
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System & Modified MasteringMicrobiology with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Microbiology with Diseases by Body System Package
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780133857122
Author: Robert W. Bauman Ph.D.
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 1CM
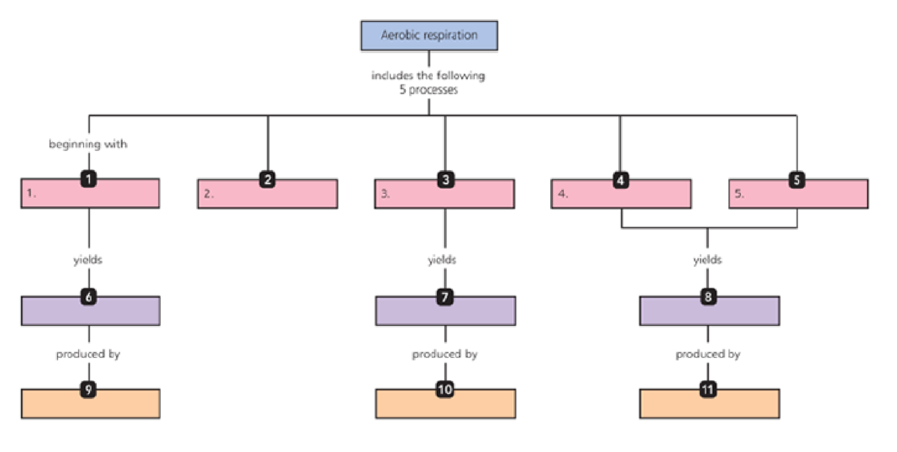
Using the following terms, fill in the following concept map that describes aerobic respiration. You can also complete this and other concept maps online by going to the MasteringMicrobiology Study Area.
2 ATP (2)
34 ATP
Chemiosmosis
Electron transport chain
Glycolysis
Krebs cycle
Oxidative phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation (2)
Synthesis of acetyl-CoA
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
-Complete the table by filling up the necessary details.-It's not incomplete.- Thank you in advance.
Complete the table ATP Yield from Anaerobic Respiration (for 1 Glucose Molecule)
Use the labels to complete this Venn diagram, comparing and contrasting the three pathways of glucose metabolism. Be sure to use
the roll-over hints to place the labels correctly.
Aerobic Respiration
2-36 ATP
Oxygen
2 ATP
Sulfate,
phosphate, and
nitrate
Glycolysis
Krebs cycle
Do not require
oxygen
Respiratory
chain
36-38 ATP
Organic
compounds
Fermentation
Anaerobic Respiration
Total ATP yield
Reset
Chapter 5 Solutions
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System & Modified MasteringMicrobiology with Pearson eText -- ValuePack Access Card -- for Microbiology with Diseases by Body System Package
Ch. 5 - How can oxidation take place in an anaerobic...Ch. 5 - Why do electrons carried by NADH allow for...Ch. 5 - Why does catabolism of amino acids for energy...Ch. 5 - An uninformed student describes the Calvin-Benson...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5TMWCh. 5 - Why is feedback inhibition necessary for...Ch. 5 - Breaks a large molecule into smaller ones a....Ch. 5 - Includes dehydration synthesis reactions a....Ch. 5 - Prob. 3MCCh. 5 - Prob. 4MC
Ch. 5 - Involves the production of cell membrane...Ch. 5 - Includes hydrolytic reactions a. anabolism only b....Ch. 5 - Includes metabolism a. anabolism only b. both...Ch. 5 - Prob. 8MCCh. 5 - A reduced molecule _________. a. has gained...Ch. 5 - Prob. 10MCCh. 5 - Coenzymes are ________. a. types of apoenzymes b....Ch. 5 - Which of the following statements best describes...Ch. 5 - Which of the following does not affect the...Ch. 5 - Most oxidation reactions in bacteria involve the...Ch. 5 - Under ideal conditions, the fermentation of one...Ch. 5 - Under ideal conditions, the complete aerobic...Ch. 5 - Which of the following statements about the...Ch. 5 - Reactions involved in the light-independent...Ch. 5 - The glycolysis pathway is basically __________. a....Ch. 5 - A major difference between anaerobic respiration...Ch. 5 - 1. _______ Occurs when energy from a compound...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 1. The final electron acceptor...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 2. Two ATP molecules are used...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 3. The initial catabolism of...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 4. ________ is a cyclic series...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 5. The final electron acceptor...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 6. Three common inorganic...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 7. Anaerobic respiration...Ch. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 8. Complete the following...Ch. 5 - Prob. 9FIBCh. 