
Concept explainers
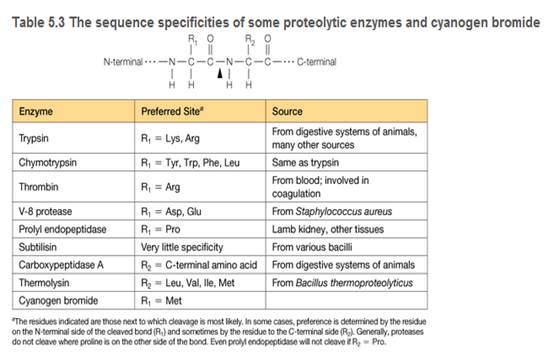
You are a summer intern in a clinical hematology lab. The lab director gives you a sample of a patient's blood proteins and asks you to characterize the thrombin in the sample. She also tells you that thrombin is a serine protease important in blood clotting (see Table 5.3), and this patient is a newborn with uncontrolled bleeding.
a. To characterize the thrombin in the sample, you must remove two proteins that interfere with the thrombin activity assay: cytochrome c and lactoglobin. You find some CM-cellulose (see Figure 5A.5) and a phosphate buffer (pH 6.4) on the shelf in your lab. You decide to load the protein sample onto a column of CM-cellulose equilibrated in the pH = 6.4 buffer. Predict the order of elution for the three proteins shown in the accompanying table. At pH = 6.4, which protein(s) do you predict will remain bound to the column?
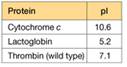
b. List two different ways you could change the buffer to elute the bound protein(s) and achieve proper separation of the proteins.
c. You are surprised to observe that the patient's thrombin flows through the CM-cellulose column at pH = 6.4 and does not bind. Confident in your technique, you suspect the patient's thrombin is different from wild-type thrombin. Using a different buffer system, you manage to purify some of the patient's thrombin, and you submit the purified sample for amino acid sequencing. The sequence analysis shows that the patient's thrombin contains a mutation in the enzyme active site. A lysine residue in the wild type has been mutated to an asparagine in the patient's thrombin. Does this mutation explain the anomalous CM- cellulose binding behavior you observed?
d. How many
e. Based on their side-chain structures, compare and contrast the potential of Lys and Asn to form noncovalent interactions. In other words, can each form H bonds and/or salt bridges and/or van der Waals contacts?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
BIOCHEMISTRY BOOKS ALC&MOD MST/ET PKG
- Biochemistry Please help. Thank you When carbamyl phosphate is joined to L-ornathine, where does the energy for the reaction come from?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you What is the function of glutamate dehydrogenase?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question Please help. Thank you How and why does a high protein diet affect the enzymes of the urea cycle?arrow_forward
- Biochemistry What is the importance of the glucose-alanine cycle?arrow_forwardBiochemistry Assuming 2.5 molecules of ATP per oxidation of NADH/(H+) and 1.5molecules of ATP per oxidation of FADH2, how many ATP are produced per molecule of pyruvate? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. How would you explain the term ‘good food’? 2. How would you define Nutrition? 3. Nutrients are generally categorised into two forms. Discuss.arrow_forward
- Biochemistry Question. Please help solve. Thank you! Based upon knowledge of oxidation of bioorganic compounds and howmuch energy is released during their oxidation, rank the following, from most to least, with respect to how much energy would be produced from each during their oxidation. Explain your placement for each one.arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question.For the metabolism of amino acids what is the first step for theirbreakdown? Why is it necessary for this breakdown product to be transported to the liver? For the catabolism of the carbon backbone of these amino acids, there are 7 entry points into the “standard” metabolic pathways. List these 7 entry points and which amino acids are metabolized to these entry points. Please help. Thank you!arrow_forwardBiochemistry Question. Please help. Thank you. You are studying pyruvate utilization in mammals for ATP production under aerobic conditions and have synthesized pyruvate with Carbon #1 labelled with radioactive C14. After only one complete cycle of the TCA cycle, which of the TCA cycle intermediates would be labeled with C14? Explain your answer. Interestingly, you find C14 being excreted in the urine. How does it get there?arrow_forward
- Biochemistry question. Please help with. Thanks in advance For each of the enzymes listed below, explain what the enzyme does including function, names (or structures) of the substrate and products and the pathway(s) (if applicable) it is/are found in. (a) ATP synthetase (b) succinate dehydrogenase (c) isocitrate lyase (d) acetyl CoA carboxylase (e) isocitrate dehydrogenase (f) malate dehydrogenasearrow_forwardDraw and name each alcohol and classify it as primary, secondary, or tertiary. Explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forwardDraw the product of each reaction. If there are multiple products, draw only the major product. Explain your answer thoroughly.arrow_forward
 Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College





