
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134382593
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4.6, Problem 2PP
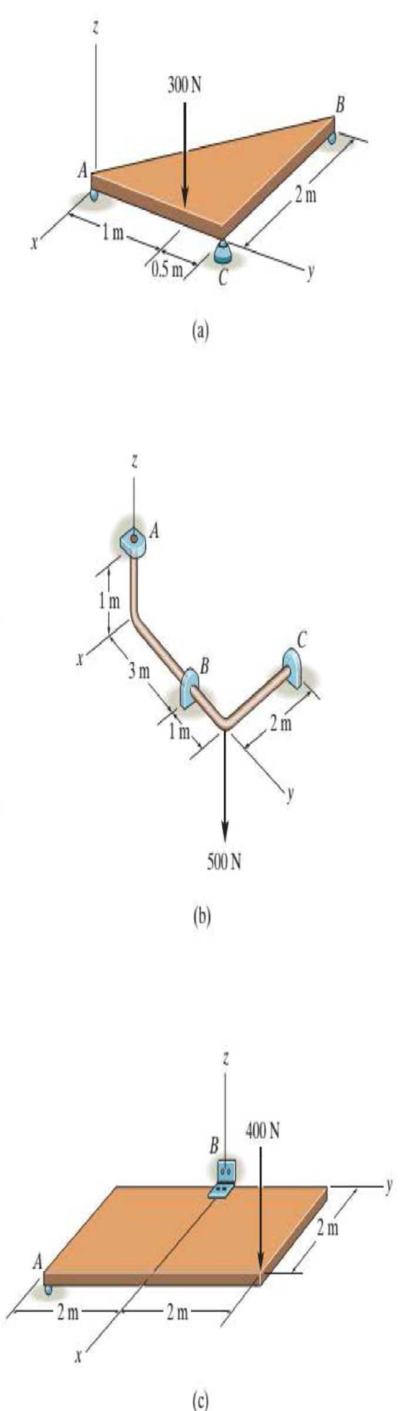
Draw the free-body diagram of each object.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer
CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer
CE-112 solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer please
Chapter 4 Solutions
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
Ch. 4.4 - Draw the free-body diagram of each object. Prob....Ch. 4.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 4.4 - The truss is supported by a pin at A and a roller...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the components of reaction at the fixed...Ch. 4.4 - The 25-kg bar has a center of mass at G. If it is...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the reactions at the smooth contact...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the components of the support reactions...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob. 4-2Ch. 4.4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...
Ch. 4.4 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob. 4-4Ch. 4.4 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob. 4-5Ch. 4.4 - Determine the reactions at the supports. Prob. 4-6Ch. 4.4 - Determine the magnitude of force at the pin A and...Ch. 4.4 - The dimensions of a jib crane are given in the...Ch. 4.4 - The dimensions of a jib crane are given in the...Ch. 4.4 - The smooth pipe rests against the opening at the...Ch. 4.4 - The beam is horizontal and the springs are...Ch. 4.4 - The 10-kg uniform rod is pinned at end A. If it is...Ch. 4.4 - The man uses the hand truck to move material up...Ch. 4.4 - Three uniform books, each having a weight W and...Ch. 4.4 - Determine the reactions at the pin A and the...Ch. 4.4 - If rope BC will fail when the tension becomes 50...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 17PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 18PCh. 4.4 - The cantilever footing is used to support a wall...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 20PCh. 4.4 - A boy stands out at the end of the diving board,...Ch. 4.4 - Prob. 22PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 23PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 24PCh. 4.4 - Prob. 25PCh. 4.4 - The man attempts to pull the four wheeler up the...Ch. 4.6 - Draw the free-body diagram of each object.Ch. 4.6 - In each case, write the moment equations about the...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 7FPCh. 4.6 - Prob. 8FPCh. 4.6 - The rod is supported by smooth journal bearings at...Ch. 4.6 - Determine the support reactions at the smooth...Ch. 4.6 - Determine the force developed in the short link...Ch. 4.6 - Determine the components of reaction that the...Ch. 4.6 - The uniform load has a mass of 600 kg and is...Ch. 4.6 - Due to an unequal distribution of fuel in the wing...Ch. 4.6 - Determine the components of reaction at the fixed...Ch. 4.6 - The 50-lb mulching machine has a center of gravity...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 30PCh. 4.6 - The uniform concrete slab has a mass of 2400 kg....Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 32PCh. 4.6 - Determine the tension in each cable and the...Ch. 4.6 - The bent rod is supported at A, B, and C by smooth...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 35PCh. 4.6 - The bar AB is supported by two smooth collars. At...Ch. 4.6 - The rod has a weight of 6 lb/ft. If it is...Ch. 4.6 - The sign has a mass of 100 kg with center of mass...Ch. 4.6 - Both pulleys cite fixed to the shaft and as the...Ch. 4.6 - Both pulleys are fixed to the shaft and as the...Ch. 4.6 - Prob. 41PCh. 4.8 - Determine the friction force at the surface of...Ch. 4.8 - Determine the couple moment M needed to cause...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 6PPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 7PPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 13FPCh. 4.8 - Determine the minimum force P to prevent the 30-kg...Ch. 4.8 - Determine the maximum force P that can be applied...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 16FPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 17FPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 18FPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 19FPCh. 4.8 - If the coefficient of static friction at all...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 21FPCh. 4.8 - Prob. 42PCh. 4.8 - The tractor exerts a towing force T = 400 lb....Ch. 4.8 - The mine car and its contents have a total mass of...Ch. 4.8 - The winch on the truck is used to hoist the...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 46PCh. 4.8 - The automobile has a mass of 2 Mg and center of...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 48PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 49PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 50PCh. 4.8 - Determine the angle at which the applied force P...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 52PCh. 4.8 - The 180-lb man climbs up the ladder and stops at...Ch. 4.8 - The 180-lb man climbs up the ladder and stops at...Ch. 4.8 - The spool of wire having a weight of 300 lb rests...Ch. 4.8 - The spool of wire having a weight of 300 lb rests...Ch. 4.8 - The ring has a mass of 0.5 kg and is resting on...Ch. 4.8 - Determine the smallest force P that must be...Ch. 4.8 - The man having a weight of 200 lb pushes...Ch. 4.8 - The uniform hoop of weight W is subjected to the...Ch. 4.8 - Prob. 61PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 62PCh. 4.8 - Prob. 63PCh. 4.8 - The coefficient of static Friction between the...Ch. 4 - If the roller at B can sustain a maximum load of 3...Ch. 4 - Determine the reactions at the supports A and B...Ch. 4 - Determine the normal reaction at the roller A and...Ch. 4 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 4 - Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at...Ch. 4 - Prob. 6RPCh. 4 - Prob. 7RPCh. 4 - The uniform 60-kg crate C rests uniformly on a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forward
- CE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct asnwerarrow_forwardthis is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = -4, Ay = -12,Az = 32.5, Bx= 34, Bz = 5, By = 0 but how?arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam, the answer is Ax = Az = 0, Ay = 2000, TDE = 4750, Cx = 2000, Cy = 2000, Cz = -800 but how?arrow_forward
- this is an old practice exam, the answer is Fmin = 290.5lb but howarrow_forwardThis is an exam review question. The answer is Pmin = 622.9 lb but whyarrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
- Please do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardThis is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Chemical and Phase Equilibrium; Author: LearnChemE;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SWhZkU7e8yw;License: Standard Youtube License