
Figure 5-19 gives the free-body diagram for four situations in which an object is pulled by several forces across a frictionless floor, as seen from overhead. In which situations does the acceleration
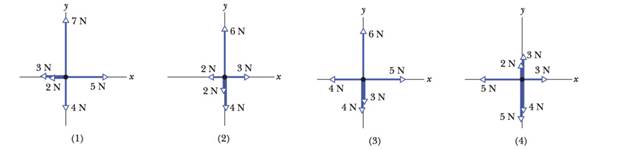
To Find
a) Which situation have x component of acceleration.
b) Which situation have y component of acceleration.
c) Direction of acceleration for each situation.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution
a) 2, 3 and 4.
b) 1, 3 and 4.
c) 1 – Along + y-axis, 2- Along + x-axis, 3- In 4th quadrant and 4- In 3rd quadrant.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Using the concept of net force from the Newton’s second law of motion, we can find the net force acting on the given object for given conditions.
2) Calculations:
a) According to Newton’s second law net force is product of mass and acceleration.
If we want x component acceleration there must be net force in x direction
So, For situation 1
Net force in x direction
So, there is no x component of acceleration.
For Situation 2
Net Force in x direction
As net force is 1N, x component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 3
Net Force in x direction
As net force is 1N, x component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 4
Net Force in x direction
As net force is 1N, x component of acceleration is present.
b)
For situation 1
Net force in y direction
So, there is y component of acceleration.
For Situation 2
Net Force in y direction
As net force is no y component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 3
Net Force in y direction
As net force is -1N, y component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 4
Net Force in y direction
As net force is -4N, y component of acceleration is present.
c) Direction of acceleration is in direction of net force.
For situation 1 there is only net force is only in +y direction so acceleration is also in +y direction.
For situation 2 there is only net force is only +x direction so acceleration is also +x direction.
For situation 3 as there is net force both in x and y direction and total net force is in fourth quadrant.
For situation 4 as there is net force both in x and y direction and total net force is in third quadrant.
Conclusion: Using the equations from the Newton’s second law of motion and vector algebra, it is possible to find the net force acting on the system.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS,AP ED.
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardA rectangular current loop (a = 15.0 cm, b = 34.0 cm) is located a distance d = 10.0 cm near a long, straight wire that carries a current (Iw) of 17.0 A (see the drawing). The current in the loop is IL = 21.0 A. Determine the magnitude of the net magnetic force that acts on the loop. Solve in N. a b IL Iwarrow_forward
- Two long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forwardI tried to solve this question, and I had an "expert" answer it and they got it wrong. I cannot answer this questionarrow_forwardEddie Hall is the current world record holder in the deadlift, a powerlifting maneuver in which a weighted barbell is lifted from the ground to waist height, then dropped. The figure below shows a side view of the initial and final positions of the deadlift. a 0 = 55.0° Fift h22.5 cm i hy = 88.0 cm b iarrow_forward
- solve for (_) Narrow_forwardTwo boxes of fruit on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light string as in the figure below, where m₁ = 11 kg and m₂ = 25 kg. A force of F = 80 N is applied to the 25-kg box. mq m1 Applies T Peaches i (a) Determine the acceleration of each box and the tension in the string. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s² N (b) Repeat the problem for the case where the coefficient of kinetic friction between each box and the surface is 0.10. acceleration of m₁ acceleration of m₂ tension in the string m/s² m/s2 Narrow_forwardAll correct but t1 and t2 from part Aarrow_forward
- Three long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I₁ = 3.50 A, I2 = 5.50 A, and I3 = 8.50 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 34.0 cm, and the point (A) is located half way between (11) and (12) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (A). Solve in Teslas (T). I₁arrow_forwardNumber There are four charges, each with a magnitude of 2.38 μC. Two are positive and two are negative. The charges are fixed to the corners of a 0.132-m square, one to a corner, in such a way that the net force on any charge is directed toward the center of the square. Find the magnitude of the net electrostatic force experienced by any charge. ips que Mi Units estic re harrow_forwardTwo long, straight wires are separated by distance, d = 22.0 cm. The wires carry currents of I1 = 7.50 A and I2 = 5.50 A in opposite directions, as shown in the figure. Find the magnitude of the net magnetic field at point (B). Let r₁ = 12.0 cm, r2 = 7.00 cm, and r3 = 13.0 cm. Solve in T. 12 d A √3arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





