
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9781305073951
Author: Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 44, Problem 2CT
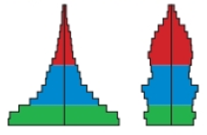
The age structure diagrams for two hypothetical populations are shown below. Describe the growth rate of each population and discuss the current and future social and economic problems that each is likely to face.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
What did the Cre-lox system used in the Kikuchi et al. 2010 heart regeneration experiment allow researchers to investigate?
What was the purpose of the cmlc2 promoter?
What is CreER and why was it used in this experiment?
If constitutively active Cre was driven by the cmlc2 promoter, rather than an inducible CreER system, what color would you expect new cardiomyocytes in the regenerated area to be no matter what? Why?
What kind of organ size regulation is occurring when you graft multiple organs into a mouse and the graft weight stays the same?
What is the concept "calories consumed must equal calories burned" in regrads to nutrition?
Chapter 44 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Ch. 44 - Most commonly, individuals of a population show a...Ch. 44 - Prob. 2SQCh. 44 - Suppose 200 fish are marked and released in a...Ch. 44 - Prob. 1DAACh. 44 - Prob. 2DAACh. 44 - Iguana Decline In 1987, Martin Wikelski began a...Ch. 44 - Prob. 4SQCh. 44 - For a given species, the maximum rate of increase...Ch. 44 - Prob. 6SQCh. 44 - A life history pattern is a set of adaptations...
Ch. 44 - The human population is now about 7 billion. It...Ch. 44 - Prob. 9SQCh. 44 - Prob. 10SQCh. 44 - Prob. 11SQCh. 44 - Prob. 12SQCh. 44 - Match each term with its most suitable...Ch. 44 - Think back to Section 44.6. When researchers moved...Ch. 44 - The age structure diagrams for two hypothetical...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
True or false? Some trails are considered vestigial because they existed long ago.
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Identify me theme or themes exemplified by (a) the sharp quills of a porcupine (b) the development of a multice...
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
What is the pH range for acidic solutions? For basic solutions?
EBK INTRODUCTION TO CHEMISTRY
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You intend to insert patched dominant negative DNA into the left half of the neural tube of a chick. 1) Which side of the neural tube would you put the positive electrode to ensure that the DNA ends up on the left side? 2) What would be the internal (within the embryo) control for this experiment? 3) How can you be sure that the electroporation method itself is not impacting the embryo? 4) What would you do to ensure that the electroporation is working? How can you tell?arrow_forwardDescribe a method to document the diffusion path and gradient of Sonic Hedgehog through the chicken embryo. If modifying the protein, what is one thing you have to consider in regards to maintaining the protein’s function?arrow_forwardThe following table is from Kumar et. al. Highly Selective Dopamine D3 Receptor (DR) Antagonists and Partial Agonists Based on Eticlopride and the D3R Crystal Structure: New Leads for Opioid Dependence Treatment. J. Med Chem 2016.arrow_forward
- The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. You are a chef in a fancy new science-themed restaurant. You have a recipe that calls for 1 teaspoon of resinferatoxin, but you feel uncomfortable serving foods with "toxins" in them. How much capsaicin could you substitute instead?arrow_forwardWhat protein is necessary for packaging acetylcholine into synaptic vesicles?arrow_forward1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward
- 50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forwardChoose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forward
- The following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forwardWhat enzyme is necessary for synthesis of all of the monoamines?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning  Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Case Studies In Health Information Management
Biology
ISBN:9781337676908
Author:SCHNERING
Publisher:Cengage

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168116
Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:OpenStax College

Human Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305112100
Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning
POPULATION REGULATION AND LIMITING FACTORS | DENSITY INDEPENDENT AND DENSITY DEPENDENT FACTORS; Author: BioVidyalaya;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mB-AB-5Wnhs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Population growth; Author: SiouxScience;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XnaC9iOumVA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY