
Concept explainers
To analyze:
The capability of the response of moths with disrupted tymbal organs to the evasive behaviors of bats. The importance of this parameter for the validity of given experiment.
Given information:
Researchers used tiger moths (Bertholdia trigona) to test whether ultrasonic clicks produced by unique tymbal organs located in the thorax of moths, jam the echolocation to avoid capture by bats. Bats are known to catch these moths by echolocation.
Experiments were conducted on two groups of moths, out of which they punctured the tymbal organs of one group carrying 41 moths that makes moth unable to produce sounds (silenced) that can protect them from capture. The other group (38 moths) were kept normal with intact tymbal organs. They were released into the areas where bats were allowed to feed on them. The following tables show the results of this experiment.
Figure 1(A) depicts the number of attacks on the bars when silenced or clicking moths exhibited a particular evasive behavior. There is clearly no difference between behaviors or between silenced moths and clicking moths. However, in Figure 1(B), the number of captures that were made when silenced or clicking moths exhibited a particular evasive behavior is depicted that shows a huge difference between them.
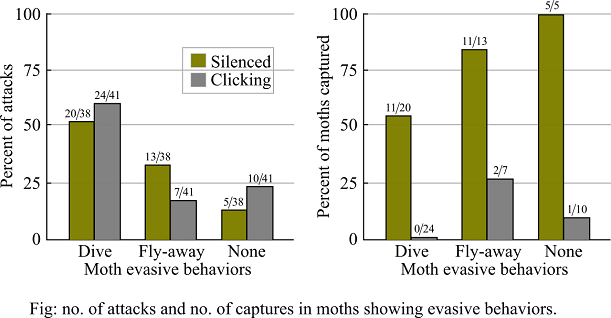
Figure 1: (A) number of attacks; (B) Number of captures in moths showing evasive behaviors.
Introduction:
Bats capture their prey moths by the mechanism of echolocation. They generate ultrasonic signals that strike on flying moths and echo back to the bat, signaling them to capture their prey. Moths have the ability to sense those ultrasonic signals with the help of tympana and exhibit some behaviors to prevent capture. Capture is prevented by changes in their flight, dives, and production of ultrasonic clicks.
Explanation of Solution
The evolution of certain mechanisms in the moths to prevent capture by prey includes the changes in their flight, dive, or by producing ultrasonic clicks. These ultrasonic clicks have echo jamming mechanisms and are produced by tymbal membranes of moths to protect them from being captured.
The data given in Figure 1(A) shows the number of moths that showed evasive behaviors when attacked. It was observed that both the silenced moths and clicked moths respond to the attack by the bats. The silenced moths do not lose its ability to respond and prevent capture by other mechanisms like changes in flight and diving mechanisms. This shows that silencing affects only the responses that are caused by tymbal membranes and moths respond to the ultrasonic waves of bats by showing evasive behaviors.
This is significant for validity of experiment to effectively test the hypothesis made by the researchers that the clicks served as the echolocation jammers.
Thus, moths in the given experiment with disrupted tymbal organ are capable of responding to the ultrasonic waves of the bats with evasive behavior. This indicates that even in the absence of tymbal organs moths prevent capture by other mechanisms.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 45 Solutions
Life: The Science of Biology
- Describe the principle of homeostasis.arrow_forwardExplain how the hormones of the glands listed below travel around the body to target organs and tissues : Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardWhat are the functions of the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forward
- Describe the hormones produced in the glands listed below: Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Pancreas(islets of langerhans) Gonads (testes and ovaries) Placentaarrow_forwardPlease help me calculate drug dosage from the following information: Patient weight: 35 pounds, so 15.9 kilograms (got this by dividing 35 pounds by 2.2 kilograms) Drug dose: 0.05mg/kg Drug concentration: 2mg/mLarrow_forwardA 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, severe headache, and confusion. She recently returned from a trip to sub-Saharan Africa, where she did not take malaria prophylaxis. On examination, she is febrile (39.8°C/103.6°F) and hypotensive. Laboratory studies reveal hemoglobin of 8.0 g/dL, platelet count of 50,000/μL, and evidence of hemoglobinuria. A peripheral blood smear shows ring forms and banana-shaped gametocytes. Which of the following Plasmodium species is most likely responsible for her severe symptoms? A. Plasmodium vivax B. Plasmodium ovale C. Plasmodium malariae D. Plasmodium falciparumarrow_forward
- please fill in missing parts , thank youarrow_forwardplease draw in the answers, thank youarrow_forwarda. On this first grid, assume that the DNA and RNA templates are read left to right. DNA DNA mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide _strand strand C с A T G A U G C A TRP b. Now do this AGAIN assuming that the DNA and RNA templates are read right to left. DNA DNA strand strand C mRNA codon tRNA anticodon polypeptide 0 A T G A U G с A TRParrow_forward
 Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





