
An elevator suspended by a cable is descending at constant velocity. How many forcevector would be shown on a free-body diagram? Name them.
The force vectors acting on the elevator under given conditions
Explanation of Solution
The elevator is descending at a constant velocity.
Since the elevator is descending at a constant velocity, it experiences no acceleration. Therefore, the net force acting on the elevator is zero. The elevator is supported by the cable. Therefore, the tension of the cable acts upward. The other force on the elevator is its weight. The situation is explained by the free-body diagram given below.
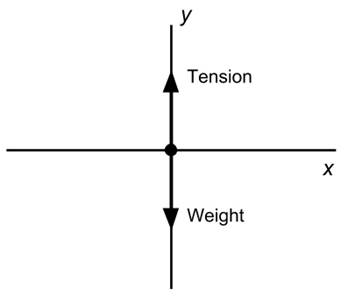
When the net force acting on the elevator is zero and two forces act on it, both forces will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Conclusion:
There are two forces acting on the elevator when it is descending with a constant velocity. The forces are the tension of the cable and the weight of the elevator.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics, Books a la Carte Edition; Student Workbook for Physics for Scientists ... eText -- ValuePack Access Card (4th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Car P moves to the west with constant speed v0 along a straight road. Car Q starts from rest at instant 1, and moves to the west with increasing speed. At instant 5, car Q has speed w0 relative to the road (w0 < v0). Instants 1-5 are separated by equal time intervals. Sketch and label a vector diagram illustrating the Galilean transformation of velocities that relates velocity of car P relative to the road, velocity of car Q relative to road, and velocity of car Q relative to car P at instant 3. In the frame of car P, at instant 3 is car Q moving to the west, moving to the east, or at rest? Explain.arrow_forwardJust 5 and 6 don't mind 7arrow_forwardIn an electron gun, electrons are accelerated through a region with an electric field of magnitude 1.5 × 104 N/C for a distance of 2.5 cm. If the electrons start from rest, how fast are they moving after traversing the gun?arrow_forward
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardPlease solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwarda) Use the node-voltage method to find v1, v2, and v3 in the circuit in Fig. P4.14. b) How much power does the 40 V voltage source deliver to the circuit? Figure P4.14 302 202 w w + + + 40 V V1 80 Ω 02 ΣΑΩ 28 A V3 + w w 102 202arrow_forward
- Please solve and answer this problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardYou're on an interplanetary mission, in an orbit around the Sun. Suppose you make a maneuver that brings your perihelion in closer to the Sun but leaves your aphelion unchanged. Then you must have Question 2 options: sped up at perihelion sped up at aphelion slowed down at perihelion slowed down at aphelionarrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
- The force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE DO NOT USE LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardThe force of the quadriceps (Fq) and force of the patellar tendon (Fp) is identical (i.e., 1000 N each). In the figure below angle in blue is Θ and the in green is half Θ (i.e., Θ/2). A) Calculate the patellar reaction force (i.e., R resultant vector is the sum of the horizontal component of the quadriceps and patellar tendon force) at the following joint angles: you need to provide a diagram showing the vector and its components for each part. a1) Θ = 160 degrees, a2) Θ = 90 degrees. NOTE: USE ONLY TRIGNOMETRIC FUNCTIONS (SIN/TAN/COS, NO LAW OF COSINES, NO COMPLICATED ALGEBRAIC EQUATIONS OR ANYTHING ELSE, ETC. Question A has 2 parts!arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





