
Concept explainers
For each configuration in Fig. 5.88, find the individual (not combinations of) elements (voltage sources and/or resistors) that are in series.
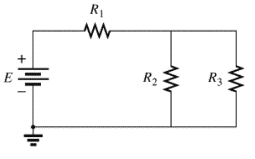
(a)
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration.
Answer to Problem 1P
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circuit is given below.

Calculation:
The given circuit is analyzed by the rules of series-parallel combination.
As per the series combination rule,
Conclusion:
(b)
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration.
Answer to Problem 1P
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circuit is given below,
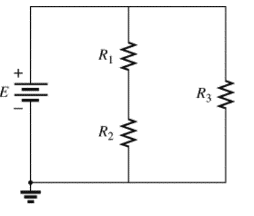
Calculation:
The given circuit is analyzed by the rules of series-parallel combination.
As per the series combination rule,
Conclusion:
(c)
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration.
Answer to Problem 1P
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circuit is given below,
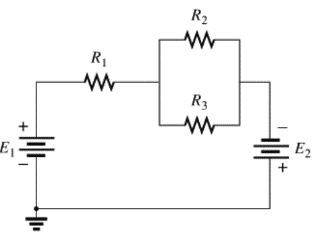
Calculation:
The given circuit is analyzed by the rules of series-parallel combination.
As per the series combination rule,
Conclusion:
(d)
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration.
Answer to Problem 1P
The individual elements that are connected in series for the given configuration are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The circuit is given below,
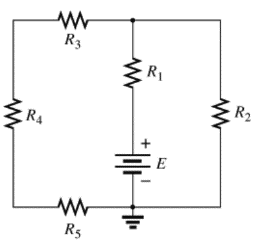
Calculation:
The given circuit is analyzed by the rules of series-parallel combination.As per the series combination rule of resistances,
Conclusion:
Therefore,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis; Laboratory Manual For Introductory Circuit Analysis Format: Kit/package/shrinkwrap
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
- NO AI PLEASE SHOW WORKarrow_forwardConsider a Continuous- time LTI System. described by y' (+)+ nycH) = x(+) find yet for усн b) x(+) = u(+) Sul. a) x(+)= ētu(+). c) X(+= √(+) jw few) +2 kW) = X (w) (jw+2) Y(W)= X(w) Han Youn X(w) ½ztjuk a) X (W) = 1 + jw Y(W)= X(w) H(W). I tjw z+jw tjw = 1+jw 2+jw y (+) = (e+ - e²+) 4(+) b) XIW): π (W) + |/|/w Y₁W) = [π √(W) + 1/w] =² + j w zxjw How = π √(w) 1 ㅠ беш) 24jw + *= II 8 (W) + 1 1 1 1 2 4 jw = 2 y(+)= \uct) - e²+us+] - SINAALINE ju 2+ jwarrow_forwardNO AI PLEASE SHOW WORKarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardCompute the Laplace transform of the following time domain function using only L.T. properties: f(t)=(t-3)eu(t-2) The Laplace Transform of x(t) = 8(-1) - u(1) is X(s): = (a) 2πδ(s) (b) 1-1 S (c) j2πδ (s) (d) - 1/3 Sarrow_forwardUf you don't know, don't attempt this questions,no Ai or it's screen shot should be usedarrow_forward
- Find the initial and final values of sequence x(n) from X(Z) below using the initial and final value properties X(Z) = = z-1arrow_forwardOnly expert should attempt,no Ai or screen shot it solving, I need solution s to all of themarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- Find the autocorrelation function of the periodic function x(t) 1 0 1 2 3 tarrow_forwardFind Laplace transform for x(t) = e−³t √∞ (1 − t) sin(t − 2) §(t)dt Find Laplace transform and the corresponding ROC for x(t) = e˜³τsin(2t) u(t)dtarrow_forwardfind the inverse Laplace transform of X(s)=- s+5 (s-1)(s-2)(s-3) i) Re[s]> 3 ii) Re[s]<1 iii) 1arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 EBK ELECTRICAL WIRING RESIDENTIALElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337516549Author:SimmonsPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK ELECTRICAL WIRING RESIDENTIALElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337516549Author:SimmonsPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
