
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
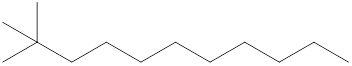
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
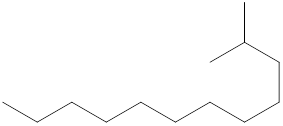
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
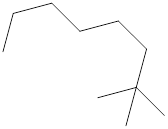
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
Rules of naming alkanes are:
- First, choose the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms known as the parent chain and determines the base name of the alkane.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number.
- The alkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name for the following compound should be determined.
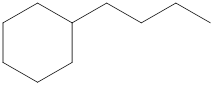
Concept Introduction:
Compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbons. Saturated hydrocarbon is known as alkane having general molecular formula
The compounds in which a series of atoms are connected to form a ring is known as cyclic compound whereas the compounds which are open chain compounds and their atoms don't form a ring is known as acyclic compounds. The general molecular formula of a cyclic alkane is
Rules of naming cycloalkanes are:
- First, determine the cycloalkane present in the structure which is considered as a parent chain (maximum number of carbon atoms). If the acyclic alkane chain has more carbon atoms, then the alkyl chain is considered a parent chain.
- For a cyclic system, the number of carbon atoms must be identified as present in different paths connected with two bridgeheads.
- The numbering of the parent chain should be done in a way that the substituents get the lowest number.
- The appropriate name should be given to every alkyl group or cycloalkyl group and denote its position on the parent chain with the number
- The alkyl groups or cycloalkyl groups are written in alphabetical order.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-STUD.SOLNS.MAN+SG
- Can you explain step by step behind what the synthetic strategy would be?arrow_forwardPlease explain step by step in detail the reasoning behind this problem/approach/and answer. thank you!arrow_forward2. Predict the product(s) that forms and explain why it forms. Assume that any necessary catalytic acid is present. .OH HO H₂N OHarrow_forward
- consider the rate of the reaction below to be r. Whats the rate after each reaction? Br + NaCN CN + NaBr a. Double the concentration of alkyl bromide b. Halve the concentration of the electrophile & triple concentration of cyanide c. Halve the concentration of alkyl chloridearrow_forwardPredict the organic reactant that is involved in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic reactant. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forward
- What is the organic molecule X of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardWhat are is the organic molecule X and product Y of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forwardAt 300 K, in the decomposition reaction of a reactant R into products, several measurements of the concentration of R over time have been made (see table). Without using graphs, calculate the order of the reaction. t/s [R]/(mol L-1) 0 0,5 171 0,16 720 0,05 1400 0,027arrow_forward
- Predict the organic products that form in the reaction below, and draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic products. Please include all steps & drawings & explanations.arrow_forwardWhat are the missing reagents for the spots labeled 1 and 3? Please give a detailed explanation and include the drawings and show how the synthesis proceeds with the reagents.arrow_forwardWhat are the products of the following acetal hydrolysis? Please draw a skeletal line structure and include a detailed explanation and drawing of how the mechanism proceeds. Please include any relevant information that is needed to understand the process of acetal hydrolysis.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