5 - Fill in the Blanks 10 The main coenzymes that...Ch. 5 - VISUALIZE IT! 1 Label the mitochondrion to...Ch. 5 - Label the diagram below to indicate acetyl-CoA,...Ch. 5 - Examine the biosynthetic pathway for the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 1SACh. 5 - Why we enzymes necessary for anabolic reactions to...Ch. 5 - How do organisms control the rate of metabolic...Ch. 5 - How does a nor-competitive inhibitor at a single...Ch. 5 - Explain the mechanism of negative feedback with...Ch. 5 - Facultative anaerobes can live under either...Ch. 5 - How does oxidation of a molecule occur without...Ch. 5 - List at least four groups of microorganisms that...Ch. 5 - Why do we breathe oxygen and give of carbon...Ch. 5 - Why do cyanobacteria and algae take in carbon...Ch. 5 - What happens to the carbon atoms in sugar...Ch. 5 - How do yeast cells make alcohol and cause bread to...Ch. 5 - Where specifically does the most significant...Ch. 5 - Why are vitamins essential metabolic factors for...Ch. 5 - A laboratory scientist notices that a cer1ain...Ch. 5 - Arsenic is a poison that exists in two states in...Ch. 5 - Explain why an excess of all three of the amino...Ch. 5 - Why might an organism that uses glycolysis and the...Ch. 5 - Describe how bacterial fermentation causes milk to...Ch. 5 - Giardia intestinalis and Entamoeba histolytica are...Ch. 5 - Two cultures of a facultative anaerobe are grown...Ch. 5 - What is the maximum number of molecules of ATP...Ch. 5 - In terms of its effects on human metabolism, why...Ch. 5 - Cyanide is a potent poison because it irreversibly...Ch. 5 - How are photophosphorylation and oxidative...Ch. 5 - Members of the pathogenic bacterial genus...Ch. 5 - Compare and contrast aerobic respiration,...Ch. 5 - Scientists estimate that up to one-third of Earths...Ch. 5 - A young student was troubled by the idea that a...Ch. 5 - If a bacterium uses beta-oxidation to catabolize a...Ch. 5 - Some desert rodents rarely have water to drink....Ch. 5 - Prob. 17CTCh. 5 - We have examined the total ATP, NADH, and FADH2...Ch. 5 - Explain why hyperthermophiles do not cause disease...Ch. 5 - In addition to extremes in temperature and pH,...Ch. 5 - Figure 5.18b illustrates events in aerobic...Ch. 5 - Suppose you could insert a tiny pH probe into the...Ch. 5 - Even though Pseudomonas aeruginosa and...Ch. 5 - Photosynthetic organisms are rarely pathogenic....Ch. 5 - Prob. 25CTCh. 5 - A scientist moves a green plant grown in sunlight...Ch. 5 - What class of enzyme is involved in amination...Ch. 5 - Using the following terms, fill in the following...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following are correct statements pertaining to the glycolytic pathway? Choose all correct statements. Glucose is a substrate for the first reaction of glycolysis, Glycolysis is an aerobic process Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Glycolysis is the process by which glucose is converted to acetyl CoA Major products of glycolysis include pyruvate, ATP and NADH Dago Next Page Page 31 of 36arrow_forward5 Complete this chart to help organize the catabolic pathways including ATP/NAD+ production.arrow_forwardWord Bank 2 Acetyl-CoA 2 ATP 2 ATP 34 ATP 2€0€ 4 CO₂ Electron transport chain 2 FADH₂ Fermentation Glucose- Glycolysis Krebs cycle Lactic Acid 2 NADH -2 NADH- 6 NADH NADT 2-Pyruvate Fermentation whose products include ↓ Lactic Acid and regenerates Cellular Respiration begins with CO NADE Glucose In the absence of 0₂ can be used in which is broken down during Glycolysis 1 which produces ↓ 2 Pyruvate 2002 2ATP + yielding a net gain of 2NADH In the presence of 0₂ can be used to produce + which is catabolized via the Krebs cycle with a net yield of used in the Electron transport Chain to produce 34ATP used in thearrow_forward
