
Eight identical 500 × 750-mm rectangular plates, each of mass = 40 kg, are held in a vertical plane as shown. All connections consist of frictionless pins, rollers, or short links. In each case, determine whether (a) the plate is completely, partially, or improperly constrained, (b) the reactions are statically determine or indeterminate, (c) the equilibrium of the plate is maintained the position shown. Also, wherever possible, compute the reactions.
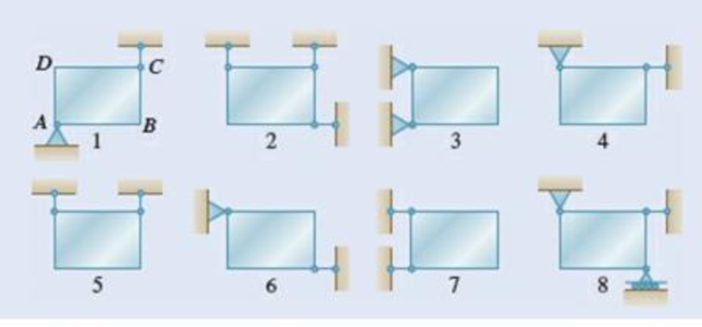
(a)
Find whether the plate is completely, partially, or improperly constrained.
Answer to Problem 4.59P
The plate in figure 1 is
The plate figure 2 is
The plate figure 3 is
The plate figure 4 is
The plate figure 5 is
The plate figure 6 is
The plate figure 7 is
The plate figure 8 is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The size of the identical plates is
Number of plates is 8.
The mass of each plate is
Calculation:
Find the weight (W) of the plate using the relation.
Here, the acceleration due to gravity is g.
Consider the acceleration due to gravity as
Substitute 40 kg for m and
Figure 1:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 1.
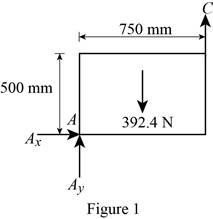
The three reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate in figure 1 is
Figure 2:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 2.
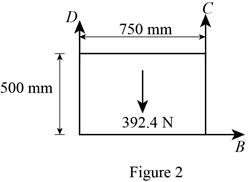
The three reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 2 is
Figure 3:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 3.
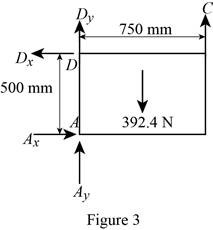
The four reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 3 is
Figure 4:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 4.
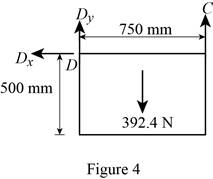
The three reactions in the plate behave like concurrent force system.
The plate figure 4 is
Figure 5:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 5.
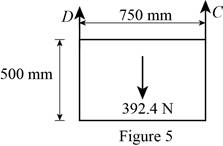
The two reactions in the plate behave like concurrent force system.
The plate figure 5 is
Figure 6:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 6.
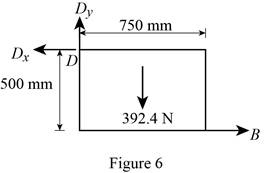
The three reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 6 is
Figure 7:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 7.
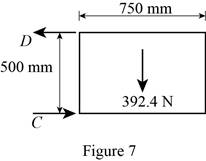
The two reactions in the plate behave like concurrent force system.
The plate figure 7 is
Figure 8:
Show the free-body diagram of the Figure 8.
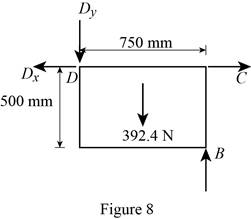
The four reactions in the plate behave like non-concurrent and non-parallel force system.
The plate figure 8 is
(b)
Find whether the reactions are statically determinate or indeterminate.
Answer to Problem 4.59P
The reactions in figure 1 is
The reactions in figure 2 is
The reactions in figure 3 is
The reactions in figure 4 is
The reactions in figure 5 is
The reactions in figure 6 is
The reactions in figure 7 is
The reactions in figure 8 is
Explanation of Solution
Refer Figure 1:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 1 is
Refer Figure 2:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 2 is
Refer Figure 3:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are not enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 3 is
Refer Figure 4:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
But the plate is improperly constrained and the plate is not in equilibrium.
The reactions in figure 4 is
Refer Figure 5:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 5 is
Refer Figure 6:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 6 is
Refer Figure 7:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are enough to determine the unknown reactions.
