps denaturation, hybridization, and elongation. Please describe what occurs in the annealing step of the PCR reaction. (I think annealing step is hybridization). What are the other two steps of PCR, and what are their functions? Next, suppose the Tm for the two primers being used are 54C for Primer A and 67C for Primer B. Regarding annealing step temperature, I have the following choices for the temperature used during the annealing step:(a) 43C (b) 49C (c) 62C (d) 73C Which temperature/temperatures should I choose? What is the corresponding correct explanation, and why would I not use the other temperatures? Have a good day!arrow_forward
- Using the data provided on the mean body mass and horn size of 4-year-old male sheep, draw a scatterplot graph to examine how body mass and horn size changed over time.arrow_forwardPlease write a 500-word report about the intake of saturated fat, sodium, alcoholic beverages, or added sugar in America. Choose ONE of these and write about what is recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans (guideline #4) and why Americans exceed the intake of that nutrient. Explain what we could do as a society and/or individuals to reduce our intake of your chosen nutrient.arrow_forwardWrite a 500-word report indicating how you can change the quantity or quality of TWO nutrients where your intake was LOWER than what is recommended by the Dietary Guidelines for Americans and/or the DRIs. Indicate how the lack of the nutrient may affect your health. For full credit, all of the following points must be addressed and elaborated on in more detail for each nutrient: The name of the nutrient At least 2 main functions of the nutrient (example: “Vitamin D regulates calcium levels in the blood and calcification of bones.”) Your percent intake compared to the RDA/DRI (example “I consumed 50% of the RDA for vitamin D”) Indicate why your intake was below the recommendations (example: “I only had one serving of dairy products and that was why I was below the recommendations for vitamin D”) How would you change your dietary pattern to meet the recommendations? – be sure to list specific foods (example: “I would add a yogurt and a glass of milk to each day in order to increase my…arrow_forward
- Why are nutrient absorption and dosage levels important when taking multivitamins and vitamin and mineral supplements?arrow_forwardI'm struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? . Gonads . Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts . ⚫ Testes . Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) . Epididymis • Vas deferens ⚫ Seminal vesicles ⚫ 5-alpha reductase ⚫ DHT - Penis . Scrotum . Ovaries • Uterus ⚫ Fallopian tubes - Vagina - Clitoris . Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardRequisition Exercise A phlebotomist goes to a patient’s room with the following requisition. Hometown Hospital USA 125 Goodcare Avenue Small Town, USAarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