- Consider the Kreb's Cycle below. Fill in the blanks using the pool of answers below. Acetyl-SCOA A enzyme N B substrate NADH substrate Aconitase NAD+ M enzyme malate substrate NAD* fumarase Isocitrate NADH dehydrogenase CO2 fumarate K a-ketoglutarate a-ketoglutarate CoA dehydrogenase product enzyme substrate CoA CO2 substrate H substrate succinyl-SC0A product substrate product Pool of Answers: isocitrate. malate dehydrogenase oxaloacetate FADH2 FAD ATP ADP citrate NADH NAD+ GDP GTP citrate synthase citrate lyase succinate succinate dehydrogenasearrow_forwardBelow is an image showing how cellular respiration is regulated. Imagine someone ingested a toxin that prevents pyruvate from entering the mitochondria. Which of the following statements is true? Inhibits ATP Glucose GLYCOLYSIS Copyright 2018 Pearson Canada Inc. Fructose 6-phosphate Phosphofructokinase Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Pyruvate Acetyl COA CITRIC ACID CYCLE Oxidative phosphorylation AMP I Stimulates Inhibits Citrate The amount of citrate in the cell would decrease, leading to a decrease in the activity of phosphofructokinse. The amount of citrate in the cell would increase, leading to a decrease in the activity of phosphofructokinse. The amount of citrate in the cell would decrease, leading to an increase in the activity of phosphofructokinse. The amount of citrate in the cell would increase, leading to an increase in the activity of phosphofructokinse.arrow_forward-Complete the table by filling up the necessary details.-It's not incomplete.- Thank you in advance.arrow_forward
- All of the following are true for both anaerobic respiration and fermentation except: Lack the electron transport chain Result in the production of NADH Produce less ATP than aerobic respiration Involve the breakdown of glucose to pyruvic acid Can proceed in the absence of oxygenarrow_forwardPlease help fill out the tablearrow_forwardFill in table below. In addition, understand the differences in ATP generated via the Aerobic VS Anaerobic route and fill in a fifth submpathway (labelled 5.) that defines this info for the Anaerobic route. Subpathway Molecule In Molecule Out Energy Obtained 1. glycolysis 2. synth acetyl-CoA 3. Krebs cycle 4. ETCarrow_forward
- Place the following molecules in the order in which they appear during aerobic respiration: Citrate G3P Glucose-6-phosphate Pyruvate Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate Glucose Acetyl-CoAarrow_forwardAnswer J,N and Harrow_forwardWhich of the following statements best explains why anaerobic respiration releases energy from organic compounds Anaerobic respiration partially oxidizes glucose, which is an organic compound This happens during glycolysis The result of the glycolysis is the net production of 2 ATP molecules which are used by the cell for energy Anaerobic respiration partially oxidizes glucose, which is an inorganic compound This happens during glycolysis The result of the glycolysis is the net production of 4 ATP molecules which are used by the cell for energy Anaerobic respiration partially oxidizes glucose, which is an organic compound This happens during glycolysis The result of the glycolysis is the net production of 4 ATP molecules which are used by the cell for energy Anaerobic respiration fully oxidizes glucose, which is an organic compound This happens during glycolysis The result of the glycolysis is the net production of 4 ATP molecules which are used by the cell for energyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning


Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...
Biology
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Anaerobic Respiration; Author: Bozeman Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cDC29iBxb3w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY