
Concept explainers
To review:
The change in blood flow after the surgical removal of the pulmonary bypass shunt in alligators, with the help of a diagram, and how the surgery made the alligator heart behave like a bird heart.
Introduction:
The heart in crocodiles and alligators has four chambers, but they differ from bird hearts because they have two aortas. The two aortas are connected by a shunt known as the pulmonary bypass shunt. A surgery was performed in order to remove this shunt by closing the left aorta near the left ventricle.
Explanation of Solution
The surgery was performed and the flow of blood after the surgical removal of the pulmonary bypass shunt in alligator heart is shown in the figure below:
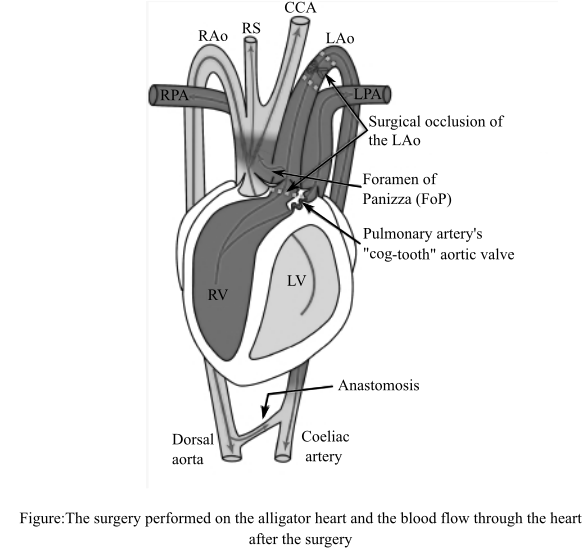
The diagram shows the potential flow of blood through the alligator’s heart at the time of the cardiac shunt. The blood flows from the left aorta, foramen of Panizza, and into the right aortic arch. The scissors symbol and the dotted lines in the diagram show the location at which the surgery was performed and the flow of blood to the left aorta was blocked.
After the surgical removal of the cardiac shunt, the alligator heart became similar to a bird heart. The major difference between the bird and alligator heart is that the alligator heart has two aortas, while the heart in birds has only one. The occlusion of the left aorta in alligator meant that it was only left with one functional aorta through which the blood could flow.
The right ventricle would pump blood into the lungs through the pulmonary artery and the left ventricle would pump blood to the rest of the body through the aorta.
Therefore, it can be concluded that by blocking the left aorta or by removing the pulmonary bypass shunt surgically, the alligator heart starts behaving like a bird’s heart.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 49 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- Molecular Biology Please help and there is an attached image. Thank you. A bacteria has a gene whose protein/enzyme product is involved with the synthesis of a lipid necessary for the synthesis of the cell membrane. Expression of this gene requires the binding of a protein (called ACT) to a control sequence (called INC) next to the promoter. A. Is the expression/regulation of this gene an example of induction or repression?Please explain:B. Is this expression/regulation an example of positive or negative control?C. When the lipid is supplied in the media, the expression of the enzyme is turned off.Describe one likely mechanism for how this “turn off” is accomplished.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help. Thank you. Discuss/define the following:(a) poly A polymerase (b) trans-splicing (c) operonarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you in advance. Discuss, compare and contrast the structure of promoters inprokaryotes and eukaryotes.arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the absence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).1. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent the binding of lactose2. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent release of lactose once lactose hadbound3. Normally the lac repressor gene is located next to (a few hundred base pairs) and upstreamfrom the lac operon. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that move the lac repressor gene 100,000base pairs downstream.4. Mutations in the lac operator that would prevent binding of lac repressorarrow_forwardYou have returned to college to become a phylogeneticist. One of the first things you wish to do is determine how mammals, birds, and reptiles are related. Like any good scientist, you need to consider all available data objectively and without a preconceived “correct” answer. In pursuit of that, you should produce a phylogenetic tree based only on morphological features that show birds and mammals are more closely related. You will then produce a totally different tree, also using morphological features, that shows birds and reptiles are more closely related. Do not forget to include all three groups in both your trees. Based solely off the trees you produce, which relationship would you consider the more likely and why? Once you have answered that question, provide a brief summary of the “modern” understanding of the relationship between these three groups.arrow_forwardtrue or false, the reason geckos can walk on walls is hydrogen bonding between their foot pads and the moisture on the wall.arrow_forward
- Biology laboratory problem Please help. thank you You have 20 ul of DNA solution and 6X DNA loading buffer solution. You have to mix your DNA solution and DNA loading buffer before load DNA in an agarose gel. The concentration of the DNA loading buffer must be 1X in the DNA and DNA-loading buffer mixture after you mix them. For that, I will add _____ ul of 6X loading buffer to the 20 ul DNA solution.arrow_forwardBiology lab problem To make 20 ul of 5 mM MgCl2 solution using 50 mM MgCl2 stock solution and distilled water, I will mix ________ ul of 50 mM MgCl2 solution and ________ ul of distilled water. Please help . Thank youarrow_forwardBiology Please help. Thank you. Biology laboratory question You need 50 ml of 1% (w/v) agarose gel. Agarose is a powder. How would you make it? You can ignore the volume of agarose powder. Don't forget the unit.TBE buffer is used to make an agarose gel, not distilled water. I will add _______ of agarose powder into 50 ml of distilled water (final 50 ml).arrow_forward
- An urgent care center experienced the average patient admissions shown in the Table below during the weeks from the first week of December through the second week of April. Week Average Daily Admissions 1-Dec 11 2-Dec 14 3-Dec 17 4-Dec 15 1-Jan 12 2-Jan 11 3-Jan 9 4-Jan 9 1-Feb 12 2-Feb 8 3-Feb 13 4-Feb 11 1-Mar 15 2-Mar 17 3-Mar 14 4-Mar 19 5-Mar 13 1-Apr 17 2-Apr 13 Forecast admissions for the periods from the first week of December through the second week of April. Compare the forecast admissions to the actual admissions; What do you conclude?arrow_forwardAnalyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.arrow_forwardI have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.arrow_forward
 Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning
Medical Terminology for Health Professions, Spira...Health & NutritionISBN:9781305634350Author:Ann Ehrlich, Carol L. Schroeder, Laura Ehrlich, Katrina A. SchroederPublisher:Cengage Learning





