
Concept explainers
A 0.25-kg ball is twirled at the end of a string in a horizontal circle with a radius of 0.45 m. The ball travels with a constant speed of 3.0 m/s.
- a. What is the centripetal acceleration of the ball?
- b. What is the magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce this centripetal acceleration?
- c. What is the magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball?
- d. Draw to scale a vector diagram showing these two components of the tension and estimate the magnitude of the total tension from your diagram. (See appendix C.)
(a)
The centripetal acceleration of the ball.
Answer to Problem 1SP
The centripetal acceleration of the ball is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The radius of the circle is
Write the equation for the centripetal acceleration.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the centripetal acceleration of the ball is
(b)
The magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce the centripetal acceleration.
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce the centripetal acceleration is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The mass of the ball is
The horizontal component of tension in the string provides the centripetal force and the magnitude of horizontal component of tension is equal to the magnitude of the centripetal force.
Write the equation for centripetal force.
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the horizontal component of the tension in the string required to produce the centripetal acceleration is
(c)
The magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball.
Answer to Problem 1SP
The magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball is
Explanation of Solution
Given Info: The mass of the ball is
The vertical component of tension supports the weight of the ball so that vertical component of tension in the string is equal to the weight of the ball.
Write the equation for the weight of the ball.
Here,
The value of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Thus the magnitude of the vertical component of the tension required to support the weight of the ball is
(d)
The vector diagram showing the two components of tension in the string and to estimate the magnitude of the total tension from the diagram.
Answer to Problem 1SP
The vector diagram showing the two components of tension in the string is
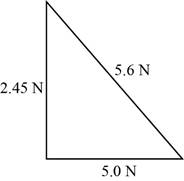
Explanation of Solution
If base of a triangle gives the horizontal component of tension and height of the triangle gives the vertical component of tension, then the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle will give the magnitude of the total tension in the string.
The vector diagram is shown in figure 1.
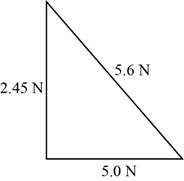
Figure 1
Write the equation for the length of the hypotenuse of the triangle.
Substitute
Conclusion:
The vector diagram showing the two components of tension in the string is plotted in figure 1 and the total tension in the string is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
- The drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m^2, while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m^2. The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Please find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (with both 1 and 2 combined) if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardThe drawing in the image attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m^2, while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m^2. The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Please find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (with both 1 and 2 combined) if the angle (theta) made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardAccording to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forward
- According to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forwardAccording to a grade 11 Physics SPH3U course Kinematics, Dynamics, and Energy answer the following questionarrow_forwardThree point-like charges in the attached image are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. Each side of the triangle has a length of 38.0 cm, and the point (C) is located half way between q1 and q3 along the side. Find the magnitude of the electric field at point (C). Let q1 = −2.80 µC, q2 = −3.40 µC, and q3 = −4.50 µC. Thank you.arrow_forward
- Three point-like charges are placed as shown in the attach image, where r1 = r2 = 44.0 cm. Find the magnitude of the electric force exerted on the charge q3. Let q1 = -1.90 uC, q2 = -2.60 uC, and q3 = +3.60 uC. Thank you.arrow_forwardThe drawing attached shows an edge-on view of two planar surfaces that intersect and are mutually perpendicular. Surface (1) has an area of 1.90 m², while Surface (2) has an area of 3.90 m². The electric field in magnitude of 215 N/C. Find the magnitude of the electric flux through surface (1 and 2 combined) if the angle theta made between the electric field with surface (2) is 30.0 degrees. Thank you.arrow_forwardA car driving at 27m/s veers to the left to avoid a deer in the road. The maneuver takes 2.0s and the direction of travel is altered by 20 degrees. What is the average acceleration during the constant speed maneuver? Do this in accordance with the example in the chapter.arrow_forward
- No No No Chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward2 C01: Physical Quantities, Units and Measurementscobris alinu zotinUD TRO Bendemeer Secondary School Secondary Three Express Physics Chpt 1: Physical Quantities, Unit and Measurements Assignment Name: Chen ShiMan loov neowled soria 25 ( 03 ) Class: 3 Respect 6 Date: 2025.01.22 1 Which group consists only of scalar quantities? ABCD A acceleration, moment and energy store distance, temperature and time length, velocity and current mass, force and speed B D. B Which diagram represents the resultant vector of P and Q? lehtele 시 bas siqpeq olarist of beau eldeo qirie-of-qi P A C -B qadmis rle mengaib priwollot erT S Quilons of qira ono mont aboog eed indicator yh from West eril to Inioqbim srij enisinoo MA (6) 08 bas 8A aldao ni nolent or animaleb.gniweb slepe eld 260 km/h D 1 D. e 51arrow_forwardThe figure gives the acceleration a versus time t for a particle moving along an x axis. The a-axis scale is set by as = 12.0 m/s². At t = -2.0 s, the particle's velocity is 11.0 m/s. What is its velocity at t = 6.0 s? a (m/s²) as -2 0 2 t(s) 4arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