But the plate is improperly constrained and the plate is not in equilibrium.
The reactions in figure 7 is
Refer Figure 8:
The equilibrium equations are;
The equilibrium equations are not enough to determine the unknown reactions.
The reactions in figure 8 is
(c)
Find whether the equilibrium of the plate is maintained.
Answer to Problem 4.59P
The reactions in the plate 1 are
The plate 1 is in
The reactions in the plate 2 are
The plate 2 is in
The reactions in the plate 3 are
The plate 3 is in
The plate 4 is in
The reactions in the plate 5 are
The plate 5 is in
The reactions in the plate 6 are
The plate 6 is in
The plate 7 is in
The reactions in the plate 8 are
The plate 8 is in
Explanation of Solution
Refer Figure 1:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 1 are
The plate 1 is in
Refer Figure 2:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point B.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 2 are
The plate 2 is in
Refer Figure 3:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 3 are
The plate 3 is in
Refer Figure 4:
The equilibrium equations are;
The moment about point D is not equal to zero.
The plate 4 is in
Refer Figure 5:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 5 are
The plate 5 is in
Refer Figure 6:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point A.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Find the resultant force at D;
Find the angle
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 6 are
The plate 6 is in
Refer Figure 7:
The equilibrium equations are;
The plate 7 is in
Refer Figure 8:
The equilibrium equations are;
Take moment about point D.
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Therefore, the reactions in the plate 8 are
The plate 8 is in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS
- ANSWER ASAP A Solution A is best B Solution B is best C Solution C is best D Solution D is bestarrow_forwardA distillation column with a total condenser and a partial reboiler is separating ethanol andwater at 1.0 atm. Feed is 0.32 mol fraction ethanol and it enters as a saturated liquid at 100mol/s on the optimum plate. The distillate product is a saturated liquid with 80 mol% ethanol.The condenser removes 5615 kW. The bottoms product is 0.05 mol fraction ethanol. AssumeCMO is valid.(a) Find the number of equilibrium stages for this separation. [6 + PR](b) Find how much larger the actual reflux ratio, R, used is than Rmin, i.e. R/Rmin. [3]Note: the heats of vaporization of ethanol and water are λe = 38.58 and λw = 40.645 arrow_forwardA ship of 7000 tonne displacement has a waterplane areaof 1500 m2. In passing from sea water into river water of1005 kg/m3 there is an increase in draught of 10 cm. Find the Idensity of the sea water. i would like to get the above question sloved in detail. ive attached the picture of the answer from the reeds book. just not sure of all the steps theyve used and the formula in which they started with.arrow_forward
- Plunger Gauses:) - True or False "A Plunger gage can read small fluctuations in pressure such as a change in pressure of 2 psi"arrow_forwardCushioning: (Q1) A cylinder is used to clamp onto rubber tires on an assembly line. The cylinder quickly extends and clamps onto the tire and robot puts a label onto the tire. The cylinder then retracts quickly to unclamp the tire. Which of these four cylinders is best for the job? A 0 A Selection A is best B Selection B is best (C) Selection C is best D) Selection D is best B Darrow_forwardBourdon Gauges: (Q4) - True of False "A Bourdon gauge is used to measure high pressures above 500 psi"arrow_forward
- Weight of Air: If you could collect the air in a square inch column of air starting at sea level going all the way to space, how much would it weigh? Answer with one decimal. Do not write the unit.arrow_forwardPiston Area: (Q2) A cylinder applies a force of 400 pounds in extension. If the pressure in the cylinder is 39 psi what is the area of the piston in square inches? Use πon your calculator Answer with two decimals. Do not write the unit.arrow_forwardA 2D incompressible flow has velocitycomponents u= X^2 - 2y^2 and v=aX^b y^c ,where a, b, and c are numbers. Find the values of a, b, and c Find the stream functionarrow_forward
- Please can you assist with the attached question please?arrow_forward(a) Find a second-order homogeneous linear ODE for which the given functions are solutions. (b) Show linear independence by the Wronskian. (c) Solve the initial value problem. a. cos(5x), sin(5x), y(0) = 3, y'(0) = −5 b. e-2.5x cos(0.3x), e-2.5x sin(0.3x), y(0) = 3, y'(0) = -7.5arrow_forwardSolve the IVP. a. y" 16y 17e* ; = y(0) = 6, y'(0) = -2 b. (D² + 41)y = sin(t) + ½ sin(3t) + sin(t) ; y(0) = 0, y'(0) : = 35 31arrow_forward
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
